
Concept explainers
Determine the number of nodes along the internuclearaxis for each of the
Interpretation: The number of nodes along the internuclear axis for each of the
Concept introduction: Born-Oppenheimer approximation state that nuclei are heavier than electrons that considered fixed in space whereas the electrons move constantly around them. The Born−Oppenheimer approximation solves the electronic Schrodinger equation for
Answer to Problem 1P
The number of nodes in
Explanation of Solution
Node is point in molecular orbitals where probability to find the electron density is zero. Nodal plane is the imaginary plane where probability to find electrons is zero.
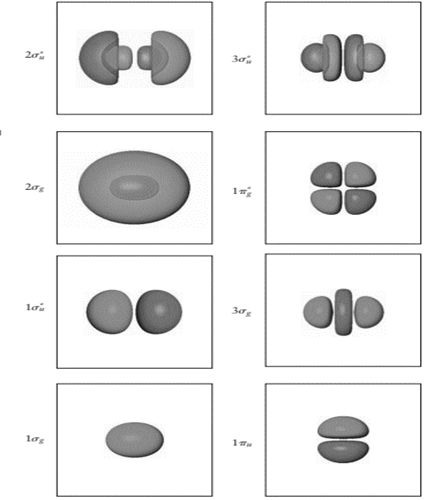
In the figure, node is the oval region. It is formed when plane white surface cut the spherical orbital into two equal halves having opposite symmetry. Also, there are six
In
In
In
In
In
In
Therefore, number of nodes in
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Bundle: Principles of Modern Chemistry, 8th + OWLv2, 1 term (6 months) Printed Access Card
- Closo-boranes and arachno-boranes are structures that exhibit B-B, B-H-B, and B-H bonds. Correct?arrow_forwardIndicate why boron hydrides cannot form large linear or planar structures.arrow_forwardNido-boranes are structures with the molecular formula BnHn+4 that exhibit B-B, B-H-B and B-H bonds. Correct?arrow_forward
- 8:07 AM Wed Dec 18 Final Exam 2024 copy Home Insert Draw Page Layout Formulas Data Review AA 田 General A G fx Alexis Cozort ☑ ⚫ 61% A B D E F H K M N P R S T U 3+ 10 125 mM that yielded peak heights of Aa = 9 1-(a)A sample solution was examined under XRF to quantify the analyte Ce³+. Find the response factor F, when standardized concentration of analyte [Ce³+]A = concentration of internal standard S i.e. [In³*]s = 151 mM was spiked with standardized 1600 and As = 3015 respectively? 11 12 (i)Define F, F = Aa As [A] [S] + X 13 (*Define with variables) 4000 14 15 (ii)Calculate F, F = numeral (You will use the F value in part 1-(b) below) As 16 (*Calculate with numerals) 17 18 1-(b)To determine the unknown conc of analyte [Ce³+], a volume of 15 mL of internal standard S having a concentration [In³+]s = 0.264 M 19 20 was added to 45 mL of unknown, and the mixture was diluted to 100 mL in a volumetric flask. XRF analysis yielded a spectrum, Figure-1, where peak heights A and As are…arrow_forwardAll structural types of Boron hydrides exhibit B-B, B-H-B and B-H bonds. Correct?arrow_forwardN-nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA) is a suspected carcinogen that can form via reactions between dimethylamine (DMA) and monochloramine (NH2Cl). The relevant elementary reactions and the corresponding rate constants are as shown below. Reaction Rate constant (M¹s¹) DMA + NH2Cl = DMCA + NH3 k =1.4×10-1, kr = 5.83×10-3 1.28×10-3 DMA + NH2Cl → UDMH UDMH + NH2Cl → NDMA -> 1.11×10-1 If the initial concentrations of DMA and NH2Cl are given, you should be able to predict the concentrations of all species at any given reaction time. Please write down the rate equations for DMA, NH2C1, DMCA, UDMH and NDMA.arrow_forward
- You wish to add enough NaOCl (sodium hypochlorite) to a 150 m³ swimming pool to provide a dose of 5.0 mg/L TOTOCI as Cl2. (a) How much NaOCI (kg) should you add? (Note: the equivalent weight of NaOCl is based on the reaction: NaOCl + 2H + 2 e→CI + Na +H₂O.) (10 pts) (atomic weight: Na 23, O 16, C1 35.5) (b) The pH in the pool after the NaOCl addition is 8.67. To improve disinfection, you want at least 90% of the TOTOCI to be in the form of HOCI (pKa 7.53). Assuming that HOCI/OCI is the only weak acid/base group in solution, what volume (L) of 10 N HCl must be added to achieve the goal? (15 pts) Note that part a) is a bonus question for undergraduate students. If you decide not to work on this part of the question, you many assume TOTOCI = 7×10-5 M for part b).arrow_forwardPart A 2K(s)+Cl2(g)+2KCI(s) Express your answer in grams to three significant figures. Part B 2K(s)+Br2(1)→2KBr(s) Express your answer in grams to three significant figures. Part C 4Cr(s)+302(g)+2Cr2O3(s) Express your answer in grams to three significant figures. Part D 2Sr(s)+O2(g) 2SrO(s) Express your answer in grams to three significant figures. Thank you!arrow_forwardA solution contains 10-28 M TOTCO3 and is at pH 8.1. How much HCI (moles per liter of solution) is required to titrate the solution to pH 7.0? (H2CO3: pKa1=6.35, pKa2=10.33)arrow_forward
- Don't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardThe standard Gibbs energies of formation of CaO(s), CaCO3 (calcite), and CO2 (g) are -604.04, -1128.80, and -394.37 kJ/mol, respectively. Find the value of AG, and Keq for the following reaction: CaCO3 CaO (s) + CO2 (g) [ap A dry mixture containing 1 g of each solid [CaCO3(s) and CaO(s)] is on the lab bench in contact with the atmosphere, which contains a partial pressure of 10-35 bar CO2 (g). What is the total Gibbs free energy of the system containing all three species before any reaction has happened? Does the equilibrium driving force favor conversion of one of the solids into the other, or are the solids equilibrated with one another?arrow_forwardClassification of boranes.arrow_forward
 Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning





