
Concept explainers
The following unadjusted
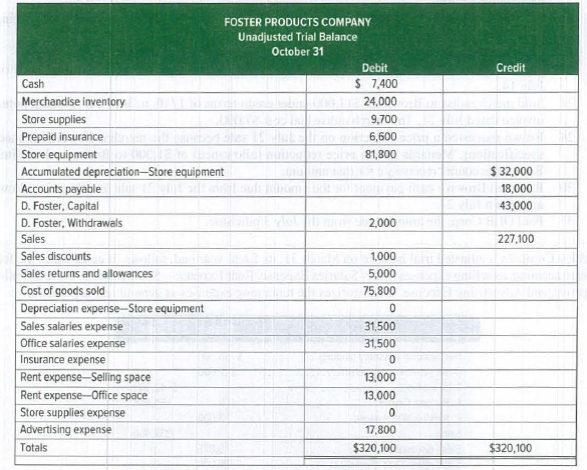
Required
- 1. Prepare
adjusting journal entries to reflect each of the following:- a. Store supplies still available at fiscal year-end amount to $3,700.
- b. Expired insurance, an administrative expense, for the fiscal year is $2,800.
- c. Depreciation expense on store equipment, a selling expense, is $3,000 for the fiscal year.
- d. To estimate shrinkage, a physical count of ending merchandise inventory is taken. It shows $21,300 of inventory is still available at fiscal year-end.
- 2. Prepare a multiple-step income statement for the year ended October 31 that begins with gross sales and includes separate categories for net sales, cost of goods sold, selling expenses, and general and administrative expenses.
- 3. Prepare a single-step income statement for the year ended October 31.
- 4. Compute the
current ratio , acid-test ratio, and gross margin ratio as of October 31. (Round ratios to two decimals.)
1.
Journalize adjusting entries of Company FP.
Explanation of Solution
Journal entry: Journal entry is a set of economic events which can be measured in monetary terms. These are recorded chronologically and systematically.
Adjusting entries: Adjusting entries are those entries which are recorded at the end of the year, to update the income statement accounts (revenue and expenses) and balance sheet accounts (assets, liabilities, and stockholders’ equity) to maintain the records according to accrual basis principle.
Record the adjusting entries of Company FP.
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| a. | Store supplies expense (1) | 6,000 | ||
| Store supplies | 6,000 | |||
| (To record store supplies expense) | ||||
| b. | Insurance expenses | 2,800 | ||
| Prepaid expenses | 2,800 | |||
| (To record prepaid selling expenses) | ||||
| c. | Depreciation expense - Store equipment | 3,000 | ||
| Accumulated Depreciation - Store equipment | 3,000 | |||
| (To record depreciation expenses) | ||||
| d. | Cost of goods sold | 2,700 | ||
| Merchandise inventory (2) | 2,700 | |||
| (To record the inventory shrinkage) |
Table (1)
a. To record store supplies expense:
- Store supplies expense is an expense account and it is increased. Therefore, debit office supplies expense with $6,000.
- Store supplies are an asset account and it is decreased. Therefore, credit office supplies with $6,000.
b. To record prepaid insurance expenses:
- Insurance expense is an expense account and it is increased. Therefore, it is debited with $2,800.
- Prepaid expense is an asset account and it is decreased. Therefore, credit prepaid selling expense with $2,800.
c. To record depreciation expenses:
- Depreciation expense is an expense account and it is increased. Therefore, it is debited with $3,000.
- Prepaid expense is an asset account and it is decreased. Therefore, credit prepaid selling expense with $3,000.
d. To record the shrinkage of inventory:
- Cost of goods sold is an expense and they are increased. Thus, it is debited with $2,700.
- Inventory is an asset account, and they are increased. Hence, debit the inventory returns estimated account by $2,700.
Working Note:
Compute the Store supplies expense.
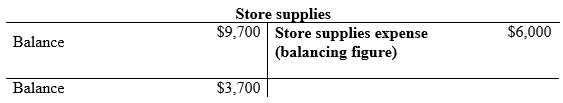
…… (1)
Compute the shrinkage of inventory.
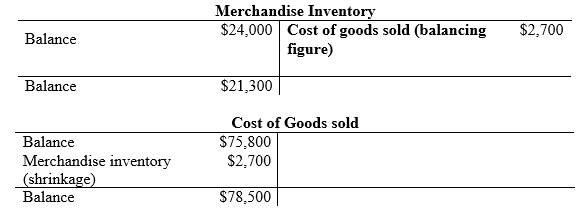
…… (2)
2.
Prepare the multi- step income statement of Company FP for the year ended October 31.
Explanation of Solution
Multi-step income statement: The income statement represented in multi-steps with several subtotals, to report the income from principal operations, and separate the other expenses and revenues which affect net income, is referred to as multi-step income statement.
Prepare the income statement of Company FP for the year ended October 31.
| Company FP | ||
| Statement of Income | ||
| For the year ended October 31 | ||
| Particulars | Amount | Amount |
| Sales | $227,100 | |
| Less: Sales discounts | $1,000 | |
| Sales returns and allowances | $5,000 | ($6,000) |
| Net sales | $221,100 | |
| Less: Cost of goods sold (2) | ($78,500) | |
| Gross profit | $142,600 | |
| Expenses | ||
| Selling expenses | ||
| Depreciation expense—Store equipment | $3,000 | |
| Sales salaries expense | $31,500 | |
| Rent expense—Selling space | $13,000 | |
| Store supplies expense (1) | $6,000 | |
| Advertising expense | $17,800 | |
| Total selling expenses | $71,300 | |
| General and administrative expenses | ||
| Insurance expense | $2,800 | |
| Office salaries expense | $31,500 | |
| Rent expense—Office space | $13,000 | |
| Total general and administrative expenses | $47,300 | |
| Total expenses | ($118,600) | |
| Net income | $24,000 | |
Table (2)
Thus, the net income of Company FP for the year ended October 31 is $24,000.
3.
Prepare the single-step income statement of Company FP for the year ended October 31.
Explanation of Solution
Single-step income statement: This statement displays the total revenues as one line item from which the total expenses including cost of goods sold is subtracted to arrive at the net profit /net loss for the period.
Prepare the income statement of Company FP for the year ended October 31.
| Company FP | ||
| Statement of Income | ||
| For the year ended October 31 | ||
| Particulars | Amount | Amount |
| Net sales | $221,100 | |
| Less: Expenses | ||
| Cost of goods sold (2) | $78,500 | |
| Selling expenses (Refer Table (2)) | $71,300 | |
| General and administrative expense (Refer Table (2)) | $47,300 | |
| Total expenses | ($197,100) | |
| Net income | $24,000 | |
Table (3)
Thus, the net income of Company FP for the year ended October 31 is $24,000.
4.
Compute current ratio, acid-test ratio and gross margin ratio.
Explanation of Solution
Current ratio: Current ratio is one of the liquidity ratios, which measures the capacity of the company to meet its short-term obligations using its current assets. Current ratio is calculated by using the formula:
Acid test ratio: It is a ratio used to determine a company’s ability to pay back its current liabilities by liquid assets that are current assets except inventory and prepaid expenses.
Gross margin ratio: The percentage of gross profit generated by every dollar of net sales is referred to as gross margin ratio. This ratio measures the profitability of a company by quantifying the amount of income earned from sales revenue generated after cost of goods sold are paid. The higher the ratio, the more ability to cover operating expenses. It is calculated by using the formula:
Compute current ratio, acid test ratio and gross margin ratio of Company FP.
| Computation of ratios | |
| Particulars | Amount |
| Cash | $7,400 |
| Merchandise inventory (2) | $21,300 |
| Store supplies (1) | $3,700 |
| Prepaid insurance | $3,800 |
| Total current assets (A) | $36,200 |
| Current liabilities (B) | $18,000 |
| Current ratio | 2.01 |
| Quick assets (Cash) (C) | $7,400 |
| Current liabilities (D) | $18,000 |
| Acid-test ratio | 0.41 |
| Net Sales (E) | $221,100 |
| Less: Cost of Goods Sold (2) | ($78,500) |
| Gross margin (F) | $142,600 |
| Gross margin ratio | 0.64 or 64% |
Table (4)
The current ratio, acid- test ratio and gross margin ratio of Company FP is 2.01, 0.41 and 0.64 or 64% respectively.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Principles of Financial Accounting.
- choose best answerarrow_forwardConsider the following information for a particular company and calculate the gross profit percentage. Sales Cost of goods sold Beginning inventory Ending inventory Beginning accounts receivable $29,100,120 $21,225,000 55,612 53,644 2,279,112 Beginning allowance for bad debts (125,560) Ending accounts receivable 2,345,591 Ending allowance for bad debts (113,824)arrow_forward5 PTSarrow_forward
 Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,Principles of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,Principles of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning- Century 21 Accounting Multicolumn JournalAccountingISBN:9781337679503Author:GilbertsonPublisher:Cengage
 College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781305084087Author:Cathy J. ScottPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781305084087Author:Cathy J. ScottPublisher:Cengage Learning





