
Physics (5th Edition)
5th Edition
ISBN: 9780321976444
Author: James S. Walker
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 6, Problem 1PCE
Predict/Explain You push two identical bricks across a tabletop with constant speed, U, as shown in Figure 6-29 in case 1, you place the bricks end to end, in case 2, you stack the bricks one on top of the other. (a) Is the
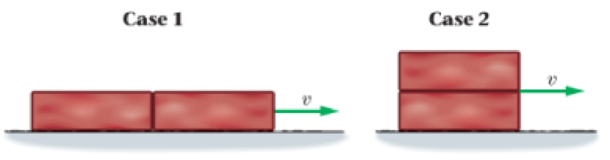
Figure 6-29
Problem 1
- I. The normal force in case 2 is larger and hence the bricks press down more firmly against the tabletop.
- II. The normal force is the same in the two cases and friction is independent of surface area.
- III. Case 1 has more surface area in contact with the tabletop, and this leads to more friction.
Expert Solution & Answer
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

schedule04:34
Students have asked these similar questions
A cylinder with a piston contains 0.153 mol of
nitrogen at a pressure of 1.83×105 Pa and a
temperature of 290 K. The nitrogen may be
treated as an ideal gas. The gas is first compressed
isobarically to half its original volume. It then
expands adiabatically back to its original volume,
and finally it is heated isochorically to its original
pressure.
Part A
Compute the temperature at the beginning of the adiabatic expansion.
Express your answer in kelvins.
ΕΠΙ ΑΣΦ
T₁ =
?
K
Submit
Request Answer
Part B
Compute the temperature at the end of the adiabatic expansion.
Express your answer in kelvins.
Π ΑΣΦ
T₂ =
Submit
Request Answer
Part C
Compute the minimum pressure.
Express your answer in pascals.
ΕΠΙ ΑΣΦ
P =
Submit
Request Answer
?
?
K
Pa
Learning Goal:
To understand the meaning and the basic applications of
pV diagrams for an ideal gas.
As you know, the parameters of an ideal gas are
described by the equation
pV = nRT,
where p is the pressure of the gas, V is the volume of
the gas, n is the number of moles, R is the universal gas
constant, and T is the absolute temperature of the gas. It
follows that, for a portion of an ideal gas,
pV
= constant.
Τ
One can see that, if the amount of gas remains constant,
it is impossible to change just one parameter of the gas:
At least one more parameter would also change. For
instance, if the pressure of the gas is changed, we can
be sure that either the volume or the temperature of the
gas (or, maybe, both!) would also change.
To explore these changes, it is often convenient to draw a
graph showing one parameter as a function of the other.
Although there are many choices of axes, the most
common one is a plot of pressure as a function of
volume: a pV diagram.
In this problem, you…
Learning Goal:
To understand the meaning and the basic applications of
pV diagrams for an ideal gas.
As you know, the parameters of an ideal gas are
described by the equation
pV = nRT,
where p is the pressure of the gas, V is the volume of
the gas, n is the number of moles, R is the universal gas
constant, and T is the absolute temperature of the gas. It
follows that, for a portion of an ideal gas,
pV
= constant.
T
One can see that, if the amount of gas remains constant,
it is impossible to change just one parameter of the gas:
At least one more parameter would also change. For
instance, if the pressure of the gas is changed, we can
be sure that either the volume or the temperature of the
gas (or, maybe, both!) would also change.
To explore these changes, it is often convenient to draw a
graph showing one parameter as a function of the other.
Although there are many choices of axes, the most
common one is a plot of pressure as a function of
volume: a pV diagram.
In this problem, you…
Chapter 6 Solutions
Physics (5th Edition)
Ch. 6.1 - A block rests on a rough, horizontal surface, as...Ch. 6.2 - When a mass is attached to a certain spring, the...Ch. 6.3 - Suppose the tension in the clothesline in Quick...Ch. 6.4 - Three boxes are connected by ropes and pulled...Ch. 6.5 - A system consists of an object with mass m and...Ch. 6 - A clothesline always sags a little, even if...Ch. 6 - In the Jurassic Park sequel, The Lost World, a man...Ch. 6 - When a traffic accident is investigated, it is...Ch. 6 - In a car with rear-wheel drive, the maximum...Ch. 6 - A train typically requires a much greater distance...
Ch. 6 - Give some everyday examples of situations in which...Ch. 6 - At the local farm, you buy a flat of strawberries...Ch. 6 - It is possible to spin a bucket of water in a...Ch. 6 - Water sprays off a rapidly turning bicycle wheel....Ch. 6 - Can an object be in translational equilibrium if...Ch. 6 - Prob. 11CQCh. 6 - The gravitational attraction of the Earth is only...Ch. 6 - A popular carnival ride has passengers stand with...Ch. 6 - Referring to Question 13, after the cylinder...Ch. 6 - Your car is stuck on an icy side street. Some...Ch. 6 - The parking brake on a car causes the rear wheels...Ch. 6 - BIO The foot of your average gecko is covered with...Ch. 6 - Discuss the physics involved in the spin cycle of...Ch. 6 - The gas pedal and the brake pedal are capable of...Ch. 6 - In the movie 2001: A Space Odyssey, a rotating...Ch. 6 - When rounding a corner on a bicycle or a...Ch. 6 - Predict/Explain You push two identical bricks...Ch. 6 - Predict/Explain Two drivers traveling side-by-side...Ch. 6 - A 1.8-kg block slides on a horizontal surface with...Ch. 6 - A child goes down a playground slide with an...Ch. 6 - What is the minimum horizontal force F needed to...Ch. 6 - What is the minimum horizontal force F needed to...Ch. 6 - The three identical boxes shown in Figure 6-33...Ch. 6 - To move a large crate across a rough floor, you...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate A 37-kg crate is placed on an...Ch. 6 - Coffee To Go A person places a cup of coffee on...Ch. 6 - A mug rests on an inclined surface, as shown in...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate Force Times Distance At the...Ch. 6 - Prob. 13PCECh. 6 - A certain spring has a force constant k. (a) If...Ch. 6 - A certain spring has a force constant k. (a) If...Ch. 6 - Pulling up on a rope you lift a 7.27-kg bucket of...Ch. 6 - When a 9.09-kg mass is placed on top of a vertical...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate A backpack full of books...Ch. 6 - Two springs, with force constants k1= 150N/m and...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate Illinois Jones is being pulled...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate A spring with a force constant...Ch. 6 - A spring is suspended vertically from the ceiling...Ch. 6 - Mechanical Advantage The pulley system shown in...Ch. 6 - Pulling the string on a bow back with a force of...Ch. 6 - In Figure 6-42 we see two blocks connected by a...Ch. 6 - BIO Traction After a skiing accident, your leg is...Ch. 6 - Two blocks are connected by a string, as shown in...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate The system shown in Figure 6-45...Ch. 6 - Predict/Explain (a) Referring to the hanging...Ch. 6 - BIO Spiderweb Forces An orb-weaver spider sits in...Ch. 6 - A 0.15-kg ball is placed in a shallow wedge with...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate A picture hangs on the wall...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate You want to nail a 1.6-kg board...Ch. 6 - Prob. 34PCECh. 6 - In Example 6-13 (Connected Blocks), suppose m1 and...Ch. 6 - Predict/Explain Suppose m1 and m2 in Example 6-14...Ch. 6 - Three boxes of masses m, 2m, and 3m are connected...Ch. 6 - Find the acceleration of the masses shown in...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate (a) If the hanging mass m3 in...Ch. 6 - Two blocks are connected by a string, as shown in...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate A 3 50-kg block on a smooth...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate A 7.7-N force pulls horizontally...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate (a) Find the magnitude of the...Ch. 6 - A car drives with constant speed on an elliptical...Ch. 6 - A puck attached to a string undergoes circular...Ch. 6 - BIO Bubble Net Fishing Humpback whales sometimes...Ch. 6 - When you take your 1900-kg car out for a spin, you...Ch. 6 - BIO A Human Centrifuge To test the effects of high...Ch. 6 - A car goes around a curve on a road that is banked...Ch. 6 - Clearview Screen Large ships often have circular...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate (a) As you ride on a Ferris...Ch. 6 - Driving in your car with a constant speed of v =...Ch. 6 - CE If you weigh yourself on a bathroom scale at...Ch. 6 - CE BIO Maneuvering a Jet Humans lose consciousness...Ch. 6 - CE BIO Gravitropism As plants grow, they tend to...Ch. 6 - BIO Human-Powered Centrifuge One of the hazards of...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate A 9 3-kg box slides across the...Ch. 6 - A child goes down a playground slide that is...Ch. 6 - Spin-Dry Dragonflies Some dragonflies splash down...Ch. 6 - The da Vinci Code Leonardo da Vinci (1452-1519) is...Ch. 6 - A 4 5-kg sled is pulled with constant speed across...Ch. 6 - A 0 045-kg golf ball hangs by a string from the...Ch. 6 - A physics textbook weighing 22 N rests on a desk....Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate The blocks shown in Figure 6-64...Ch. 6 - A Conical Pendulum A 0 075-kg toy airplane is tied...Ch. 6 - A tugboat tows a barge at constant speed with a...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate Two blocks, stacked one on top...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate In a daring rescue by helicopter...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate A light spring with a fore...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate The blocks in Figure 6-69 have...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate Playing a Violin The tension in...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate A 9 8-kg monkey hangs from a...Ch. 6 - As your plane circles an airport, it moves in a...Ch. 6 - At a playground, a 22-kg child sits on a spinning...Ch. 6 - A 2.0-kg box rests on a plank that is inclined at...Ch. 6 - A wood block of mass m rests on a larger wood...Ch. 6 - A hockey puck of mass m is attached to a string...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate A popular ride at amusement...Ch. 6 - A Conveyor Belt A box is placed on a conveyor belt...Ch. 6 - As part of a circus act, a person drives a...Ch. 6 - On the straight-line segment II in Figure 6-76 (b)...Ch. 6 - 82. Rank the straight segments I, II, and III in...Ch. 6 - In use on a typical human nose, the end-to-end...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate Referring to Example 6-3 Suppose...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate Referring to Example 6-3 The...Ch. 6 - Referring to Example 6-13 Suppose that the mass on...Ch. 6 - Referring to Example 6-15 (a) At what speed will...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Acetobacter is necessary for only one of the steps of vitamin C manufacture. The easiest way to accomplish this...
Microbiology: An Introduction
A human female with Turner syndrome (47, X) also expresses the X-linked trait hemophilia, as did her father. Wh...
Concepts of Genetics (12th Edition)
DNA sequences in manv human genes are very similar lo the sequences of corresponding genes in chimpanzees. The ...
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
In a population, what is the consequence of inbreeding? Does inbreeding change allele frequencies? What is the ...
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
What are the minimum and maximum ages of the island of Kauai? Minimum age: ______million yr Maximum age: ______...
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Why are BSL-4 suits pressurized? Why not just wear tough regular suits?
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (5th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- ■ Review | Constants A cylinder with a movable piston contains 3.75 mol of N2 gas (assumed to behave like an ideal gas). Part A The N2 is heated at constant volume until 1553 J of heat have been added. Calculate the change in temperature. ΜΕ ΑΣΦ AT = Submit Request Answer Part B ? K Suppose the same amount of heat is added to the N2, but this time the gas is allowed to expand while remaining at constant pressure. Calculate the temperature change. AT = Π ΑΣΦ Submit Request Answer Provide Feedback ? K Nextarrow_forward4. I've assembled the following assortment of point charges (-4 μC, +6 μC, and +3 μC) into a rectangle, bringing them together from an initial situation where they were all an infinite distance away from each other. Find the electric potential at point "A" (marked by the X) and tell me how much work it would require to bring a +10.0 μC charge to point A if it started an infinite distance away (assume that the other three charges remains fixed). 300 mm -4 UC "A" 0.400 mm +6 UC +3 UC 5. It's Friday night, and you've got big party plans. What will you do? Why, make a capacitor, of course! You use aluminum foil as the plates, and since a standard roll of aluminum foil is 30.5 cm wide you make the plates of your capacitor each 30.5 cm by 30.5 cm. You separate the plates with regular paper, which has a thickness of 0.125 mm and a dielectric constant of 3.7. What is the capacitance of your capacitor? If you connect it to a 12 V battery, how much charge is stored on either plate? =arrow_forwardLearning Goal: To understand the meaning and the basic applications of pV diagrams for an ideal gas. As you know, the parameters of an ideal gas are described by the equation pV = nRT, where p is the pressure of the gas, V is the volume of the gas, n is the number of moles, R is the universal gas constant, and T is the absolute temperature of the gas. It follows that, for a portion of an ideal gas, PV T = constant. One can see that, if the amount of gas remains constant, it is impossible to change just one parameter of the gas: At least one more parameter would also change. For instance, if the pressure of the gas is changed, we can be sure that either the volume or the temperature of the gas (or, maybe, both!) would also change. To explore these changes, it is often convenient to draw a graph showing one parameter as a function of the other. Although there are many choices of axes, the most common one is a plot of pressure as a function of volume: a pV diagram. In this problem, you…arrow_forward
- A-e pleasearrow_forwardTwo moles of carbon monoxide (CO) start at a pressure of 1.4 atm and a volume of 35 liters. The gas is then compressed adiabatically to 1/3 this volume. Assume that the gas may be treated as ideal. Part A What is the change in the internal energy of the gas? Express your answer using two significant figures. ΕΠΙ ΑΣΦ AU = Submit Request Answer Part B Does the internal energy increase or decrease? internal energy increases internal energy decreases Submit Request Answer Part C ? J Does the temperature of the gas increase or decrease during this process? temperature of the gas increases temperature of the gas decreases Submit Request Answerarrow_forwardYour answer is partially correct. Two small objects, A and B, are fixed in place and separated by 2.98 cm in a vacuum. Object A has a charge of +0.776 μC, and object B has a charge of -0.776 μC. How many electrons must be removed from A and put onto B to make the electrostatic force that acts on each object an attractive force whose magnitude is 12.4 N? e (mea is the es a co le E o ussian Number Tevtheel ed Media ! Units No units → answe Tr2Earrow_forward
- 4 Problem 4) A particle is being pushed up a smooth slot by a rod. At the instant when 0 = rad, the angular speed of the arm is ė = 1 rad/sec, and the angular acceleration is = 2 rad/sec². What is the net force acting on the 1 kg particle at this instant? Express your answer as a vector in cylindrical coordinates. Hint: You can express the radial coordinate as a function of the angle by observing a right triangle. (20 pts) Ꮎ 2 m Figure 3: Particle pushed by rod along vertical path.arrow_forward4 Problem 4) A particle is being pushed up a smooth slot by a rod. At the instant when 0 = rad, the angular speed of the arm is ė = 1 rad/sec, and the angular acceleration is = 2 rad/sec². What is the net force acting on the 1 kg particle at this instant? Express your answer as a vector in cylindrical coordinates. Hint: You can express the radial coordinate as a function of the angle by observing a right triangle. (20 pts) Ꮎ 2 m Figure 3: Particle pushed by rod along vertical path.arrow_forwardplease solve and answer the question correctly. Thank you!!arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:9780534408961
Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Newton's Second Law of Motion: F = ma; Author: Professor Dave explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xzA6IBWUEDE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY