
Interpretation:
The partial pressures of methylbenzene (A) and butanone have to be calculated. The calculated partial pressures have to be plotted against the mole fraction of the liquid mixture. Henry’s law constant for both the components has to be calculated.
Concept introduction:
Henry’s law states that the partial vapour pressure is directly proportional to the amount of substance dissolved. It involves an empirical constant KH called Henry’s law constant.
Answer to Problem 5A.4P
The partial pressures of methylbenzene (A) are calculated in the table given below.
| yA | xA | p/kPa | pA/kPa |
| 0 | 0 | 36.066 | 0 |
| 0.041 | 0.0898 | 34.121 | 1.398961 |
| 0.1154 | 0.2476 | 30.9 | 3.56586 |
| 0.1762 | 0.3577 | 28.626 | 5.043901 |
| 0.2772 | 0.5194 | 25.239 | 6.996251 |
| 0.3393 | 0.6036 | 23.402 | 7.940299 |
| 0.445 | 0.7188 | 20.6984 | 9.210788 |
| 0.5435 | 0.8019 | 18.592 | 10.10475 |
| 0.7284 | 0.9105 | 15.496 | 11.28729 |
| 1 | 1 | 12.295 | 12.295 |
The partial pressures of butanone are calculated in the table given below.
| yB | xB | p/kPa | pB/kPa |
| 1 | 1 | 36.066 | 36.066 |
| 0.959 | 0.9102 | 34.121 | 32.72204 |
| 0.8846 | 0.7524 | 30.9 | 27.33414 |
| 0.8238 | 0.6423 | 28.626 | 23.5821 |
| 0.7228 | 0.4806 | 25.239 | 18.24275 |
| 0.6607 | 0.3964 | 23.402 | 15.4617 |
| 0.555 | 0.2812 | 20.6984 | 11.48761 |
| 0.4565 | 0.1981 | 18.592 | 8.487248 |
| 0.2716 | 0.0895 | 15.496 | 4.208714 |
| 0 | 0 | 12.295 | 0 |
The partial pressure of methylbenzene (A) is plotted against the mole fraction of the liquid mixture in the graph shown below.
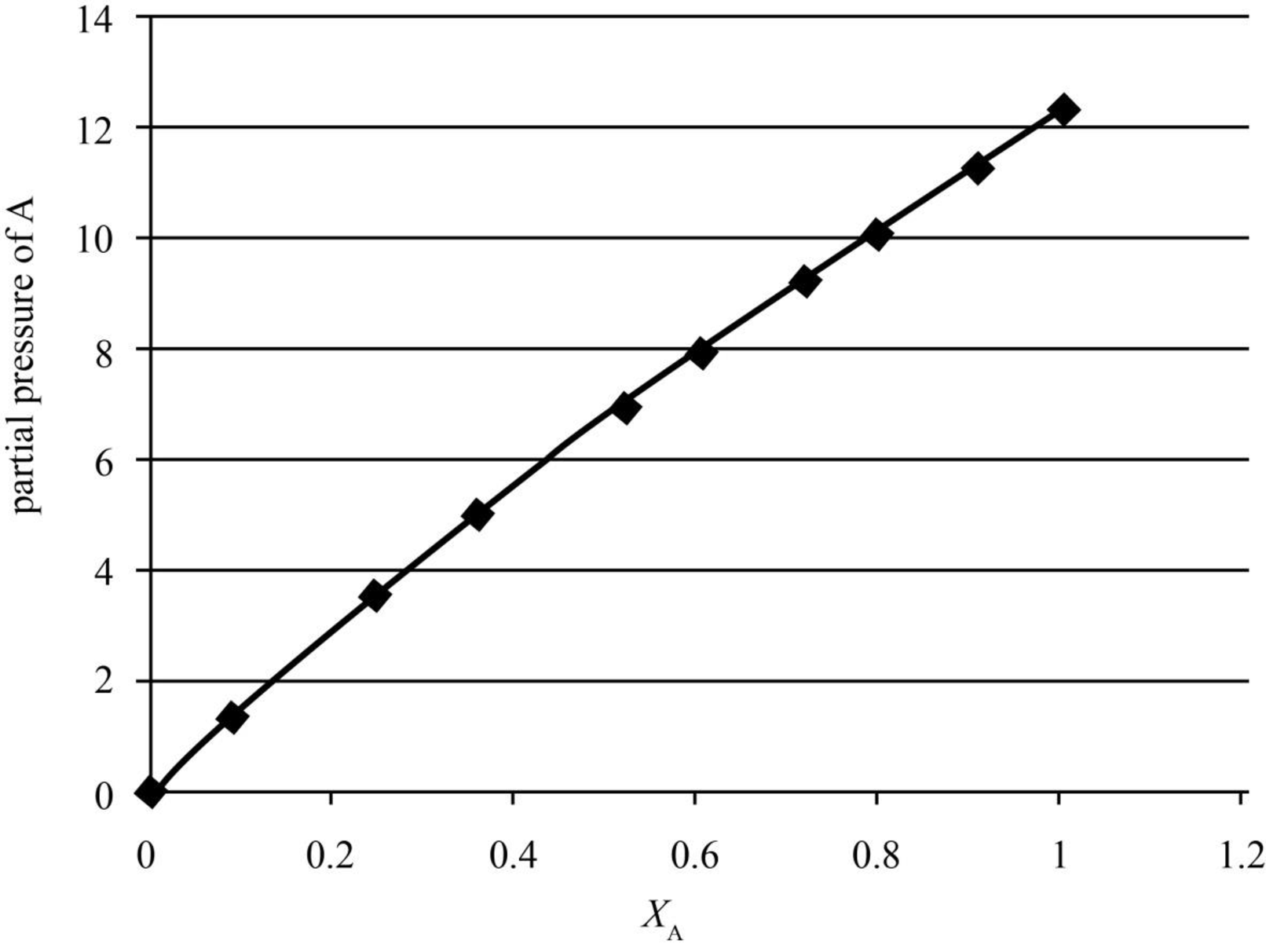
Figure 1
The partial pressure of butanone is plotted against the mole fraction of the liquid mixture in the graph shown below.
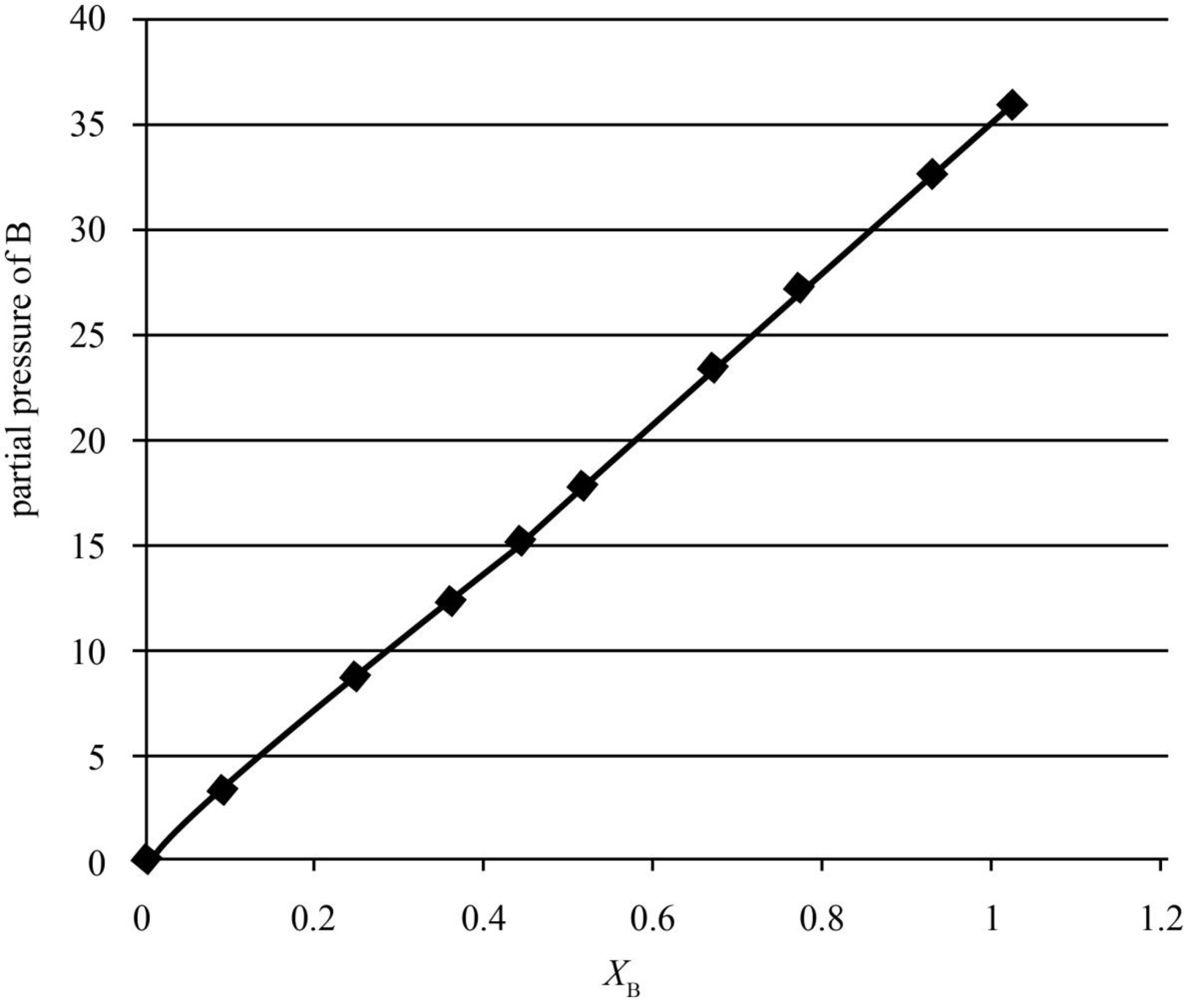
Figure 2
The value of Henry’s law constant for methylbenzene (A) is 15.578 kPa_. The value of Henry’s law constant for butanone is 47.025 kPa_.
Explanation of Solution
The data for the mole fraction of methylbenzene (A) in the liquid phase, xA, vapour phase, yA and the total pressure, p is given below.
| xA | yA | p/kPa |
| 0 | 0 | 36.066 |
| 0.0898 | 0.041 | 34.121 |
| 0.2476 | 0.1154 | 30.9 |
| 0.3577 | 0.1762 | 28.626 |
| 0.5194 | 0.2772 | 25.239 |
| 0.6036 | 0.3393 | 23.402 |
| 0.7188 | 0.445 | 20.6984 |
| 0.8019 | 0.5435 | 18.592 |
| 0.9105 | 0.7284 | 15.496 |
| 1 | 1 | 12.295 |
According to Dalton’s law of partial pressures, the partial pressure of methylbenzene (A) (pA) is calculated by the formula given below.
pA=yAp (1)
Where,
- yA is the mole fraction of methylbenzene (A) in the vapour phase.
- p is the total vapour pressure.
The total pressure (p) at yA=0.0410 is 34.121 kPa.
Substitute the value of p and yA in equation (1).
pA=0.0410×34.121 kPa=1.398961 kPa_
Therefore, the partial pressure of methylbenzene (A) (pA) is calculated for all vapour phase composition (yA) in the table below.
| yA | xA | p/kPa | pA/kPa |
| 0 | 0 | 36.066 | 0 |
| 0.041 | 0.0898 | 34.121 | 1.398961 |
| 0.1154 | 0.2476 | 30.9 | 3.56586 |
| 0.1762 | 0.3577 | 28.626 | 5.043901 |
| 0.2772 | 0.5194 | 25.239 | 6.996251 |
| 0.3393 | 0.6036 | 23.402 | 7.940299 |
| 0.445 | 0.7188 | 20.6984 | 9.210788 |
| 0.5435 | 0.8019 | 18.592 | 10.10475 |
| 0.7284 | 0.9105 | 15.496 | 11.28729 |
| 1 | 1 | 12.295 | 12.295 |
The graph between the mole fraction in the liquid phase, xA and the partial pressure, pA is given below.
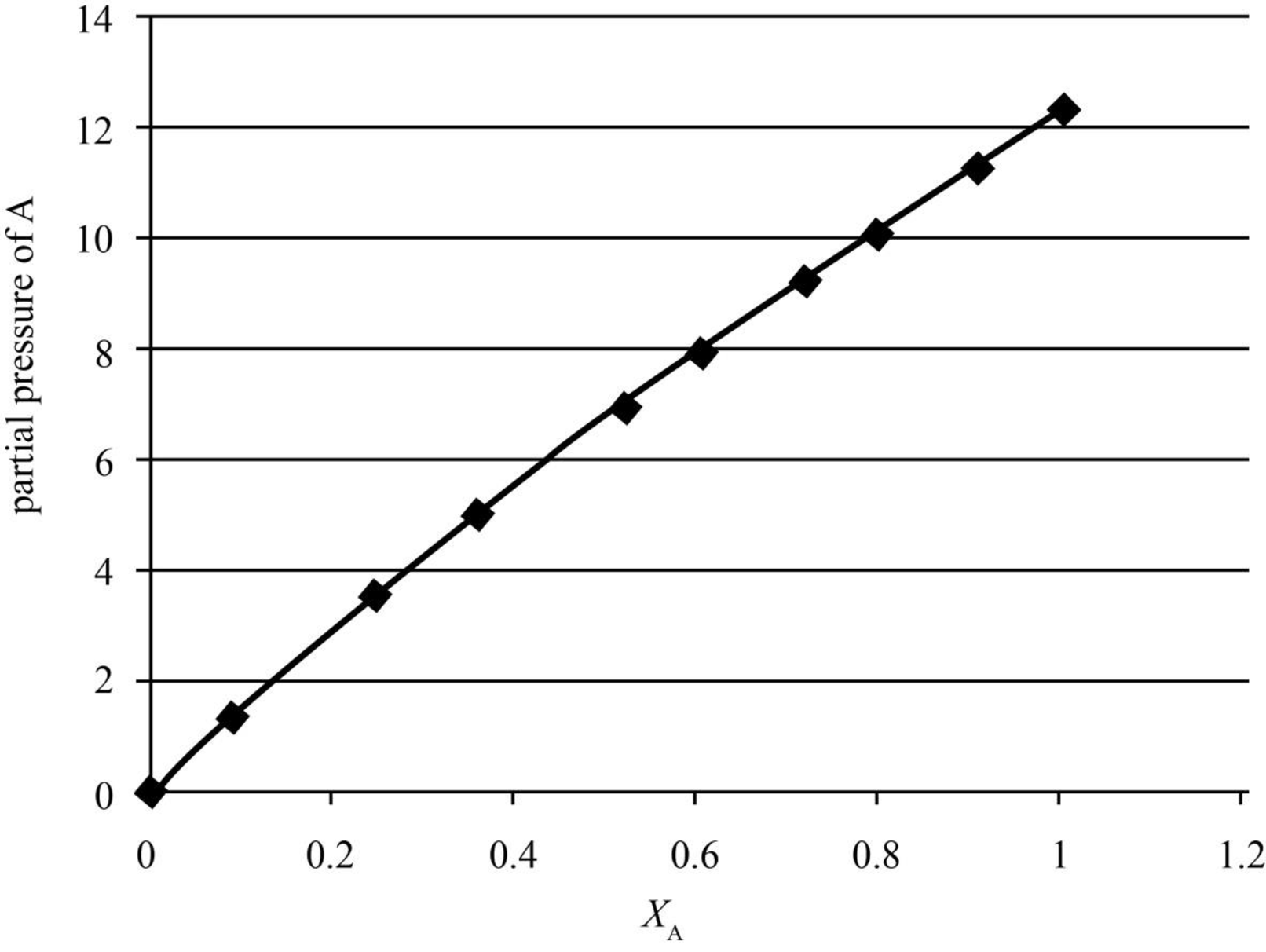
Figure 1
In the above graph, when xA is 0.0898, pA is 1.398961 kPa.
According to Henry’s law, the partial pressure of methylbenzene (A) is given as,
pA=xAKH (2)
Where,
- pA is the partial pressure of methylbenzene (A).
- KH is Henry’s law constant.
- xA is the mole fraction of methylbenzene (A) in the liquid phase.
Substitute the value of xA and pA in equation (2).
1.398961 kPa=0.0898×KHKH=1.398961 kPa0.0898=15.578 kPa_
Therefore, the value of Henry’s law constant for methylbenzene (A) is 15.578 kPa_.
The total mole fraction in the vapour phase equal to 1.
yA+yB=1yB=1−yA (3)
Where,
- yB is the mole fraction of butanone in the vapour phase.
The mole fraction of methylbenzene (A) in the vapour phase (yA) is 0.0410.
Substitute the value of yA in equation (3).
yB=1−0.0410=0.959
According to Dalton’s law of partial pressures, the partial pressure of butanone (B) (pB) is calculated by the formula given below.
pB=yBp (4)
Where,
- yB is the mole fraction of butanone (B) in the vapour phase.
- p is the total vapour pressure.
The total pressure (p) at yB=0.959 is 34.121 kPa.
Substitute the value of p and yB in equation (4).
pB=0.959×34.121 kPa=32.722 kPa_
Therefore, the partial pressure of butanone (B) (pB) is calculated for all vapour phase composition (yB) in the table below.
| yB | xB | p/kPa | pB/kPa |
| 1 | 1 | 36.066 | 36.066 |
| 0.959 | 0.9102 | 34.121 | 32.72204 |
| 0.8846 | 0.7524 | 30.9 | 27.33414 |
| 0.8238 | 0.6423 | 28.626 | 23.5821 |
| 0.7228 | 0.4806 | 25.239 | 18.24275 |
| 0.6607 | 0.3964 | 23.402 | 15.4617 |
| 0.555 | 0.2812 | 20.6984 | 11.48761 |
| 0.4565 | 0.1981 | 18.592 | 8.487248 |
| 0.2716 | 0.0895 | 15.496 | 4.208714 |
| 0 | 0 | 12.295 | 0 |
The graph between the mole fraction in the liquid phase, xB and the partial pressure, pB is given below.
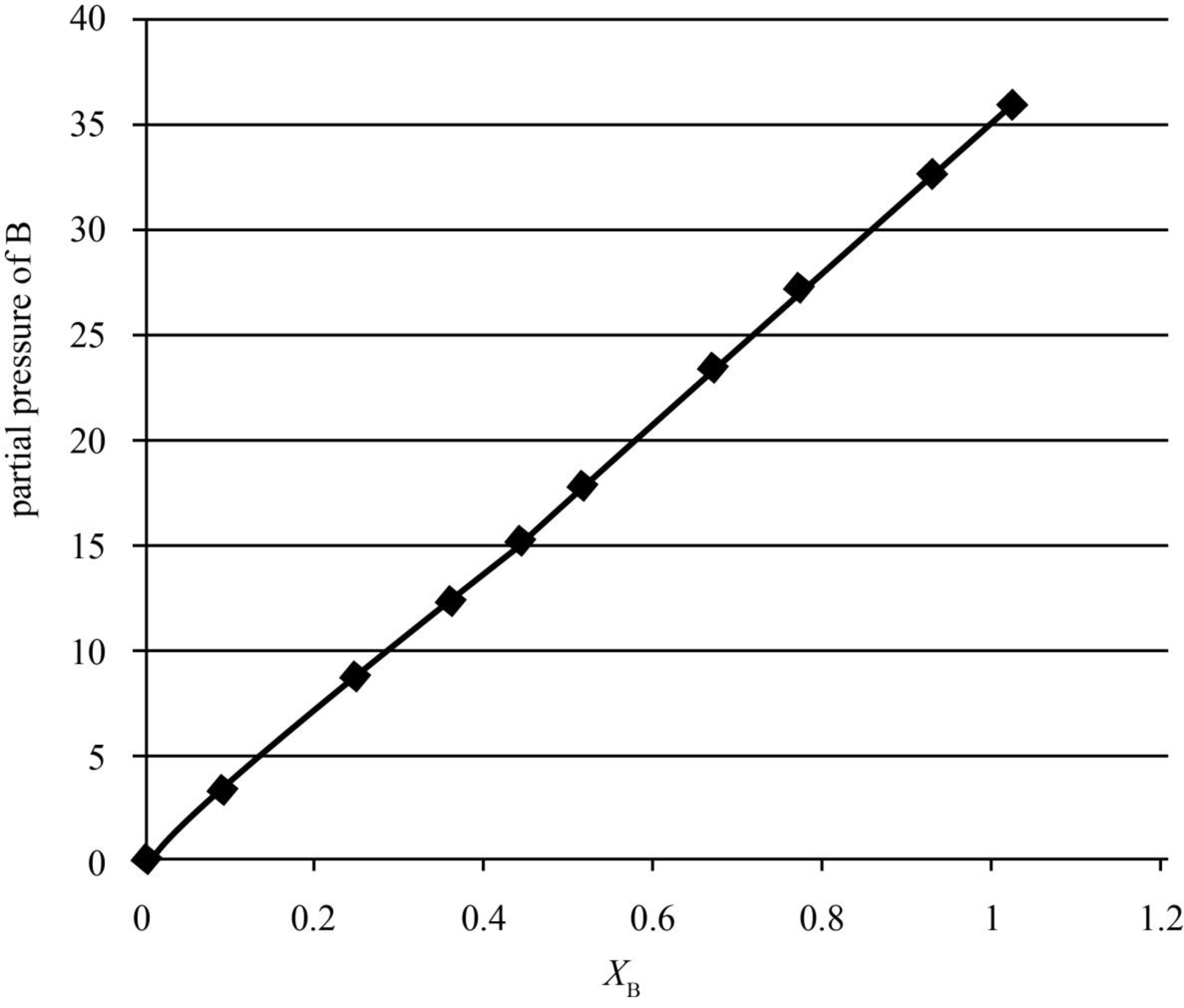
Figure 2
In the above graph, when xB is 0.0895, pB is 4.208714 kPa.
According to Henry’s law, the partial pressure of butanone (B) is given as,
pB=xBKH (5)
Where,
- pB is the partial pressure of butanone (B).
- KH is Henry’s law constant.
- xB is the mole fraction of butanone (B) in the liquid phase.
Substitute the value of xB and pB in equation (5).
4.208714 kPa kPa=0.0895×KHKH=4.208714 kPa0.0895=47.025 kPa_
Therefore, the value of Henry’s law constant for butanone is 47.025 kPa_.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Atkins' Physical Chemistry
- H2O2(aq) +3 I¯(aq) +2 H+(aq) → 13(aq) +2 H₂O(l)· ••• Experiment [H2 O2]o (M) [I]o (M) [H+]。 (M) Initial rate (M/s) 1 0.15 0.15 0.05 0.00012 234 0.15 0.3 0.05 0.00024 0.3 0.15 0.05 0.00024 0.15 0.15 0.1 0.00048 Calculate the overall order of this reaction using the table data.arrow_forwardThe U. S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) sets limits on healthful levels of air pollutants. The maximum level that the EPA considers safe for lead air pollution is 1.5 μg/m³ Part A If your lungs were filled with air containing this level of lead, how many lead atoms would be in your lungs? (Assume a total lung volume of 5.40 L.) ΜΕ ΑΣΦ = 2.35 1013 ? atoms ! Check your rounding. Your final answer should be rounded to 2 significant figures in the last step. No credit lost. Try again.arrow_forwardY= - 0.039 (14.01) + 0.7949arrow_forward
- Suppose 1.76 g of magnesium acetate (Mg (CH3CO2)2) are dissolved in 140. mL of water. Find the composition of the resulting electrolyte solution. In particular, list the chemical symbols (including any charge) of each dissolved ion in the table below. List only one ion per row. mEq Then, calculate the concentration of each ion in dwrite the concentration in the second column of each row. Be sure you round your answers to the L correct number of significant digits. ion Add Row mEq L x 5arrow_forwardA pdf file of your hand drawn, stepwise mechanisms for the reactions. For each reaction in the assignment, you must write each mechanism three times (there are 10 reactions, so 30 mechanisms). (A) do the work on a tablet and save as a pdf., it is expected to write each mechanism out and NOT copy and paste the mechanism after writing it just once. Everything should be drawn out stepwise and every bond that is formed and broken in the process of the reaction, and is expected to see all relevant lone pair electrons and curved arrows.arrow_forwardNonearrow_forward
- Nonearrow_forwardDraw the structure of the product of the reaction given the IR and MS data. Spectral analysis of the product reveals: MS: M 150, M-15, M-43 CH.COCI AICI, IR: 3150-3000 cm, 2950-2850 cm and 1700 cmarrow_forwardPart II. Identify whether the two protons in blue are homotopic, enantiopic, diasteriotopic, or heterotopic. a) HO b) Bri H HH c) d) H H H Br 0arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





