Package: Loose Leaf Organic Chemistry with Connect 2-year Access Card
5th Edition
ISBN: 9781259729980
Author: SMITH
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 6, Problem 6.12P
The equilibrium constant for the conversion of the axial to the equatorial conformation of methoxycyclohexane is
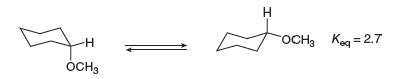
a. Given these data, which conformation is present in the larger amount at equilibrium?
b. Is
c. From the values in Table
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Consider these hydrocarbons: Butane, Hexane, Methane, Propane First look up the formulas, and write them down. Then put them in order from least entropy to most entropy. (Assume the temperature is hot enough that all are in gaseous form.)
Following are the steps in the industrial synthesis of glycerin.
NaOH, H₂O B (C₂H₂O)
CH₂=CHCH,
Propene
Cl₂A (C₂H₂CI)
heat
C (C₂H,ClO₂)
Ca(OH)2, D (C3H6O2)
heat
Cl₂, H₂O
H₂O, HCI
OH
HOCH₂CHCH₂OH
1,2,3-Propanetriol
(glycerol, glycerin)
1. The condensation of glutamate and ammonia to yield glutamine and water has a AG'° of +14.23 kJ/mol. Depict
this reaction in its thermodynamically favorable direction.
Chapter 6 Solutions
Package: Loose Leaf Organic Chemistry with Connect 2-year Access Card
Ch. 6 - Problem 6.1 Classify each transformation as...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.2PCh. 6 - Problem 6.3 By taking into account...Ch. 6 - Problem 6.4 Use curved arrows to show the movement...Ch. 6 - Problem 6.5 Follow the curved arrows and draw the...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.6PCh. 6 - Problem 6.7 Use the values in Table 6.2 to...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.8PCh. 6 - aWhich Keq corresponds to a negative value of G,...Ch. 6 - Given each of the following values, is the...
Ch. 6 - Given each of the following values, is the...Ch. 6 - The equilibrium constant for the conversion of the...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.13PCh. 6 - For a reaction with H=40kJ/mol, decide which of...Ch. 6 - For a reaction with H=20kJ/mol, decide which of...Ch. 6 - Draw an energy diagram for a reaction in which the...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.17PCh. 6 - Prob. 6.18PCh. 6 - Problem 6.19 Consider the following energy...Ch. 6 - Draw an energy diagram for a two-step reaction,...Ch. 6 - Which value if any corresponds to a faster...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.22PCh. 6 - Problem 6.23 For each rate equation, what effect...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.24PCh. 6 - Identify the catalyst in each equation. a....Ch. 6 - Draw the products of homolysis or heterolysis of...Ch. 6 - Explain why the bond dissociation energy for bond...Ch. 6 - Classify each transformation as substitution,...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.29PCh. 6 - 6.30 Draw the products of each reaction by...Ch. 6 - 6.31 (a) Add curved arrows for each step to show...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.32PCh. 6 - Prob. 6.33PCh. 6 - Prob. 6.34PCh. 6 - Calculate H for each reaction. a HO+CH4CH3+H2O b...Ch. 6 - Homolysis of the indicated CH bond in propene...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.37PCh. 6 - Prob. 6.38PCh. 6 - 6.39. a. Which value corresponds to a negative...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.40PCh. 6 - For which of the following reaction is S a...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.42PCh. 6 - Prob. 6.43PCh. 6 - 6.44 Consider the following reaction: .
Use curved...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.45PCh. 6 - Draw an energy diagram for the Bronsted-Lowry...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.47PCh. 6 - Indicate which factors affect the rate of a...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.49PCh. 6 - 6.50 The conversion of acetyl chloride to methyl...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.51PCh. 6 - Prob. 6.52PCh. 6 - The conversion of (CH3)3Cl to (CH3)2C=CH2 can...Ch. 6 - 6.54 Explain why is more acidic than , even...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.55PCh. 6 - Prob. 6.56PCh. 6 - Prob. 6.57PCh. 6 - Although Keq of equation 1 in problem 6.57 does...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.59P
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 6H2O + 6CO2 --> C6H12O6 + 6O2 H=+2803 kJ/mol calculate the amount of sunlight energy required (in kJ) by a plant to synthesize 75.0g of glucose (C6H12O6)arrow_forwardCalculate the heat of hydrogenation of ethane, C2H4 given the following thermochemical equations: 2 C(graphite) + 3 H2 (g) —> C2H6 (g) ΔHf= - 84.5 kJ/mol 2 C (graphite) + 2 H2 (g) —> C2H4 (g) ΔHf= 52.3 kJ/molarrow_forwardWhat is the total strain energy of 2,2-dimethylpropane in an eclipsed conformation? Given: For CH3 eclipsed to H (both attached to adjacent C's), the total strain energy is 6 kJ/mol. Select one: A. 12 kJ В. 18 kJ С. 21 kJ D. 11.4 kjarrow_forward
- Explain the importance of Stereochemistry?arrow_forwardIs CaCl2 (aq) + Na₂CO₃ (aq) → CaCO3 (s) + 2NaCl (aq) reversible or irreversible reactionarrow_forward2,5-Dimethylfuran is a liquid biofuel that can be synthesized from 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF). As shown below, HMF can be synthesized from D-fructose by treatment with sulfuric acid. FOH H2SO4 HO OH DMSO HO но OH 48 h, 110 °C 68% 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural (HFM) D-Fructose 2,5-Dimethylfuran The mechanism for the formation of HMF from D-fructose is believed to involve the following series of dehydration reactions: он - H,0 HO OH - H20 - H20 но OH но HO OH HO ОН HO D-Fructose A в HO 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural Draw the complete, detailed mechanism for each of these dehydration reactions.arrow_forward
- Explain Conjugated Systems ?arrow_forwardChemistry HH H-C-O H a. glucose (an aldohexose) CH12Os 8€ H-OHHO-H Construct a model of glucose. You will need to arrange the molecules in a "chair" configuration. H H-OH нсон gam COH 4-C ночи CO-H fructose (a ketohexose) C6H12O6 Construct a model of fructose. What is the relationship between glucose and fructose? (Hint: see their molecular formulas) H H-O O-Harrow_forwardGive answer all questions with explanation pleasearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry In FocusChemistryISBN:9781305084476Author:Tro, Nivaldo J., Neu, Don.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry In FocusChemistryISBN:9781305084476Author:Tro, Nivaldo J., Neu, Don.Publisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078746376
Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co

Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079250
Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed Peters
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry In Focus
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305084476
Author:Tro, Nivaldo J., Neu, Don.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079243
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:Cengage Learning
The Laws of Thermodynamics, Entropy, and Gibbs Free Energy; Author: Professor Dave Explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8N1BxHgsoOw;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY