
Concept explainers
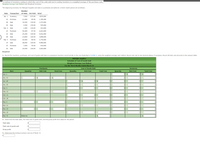
The beginning inventory for Midnight Supplies and data on purchases and sales for a three-month period are as follows.
Required:
1. Record the inventory, purchases, and cost of goods sold data in a perpetual inventory record similar to the one illustrated in Exhibit 5, using the weighted average cost method. Round unit cost to two decimal places, if necessary. Round all total cost amounts to the nearest dollar.
2. Determine the total sales, the total cost of goods sold, and the gross profit from sales for the period.
| Total sales | $_______________ |
| Total cost of goods sold | $_______________ |
| Gross profit | $_______________ |
3. Determine the ending inventory cost as of March 31.
$___________
The inventory valuation can be done using different systems like perpetual inventory system or periodic inventory system. Under the perpetual inventory system, the cost of goods sold is recorded at the time of sale transaction while under the periodic inventory system, the change in inventory is recorded at the end of the period.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 1 images

- Please help solve and explain processarrow_forwardGiven the following information Compute: (A) age of inventory; and (B) operating cycle. (check the attached picture) Choose the bullet with the correct answer (A) 18.5 days and (B) 25.5 days (A) 28.5 days and (B) 35.5 days (A) 28.5 days and (B) 55.5 days (A) 38.5 days and (B) 75.5 days (A) 38.5 days and (B) 95.5 daysarrow_forwardTrini Company had the following transactions for the month. Calculate the ending inventory dollar value for each of the following cost allocation methods, using periodic inventory updating. Provide your calculations. first-in, first-out (FIFO) last-in, first-out (LIFO) weighted average (AVG)arrow_forward
- The following units of a particular item were available for sale during the calendar year: Jan. 1 3,800 units at $40 Apr. 19 2,600 units June 30 4,400 units at $45 Sept. 2 5,200 units Nov. 15 2,100 units at $48 The firm maintains a perpetual inventory system. Determine the cost of goods sold for each sale and the inventory balance after each sale, assuming the first-in, first-out method. Present the data in the form illustrated in Exhibit 3. Under FIFO, if units are in inventory at two different costs, enter the units with the LOWER unit cost first in the Cost of Goods Sold Unit Cost column and in the Inventory Unit Cost column. Date Jan. 1 Apr. 19 June 30 Sept. 2 Nov. 15 Dec. 31 Inventory Sale Purchase Sale Purchase Quantity Balances Purchases Unit Cost Total Cost Schedule of Cost of Goods Sold FIFO Method Quantity Cost of Goods Sold Unit Cost Total Cost Quantity Inventory Unit Cost $ Total Costarrow_forwardhe following data are available for Sellco for the fiscal year ended on January 31, 2020: Sales 1,600 units Beginning inventory 500 units @ $ 4 Purchases, in chronological order 600 units @ $ 5 800 units @ $ 6 500 units @ $ 8 Required:a. Calculate cost of goods sold and ending inventory under the cost flow assumptions, FIFO, LIFO and weighted average (using a periodic inventory system): (Round unit cost to 2 decimal places.) b. Assume that net income using the weighted-average cost flow assumption is $80,000. Calculate net income under FIFO and LIFO. (Round unit cost to 2 decimal places.)arrow_forwardThe beginning inventory at ABC Supplies and data on purchases and sales for a three-month period ending March 31, are as follows: (See attached dates/transactions/units/totals list attached) 1. Record the inventory, purchases, and cost of merchandise sold data in a perpetual inventory record, using the first-in, first-out method. (I have attached an example of how the table should look as I had a hard time formatting the blank table I provided below) Date Purchases Cost of Merchandise sold Inventory Quantity Unit Cost Total Cost Quantity Unit Cost Total Cost Quantity Unit Cost Total Cost Jan. 1 10 10 28 28 30 Feb. 5 10 10 16 16…arrow_forward
- Calculate the ending inventory and cost of goods sold dollar values for ABC Company for the month, considering the following transactions under three different cost allocation methods and using periodic inventory updating: |(a) First-in, first-out (FIFO) (b) Last-in, first-out (LIFO) Number of Unit Cost Sales Price Units Beginning Inventory 100 $20 Purchase 400 22 Sold 300 $30 Purchase 200 24 Sold 180 $35 Ending Inventory 220arrow_forwardFlingen Inc. reveals the following information in their annual report for FY 2021 Selected Income Statement Items: Sales $10,500,000 Cost of goods sold $5,500,000 Pretax earnings $650,000 Selected Balance Sheet Items: Merchandise inventory $800,000 Total assets $2,500,000 Upper management plans to cut cost of goods sold by 4.5% for the coming year but retain the same sales and weeks of inventory. What is the return on assets estimated to be for 2022? Group of answer choices 33.7% 32.1% 36.8% 34.1%arrow_forwardNittany Company uses a periodic inventory system. At the end of the annual accounting period, December 31 of the current year, the accounting records provided the following information for product 1: Ending inventory Cost of goods sold Inventory, December 31, prior year For the current year: Purchase, March 21 Purchase, August 1 Inventory, December 31, current year Required: Compute ending inventory and cost of goods sold for the current year under FIFO, LIFO, and average cost inventory costing methods. Note: Round "Average cost per unit" to 2 decimal places and final answers to nearest whole dollar amount. FIFO Units 1,870 LIFO 5,030 2,980 4,090 Unit Cost $4 Average Costarrow_forward
- Ch 9 Problem Set B Problem 9-1 Part B The company uses the perpetual inventory method. It began the month of March with 100 units of inventory, at a unit cost of $55. Purchases during March March 5, 60 units at $60 each. March 18, 200 units at $65 each March 29, 40 units at $75 each. Sales during March March 12, 60 units. March 25, 210 units. All units were sold to customer for $100 each. 1. Use the following format to set up this inventory costing problem, as shown in Video #2. Inventory Date Units Cost per Total Cost Date Units Total Cost Unit Beg Balance Units Cost Beginning Balance + Purchases Goods Available for Sale - Sold Ending Balancearrow_forwardA company reports the following beginning inventory and two purchases for the month of January. On January 26, the company sells 430 units. Ending inventory at January 31 totals 170 units. Beginning inventory on January 1 Purchase on January 9 Purchase on January 25 Weighted Average - Perpetual: Goods purchased Required: Assume the perpetual inventory system is used. Determine the costs assigned to ending inventory when costs are assigned based on the weighted average method. (Round your per unit costs to 2 decimal places.) Date January 1 January 9 Average cost January 25 Average cost January 26 Totals # of units Cost per unit Units Unit Cost 390 90 120 # of units sold $3.80 4.00 4.10 Cost of Goods Sold Cost per Cost of Goods unit Sold Inventory Balance Cost per unit # of units 390 @ $ 3.80 = Inventory Balance $1,482.00arrow_forwardFancy Iron began August with 45 units of iron inventory that cost $24 each. During August, the company completed the following inventory transactions: Requirement 1. Prepare a perpetual inventory record for the merchandise inventory using the FIFO inventory costing method. Start by entering the beginning inventory balances. Enter the transactions in chronological order, calculating new inventory on hand balances after each transaction. Once all of the transactions have been entered into the perpetual record, calculate the quantity and total cost of merchandise inventory purchased, sold, and on hand at the end of the period. (Enter the oldest inventory layers first.) - X Cost of Goods Sold Inventory on Hand Requirements Unit Cost Unit Cost Purchases Unit Date Quantity Cost Aug. 1 3 81 21 30 Totals Total Cost Quantity Total Cost Quantity C Total Cost 1. Prepare a perpetual inventory record for the merchandise inventory using the FIFO inventory costing method. 2. Prepare a perpetual…arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





