
Concept explainers
Telescopes can now be operated remotely from a warm room, but until about 25 years ago, astronomers worked at the telescope to guide it so that it remained pointed in exactly the right place. In a large telescope, like the Palomar 200-inch telescope, astronomers sat in a cage at the top of the telescope, where the secondary mirror is located, as shown in Figure 6.6. Assume for the purpose of your calculation that the diameter of this cage was 40 inches. What fraction of the light is blocked?
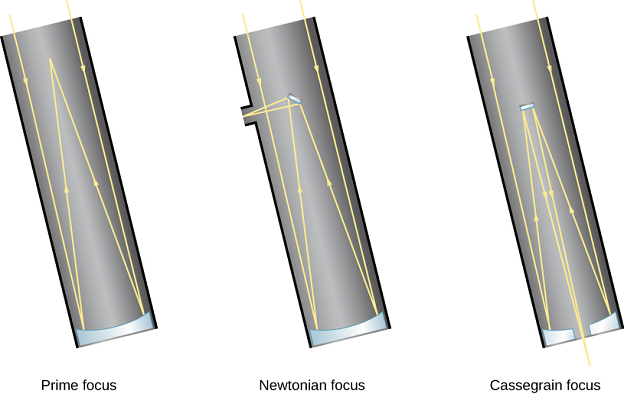
Figure 6.6 Focus Arrangements for Reflecting Telescopes. Reflecting telescopes have different options for where the light is brought to a focus. With prime focus, light is detected where it comes to a focus after reflecting from the primary mirror. With Newtonian focus, light is reflected by a small secondary mirror off to one side, where it can be detected (see also Figure 6.5). Most large professional telescopes have a Cassegrain focus in which light is reflected by the secondary mirror down through a hole in the primary mirror to an observing station below the telescope.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 6 Solutions
Astronomy
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Introduction to Electrodynamics
Conceptual Physics (12th Edition)
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach with Modern Physics (4th Edition)
College Physics
Essential University Physics: Volume 2 (3rd Edition)
- The Hooker telescope at Palomar Observatory has a diameter of 5 m, and the Keck I telescope has a diameter of 10 m. How much more light can the Keck telescope collect than the Hooker telescope in the same amount of time?arrow_forwardYou record the spectrum of a distant star using a telescope on the ground on Earth. Upon analysing the spectrum, you discover absorption lines spaced at intervals typical of oxygen atoms. Which of the following are possible interpretations of this evidence? Select all that apply. The width of the spectral lines gives the diameter of the star The star is likely orbited by habitable planets with breathable atmospheres. The height of the spectral lines above the star's general blackbody spectral curve tells us how much oxygen is in the star The atmosphere of Earth contains oxygen The red or blueshift of the set of lines can tell us the speed of the star's motion toward or away from usarrow_forwardSuppose astronomers built a 90-meter telescope. How much greater would it's light collecting area be than that of the 10-meter Keck telescope? Express your answer using two significant figures.arrow_forward
- The James Webb Telescope is an important innovation in Astronomy and its implementation was first explained to the public during the timeline of our course this summer. Prepare an explanation which includes the following: What is the James Webb Telescope? Include a description of the tool itself and a brief history. What is the importance/significance of this tool for future astronomical studies?arrow_forwardWhen astronomers discuss the apertures of their telescopes, they say bigger is better. Explain why. a) A wider aperture can observe a significantly larger portion of the sky. b) A wider aperture makes a telescope easier to aim. c) A wider aperture allows a telescope to collect more light, so it can produce images with higher resolution. d) A wider aperture allows a telescope to collect more light, so it can detect fainter light sources.arrow_forwardConsider the figure below: X a) Write a one-line figure caption appropriate for the figure b) In paragraph form, write a complete description of the figure: what is plotted in the figure (aim to give as full an answer as you can): what features are seen, what information does the figure give...arrow_forward
- Intro to Astronomy: Calculate the angular resolution of the HST (Hubble Space Telescope) operating in green light of wavelength 0.50 (mm). The HST mirror diameter is 2.4 (m). Use formula: Angular resolution (arc seconds) NOTE: wavelength must be in (mm) and mirror diameter in (m) Angular resolution = Q1 =arrow_forwardTelescope A has a 5 in. diameter whereas Telescope B has a 12 cm diameter. Which telescope gathers more light? By how much? Bright telescope = dim telescopearrow_forwardThe James Webb Space Telescope has a primary mirror of diameter ? = 6.5metres. When observing at 1100nm wavelength, calculate the minimum angular separation between two stars which can just be resolved; give your answer in arcseconds (arcsec), where 1 arcsec = 1/3600 degree, to 3 decimal places.arrow_forward
- What is the area, in square meters, of a 10-m telescope?arrow_forwardWhat was the problem with the Hubble Space Telescope and how was it solved?arrow_forwardFor a human eye with a pupil diameter (aperture diameter D) of 0.005 meters, and a focal length of 0.022 meters, there will be a resolution limit due to diffraction at 0.6 microns (10^-6 meters) wavelength. If we space light-sensitive cells on the retina at this spacing, how many retina cells per meter (of retina) are there? cells/meter. Now suppose there are giants which are exactly twice the size of humans in each dimension. So giant eyes have pupils of 0.01 meters, and a focal length of 0.044 meters. How many retina cells per meter should the giants have? cells/meterarrow_forward
 AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9781938168284Author:Andrew Fraknoi; David Morrison; Sidney C. WolffPublisher:OpenStax
AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9781938168284Author:Andrew Fraknoi; David Morrison; Sidney C. WolffPublisher:OpenStax
 Stars and Galaxies (MindTap Course List)PhysicsISBN:9781337399944Author:Michael A. SeedsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Stars and Galaxies (MindTap Course List)PhysicsISBN:9781337399944Author:Michael A. SeedsPublisher:Cengage Learning Foundations of Astronomy (MindTap Course List)PhysicsISBN:9781337399920Author:Michael A. Seeds, Dana BackmanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Foundations of Astronomy (MindTap Course List)PhysicsISBN:9781337399920Author:Michael A. Seeds, Dana BackmanPublisher:Cengage Learning



