
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The phases present in the phase diagrams have to be stated.
Concept introduction:
The azeotropic mixture is defined as a mixture of two or more liquids which evaporates without altering the composition of the mixture. The azeotropic mixture has a constant boiling point because of the same composition in liquid as well as vapor phase. The components of azeotropic mixture are not separated by distillation processes.
The phase diagram represents the changes in the mixture on changing the parameters like temperature and pressure of the mixture.
(a)
Answer to Problem 5C.5P
The phases have been stated in the phase diagrams as,
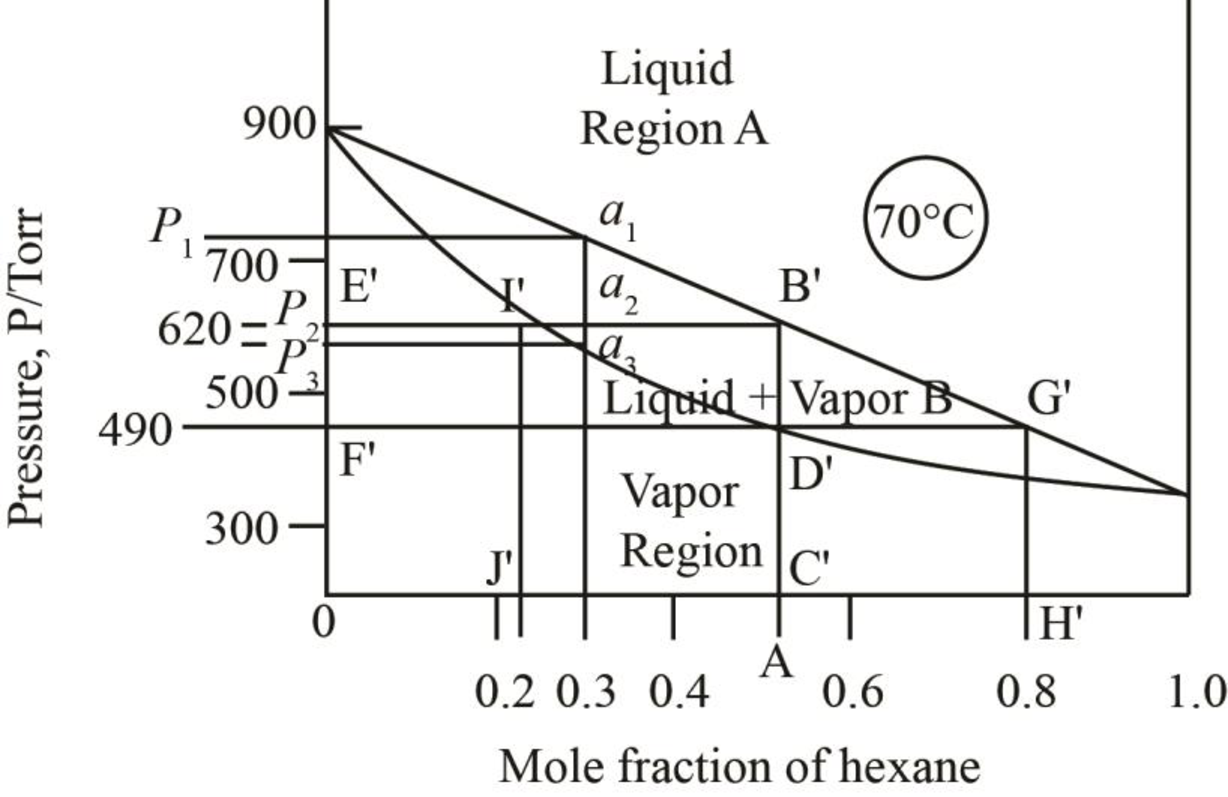
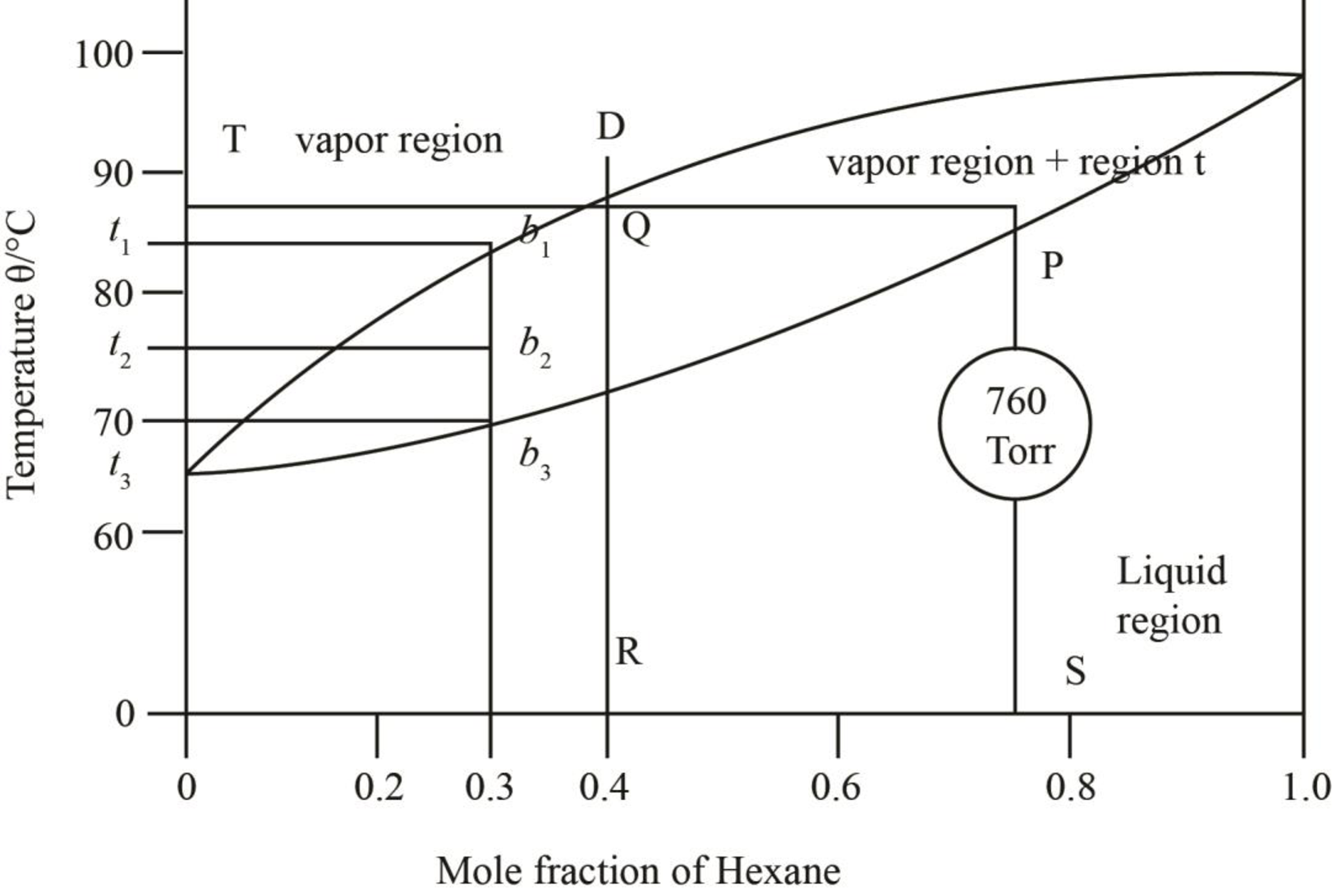
Explanation of Solution
The given phase diagrams are shown below as,
Figure 1
Figure 2
The region between the liquid phase curve and vapour phase curve has liquid and vapour phase in the equilibrium. Thus, the number of phases present in that region is
In the region above the curve, only vapour phase is present.
In the region below the curve, only liquid phase is present.
The regions are stated in the phase diagrams as,
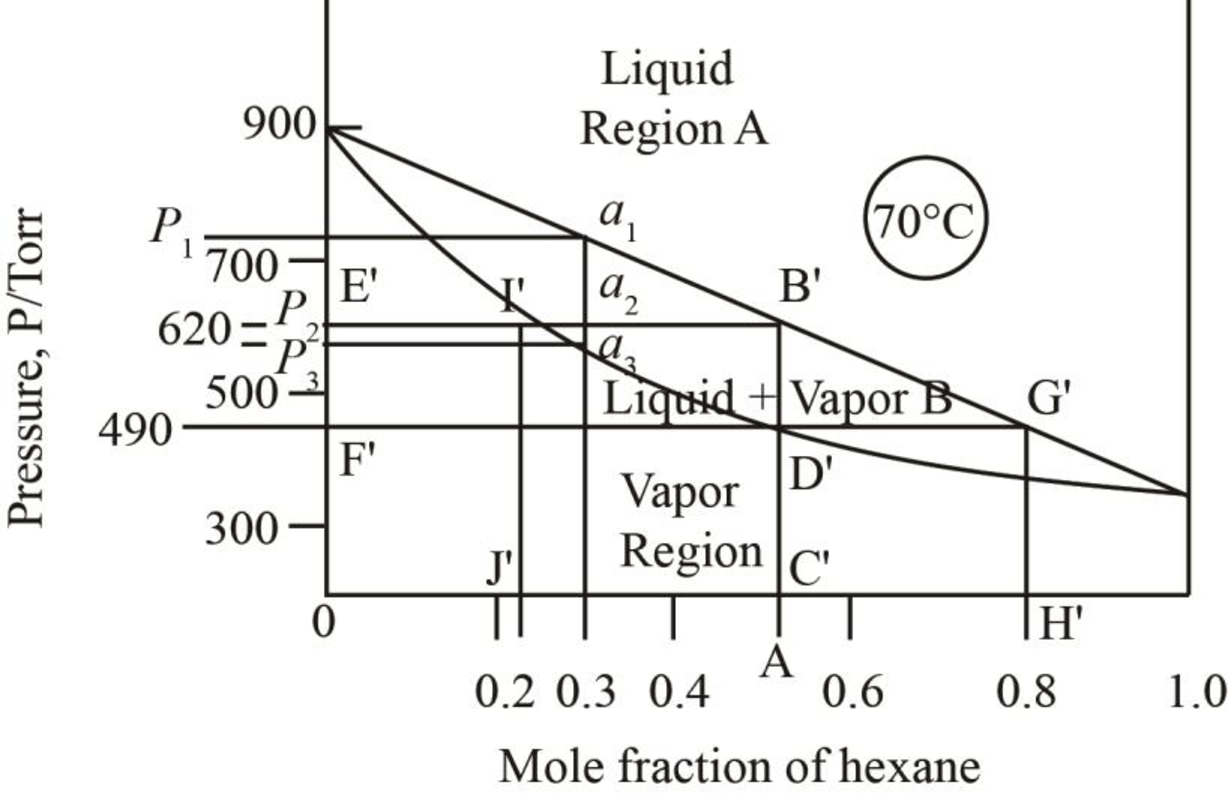
Figure 3
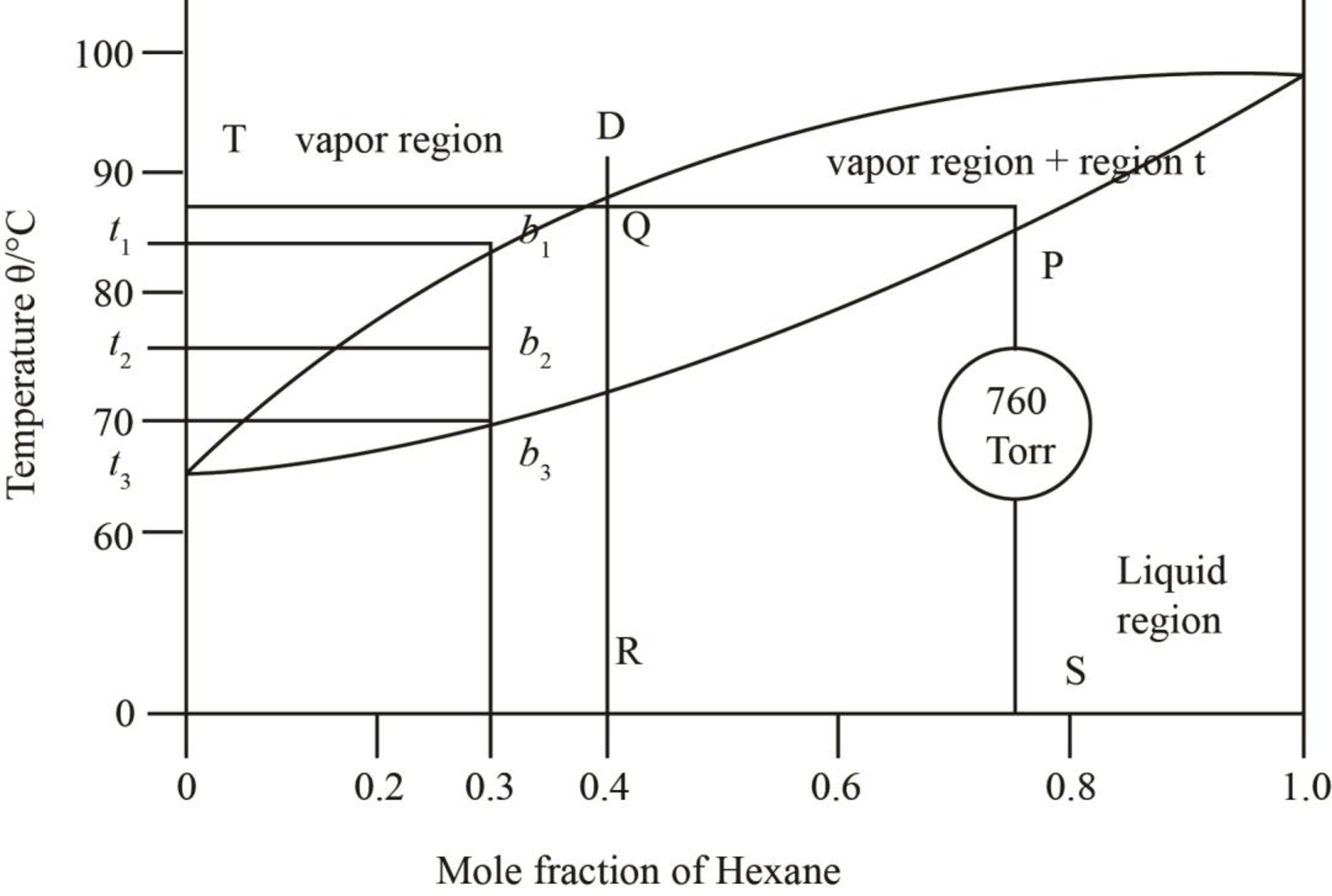
Figure 4
(b)
Interpretation:
The vapor pressure of the mixture of heptane and hexane at
Concept introduction:
The azeotropic mixture is defined as a mixture of two or more liquids which evaporates without altering the composition of the mixture. The azeotropic mixture has a constant boiling point because of the same composition in liquid as well as vapor phase. The components of azeotropic mixture are not separated by distillation processes.
The phase diagram represents the changes in the mixture on changing the parameters like temperature and pressure of the mixture.
(b)
Answer to Problem 5C.5P
The vapour pressure of the mixture of heptane and hexane at
Explanation of Solution
The number of moles of heptane and hexane present in the mixture is
The mole fraction is calculated by the formula as,
The total number of moles of the mixture is calculated as,
Substitute the values in the equation (1) to calculate the mole fraction of hexane as,
The pressure corresponding to
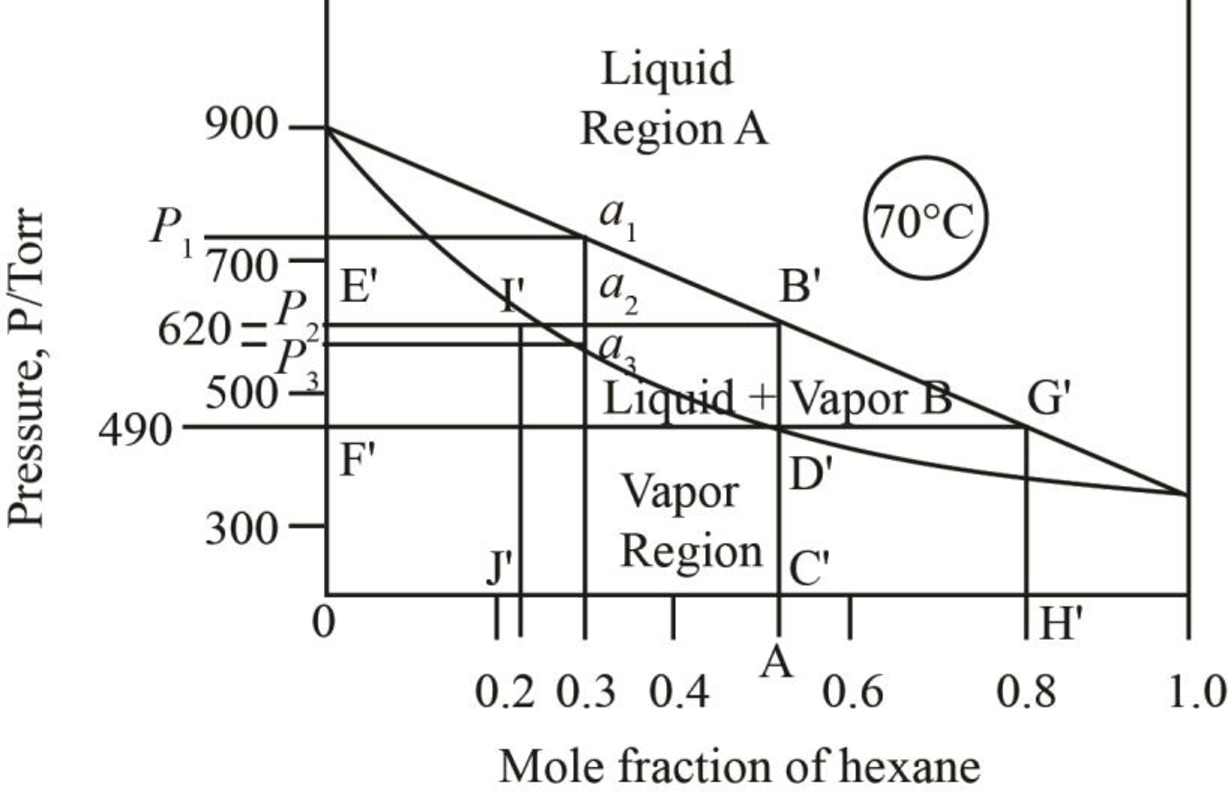
Figure 5
Thus, the vapour pressure of the mixture of heptane and hexane at
(c)
Interpretation:
The vapor pressure of the mixture of heptane and hexane at
Concept introduction:
The azeotropic mixture is defined as a mixture of two or more liquids which evaporates without altering the composition of the mixture. The azeotropic mixture has a constant boiling point because of the same composition in liquid as well as vapor phase. The components of azeotropic mixture are not separated by distillation processes.
The phase diagram represents the changes in the mixture on changing the parameters like temperature and pressure of the mixture.
(c)
Answer to Problem 5C.5P
The vapour pressure of the mixture of heptane and hexane at
Explanation of Solution
The number of moles of heptane and hexane present in the mixture is
The mole fraction is calculated by the formula as,
The total number of moles of the mixture is calculated as,
Substitute the values in the equation (1) to calculate the mole fraction of hexane as,
The pressure corresponding to
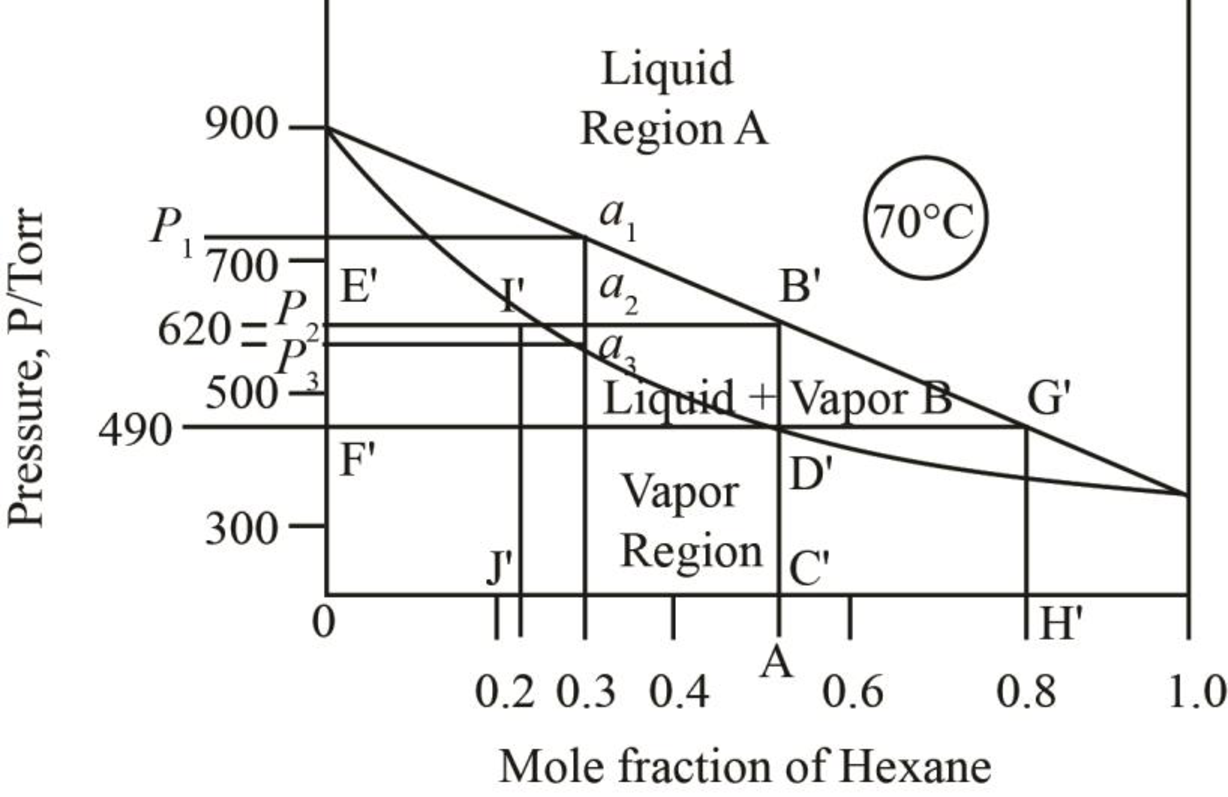
Figure 6
When just one drop of the liquid remains, then the vapour pressure of the mixture is more than
Thus, the vapour pressure of the mixture of heptane and hexane at
(d)
Interpretation:
The mole fraction of hexane in the liquid and vapour phase for the conditions of part b has to be calculated.
Concept introduction:
The azeotropic mixture is defined as a mixture of two or more liquids which evaporates without altering the composition of the mixture. The azeotropic mixture has a constant boiling point because of the same composition in liquid as well as vapor phase. The components of azeotropic mixture are not separated by distillation processes.
The phase diagram represents the changes in the mixture on changing the parameters like temperature and pressure of the mixture.
(d)
Answer to Problem 5C.5P
The mole fraction of hexane in the liquid and vapour phase for the conditions of part b has been calculated as
Explanation of Solution
The number of moles of hexane present in the mixture is given as
The mole fraction is calculated by the formula as,
The total number of moles of the mixture is calculated as,
Substitute the values in the equation (1) to calculate the mole fraction of hexane as,
The mole fraction of hexane in the liquid phase is taken by drawing the line on the liquid curve of the phase diagram which is shown by the line AB’ in phase diagram below.
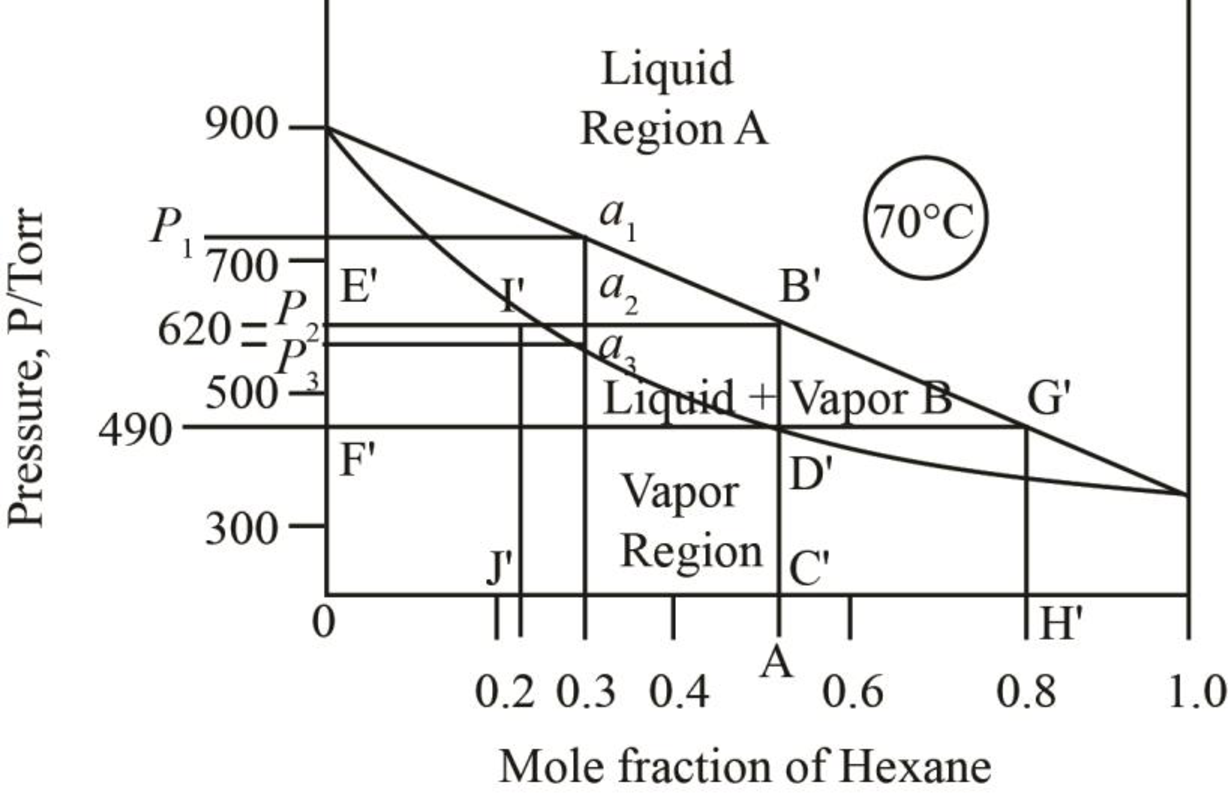
Figure 7
Thus, mole fraction of hexane in the liquid and vapour phase for the conditions of part b is
(e)
Interpretation:
The mole fraction of hexane in the liquid and vapour phase for the conditions of part c has to be calculated.
Concept introduction:
The azeotropic mixture is defined as a mixture of two or more liquids which evaporates without altering the composition of the mixture. The azeotropic mixture has a constant boiling point because of the same composition in liquid as well as vapor phase. The components of azeotropic mixture are not separated by distillation processes.
The phase diagram represents the changes in the mixture on changing the parameters like temperature and pressure of the mixture.
(e)
Answer to Problem 5C.5P
The mole fraction of hexane in the liquid and vapour phase for the conditions of part c has been calculated as
Explanation of Solution
The number of moles of hexane present in the mixture is given as
The mole fraction is calculated by the formula as,
The total number of moles of the mixture is calculated as,
Substitute the values in the equation (1) to calculate the mole fraction of hexane as,
The mole fraction of hexane in the liquid phase is taken by drawing a parallel line on the liquid curve of the phase diagram which is shown by the line F’G’ in phase diagram below.
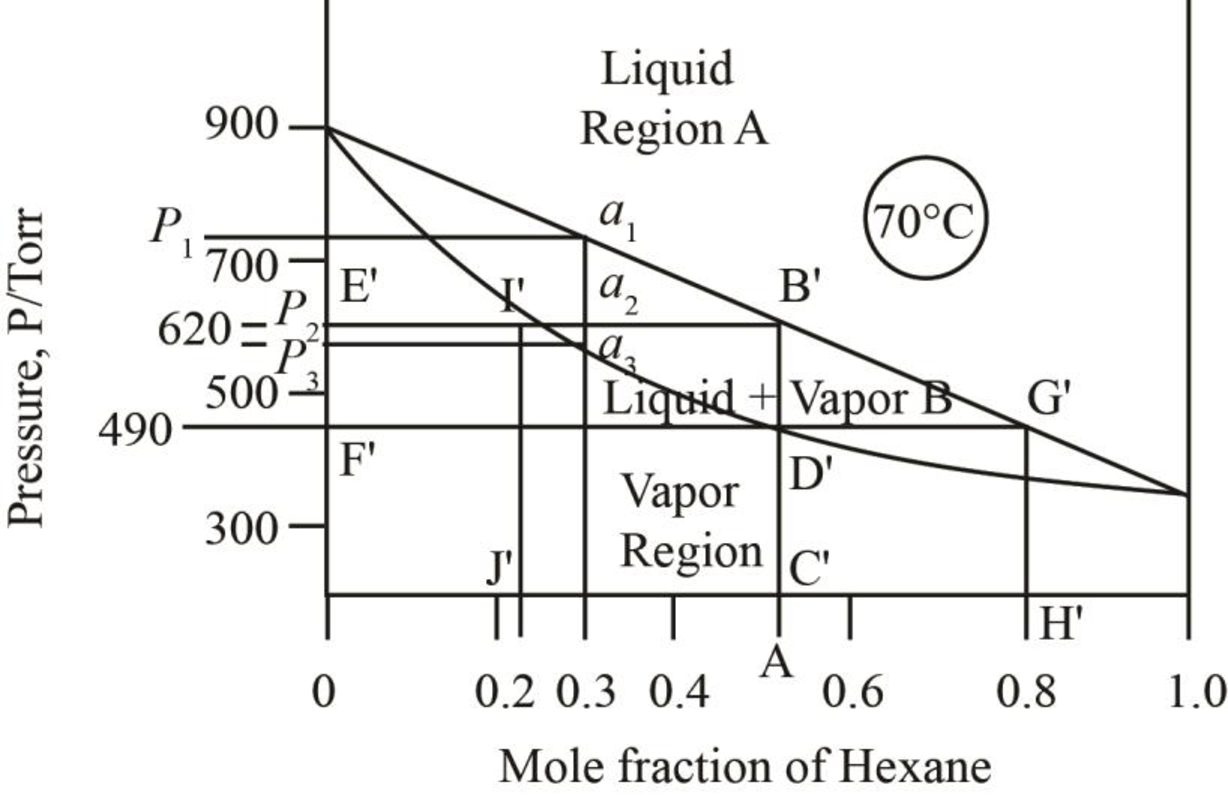
Figure 8
The mole fraction of hexane in the liquid phase is found out to be
Thus, mole fraction of hexane in the liquid and vapour phase for the conditions of part c is
(f)
Interpretation:
The amounts of substances in the liquid and vapour phase at
Concept introduction:
The azeotropic mixture is defined as a mixture of two or more liquids which evaporates without altering the composition of the mixture. The azeotropic mixture has a constant boiling point because of the same composition in liquid as well as vapor phase. The components of azeotropic mixture are not separated by distillation processes.
The phase diagram represents the changes in the mixture on changing the parameters like temperature and pressure of the mixture.
(f)
Answer to Problem 5C.5P
The mole fraction of hexane in the liquid and vapour phase at
Explanation of Solution
The overall mole fraction of heptane present in the mixture is given as
Thus, the overall mole fraction of hexane present in the mixture is calculated as,
The mole fraction of hexane in the liquid phase is taken by drawing a line passing through
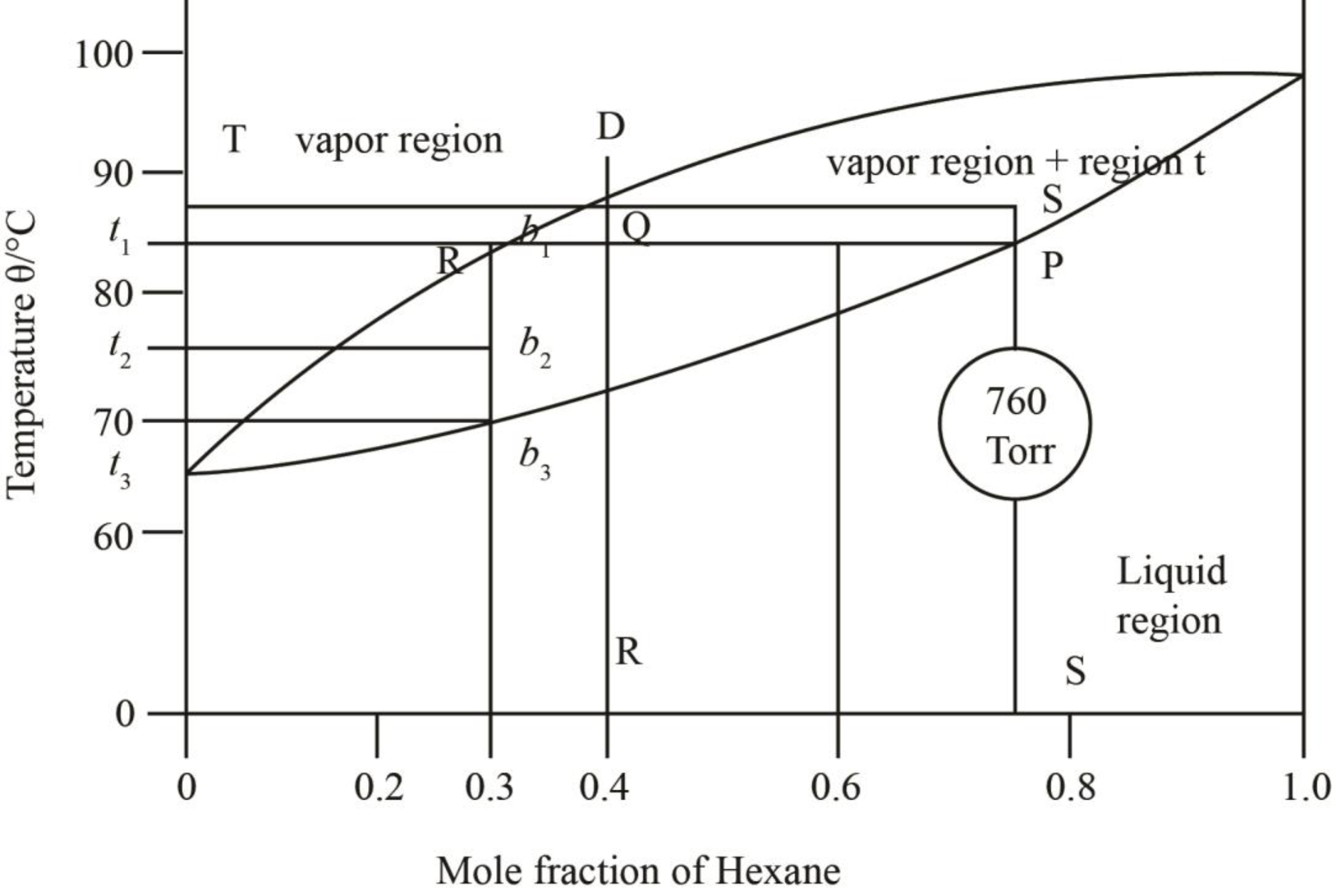
Figure 9
The mole fraction of hexane in the liquid phase is found out to be approximately
Thus, the mole fraction of heptane in the liquid phase is calculated as,
The mole fraction of hexane in the vapour phase is found out to be
Thus, the mole fraction of heptane in the vapour phase is calculated as,
Thus, mole fraction of hexane in the liquid and vapour phase at
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Atkins' Physical Chemistry
- Consider the structure of 1-bromo-2-fluoroethane. Part 1 of 2 Draw the Newman projection for the anti conformation of 1-bromo-2-fluoroethane, viewed down the C1-C2 bond. ✡ ぬ Part 2 of 2 H H F Br H H ☑ Draw the Newman projection for the gauche conformation of 1-bromo-2-fluoroethane, viewed down the C1-C2 bond. H F Br H Harrow_forwardPlease help me answer this question. I don't understand how or where the different reagents will attach and it's mostly due to the wedge bond because I haven't seen a problem like this before. Please provide a detailed explanation and a drawing showing how it can happen and what the final product will look like.arrow_forwardWhich of the following compounds is the most acidic in the gas phase? Group of answer choices H2O SiH4 HBr H2Sarrow_forward
- Which of the following is the most acidic transition metal cation? Group of answer choices Fe3+ Sc3+ Mn4+ Zn2+arrow_forwardBased on the thermodynamics of acetic acid dissociation discussed in Lecture 2-5, what can you conclude about the standard enthalpy change (ΔHo) of acid dissociation for HCl? Group of answer choices You cannot arrive at any of the other three conclusions It is a positive value It is more negative than −0.4 kJ/mol It equals −0.4 kJ/molarrow_forwardPLEASE HELP URGENT!arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





