
Concept explainers
Customers as a Cost Object
Morrisom National Bank has requested an analysis of checking account profitability by customer type. Customers are categorized according to the size of their account: low balances, medium balances, and high balances. The activities associated with the three different customer categories and their associated annual costs are as follows:

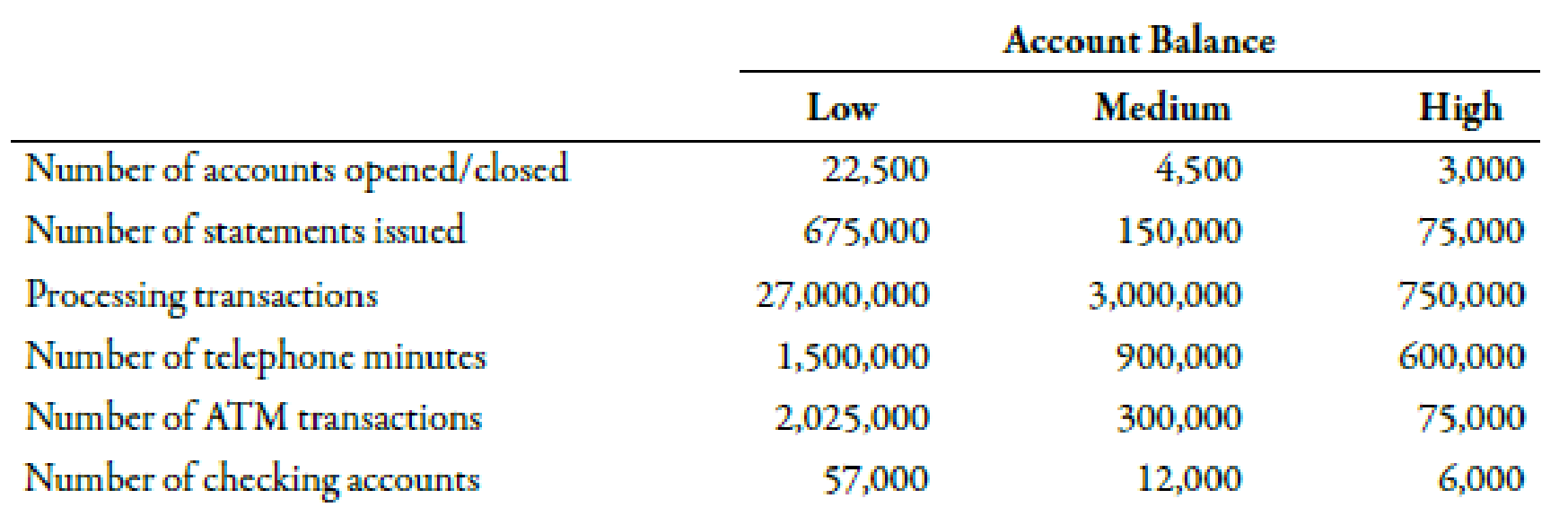
Additional data concerning the usage of the activities by the various customers are also provided:
Required:
(Note: Round answers to two decimal places.)
- 1. Calculate a cost per account per year by dividing the total cost of processing and maintaining checking accounts by the total number of accounts. What is the average fee per month that the bank should charge to cover the costs incurred because of checking accounts?
- 2. Calculate a cost per account by customer category by using activity rates.
- 3. Currently, the bank offers free checking to all of its customers. The interest revenues average $90 per account; however, the interest revenues earned per account by category are $80, $100, and $165 for the low-, medium-, and high-balance accounts, respectively. Calculate the average profit per account (average revenue minus average cost from Requirement 1). Then calculate the profit per account by using the revenue per customer type and the unit cost per customer type calculated in Requirement 2.
- 4. CONCEPTUAL CONNECTION After the analysis in Requirement 3, a vice president recommended eliminating the free checking feature for low-balance customers. The bank president expressed reluctance to do so, arguing that the low-balance customers more than made up for the loss through cross-sales. He presented a survey that showed that 50% of the customers would switch banks if a checking fee were imposed. Explain how you could verify the president’s argument by using ABC.
1.
Compute the value of costs per account per year. Also, compute the average fee per month that should be charged by the bank to cover their costs incurred in verifying the accounts.
Explanation of Solution
Activity Based Costing (ABC):
Activity based costing is an apportionment of costs that first considers the activity drivers that helps in the allocation of costs to various activities and then allocates costs to different cost objects by using the drivers.
Use the following formula to calculate value of costs per account per year:
Substitute $6,105,000 for total costs and 75,000 for number of statements used in the above formula.
Therefore, a cost per account per year is $81.40.
Use the following formula to calculate value of average fee per month:
Substitute $81.40 for costs per account per year in the above formula.
Therefore, average fee per month is $6.78.
2.
Compute the costs per account by customer category with the help of activity rates.
Explanation of Solution
Computation of costs per account by customer category:
| Activity | Rate(R) | Quantity (Q) |
Low ($) |
Medium ($) |
High ($) |
| (A)Opening and closing | 101 | 22,500 | 225,000 | ||
| 101 | 4,500 | 45,000 | |||
| 101 | 3,000 | 30,000 | |||
| (B)Issuing monthly statements | 0.502 | 675,000 | 337,500 | ||
| 0.502 | 150,000 | 75,000 | |||
| 0.502 | 75,000 | 37,500 | |||
| (C)Processing transactions | 0.103 | 27,000,000 | 2,700,000 | ||
| 0.103 | 3,000,000 | 300,000 | |||
| 0.103 | 750,000 | 75,000 | |||
| (D)Customer inquiries | 0.204 | 1,500,000 | 300,000 | ||
| 0.204 | 900,000 | 180,000 | |||
| 0.204 | 600,000 | 120,000 | |||
| (E)Providing ATM services | 0.705 | 2,025,000 | 1,417,500 | ||
| 0.705 | 300,000 | 210,000 | |||
| 0.705 | 75,000 | 67.500 | |||
|
Total Cost | 4,980,000 | 810,000 | 315,000 | ||
| Number of accounts | 57,000 | 12,000 | 6,000 | ||
|
Cost per account | 87.37 | 67.50 | 52.50 |
Table (1)
Working Note:
1. Calculation of opening and closing rates:
2. Calculation of issuing monthly transactions rate:
3. Calculation of processing transaction rate:
4. Calculation of rate of customer inquiries:
5. Calculation of rate of providing ATM services:
3.
Compute the average profit per account. Also, compute the profit per account with the help of ABC approach.
Explanation of Solution
Use the following formula to calculate average profit per account:
Substitute $90.00 for interest revenue average and $81.40 for costs per account per year in the above formula.
Therefore, an average profit per account is $8.60.
Use the following formula to calculate profit per account with the help of ABC approach of low balance customers:
Substitute $80.00 for interest revenue average and $87.37 for costs per account per year in the above formula.
Therefore, the loss per account of low balance customers is $7.37.
Use the following formula to calculate profit per account with the help of ABC approach of medium balance customers:
Substitute $100.00 for interest revenue average and $67.50 for costs per account per year in the above formula.
Therefore, the profit per account of medium balance customers is $32.5.
Use the following formula to calculate profit per account with the help of ABC approach of high balance customers:
Substitute $165.00 for interest revenue average and $52.50 for costs per account per year in the above formula.
Therefore, the profit per account of high balance customers is $112.50.
4.
Discuss the steps for verifying the argument of president with the help of ABC approach.
Explanation of Solution
The steps for verifying the argument of president with the help of ABC approach are explained below:
- • Compute the value of profits from various loans provided by the organization to their customers such as credit card with the help of ABC approach.
- • Compare the 50% of the profit of cross sales of the low balance customers with the total loss of low balance customers in verifying the accounts.
- • At the end, if the amount of profit of cross sales are more than the loss of cross sales, argue of president is valid.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Business Decision-Making
- The following information is available for Betty DeRose, Inc.: Accounts payable Inventory January 1, 2012 December 31, 2012 $70,000 $55,000 $88,000 $79,000 Betty DeRose reported $145,000 of cash paid to suppliers for purchases of inventory in its 2012 cash flow statement. Calculate Betty's cost of goods sold for 2012.arrow_forwardRock Corporation sells its product for $16 per unit. Next year, fixed expenses are expected to be $454,000 and variable expenses are expected to be $9 per unit. How many units must the company sell to generate a net operating income of $92,000?arrow_forwardCool Comfort currently sells 360 Class A spas, 520 Class C spas, and 230 deluxe model spas each year. The firm is considering adding a mid-class spa and expects that, if it does, it can sell 375 of them. However, if the new spa is added, Class A sales are expected to decline to 255 units while Class C sales are expected to decline to 240. The sales of the deluxe model will not be affected. Class A spas sell for an average of $13,500 each. Class C spas are priced at $7,200 and the deluxe model sells for $19,000 each. The new mid-range spa will sell for $11,000. What is the value of erosion? Answerarrow_forward
- Waiting for your solutionarrow_forwardRock Corporation sells its product for $16 per unit. Next year, fixed expenses are expected to be $454,000 and variable expenses are expected to be $9 per unit. How many units must the company sell to generate a net operating income of $92,000? Questionarrow_forwardCool Comfort currently sells 360 Class A spas, 520 Class C spas, and 230 deluxe model spas each year. The firm is considering adding a mid-class spa and expects that, if it does, it can sell 375 of them. However, if the new spa is added, Class A sales are expected to decline to 255 units while Class C sales are expected to decline to 240. The sales of the deluxe model will not be affected. Class A spas sell for an average of $13,500 each. Class C spas are priced at $7,200 and the deluxe model sells for $19,000 each. The new mid-range spa will sell for $11,000. What is the value of erosion? Helparrow_forward
- Cool Comfort currently sells 360 Class A spas, 520 Class C spas, and 230 deluxe model spas each year. The firm is considering adding a mid-class spa and expects that, if it does, it can sell 375 of them. However, if the new spa is added, Class A sales are expected to decline to 255 units while Class C sales are expected to decline to 240. The sales of the deluxe model will not be affected. Class A spas sell for an average of $13,500 each. Class C spas are priced at $7,200 and the deluxe model sells for $19,000 each. The new mid-range spa will sell for $11,000. What is the value of erosion?arrow_forwardGeneral accountingarrow_forwardCorrect option? ?arrow_forward
 Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Essentials of Business Analytics (MindTap Course ...StatisticsISBN:9781305627734Author:Jeffrey D. Camm, James J. Cochran, Michael J. Fry, Jeffrey W. Ohlmann, David R. AndersonPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Essentials of Business Analytics (MindTap Course ...StatisticsISBN:9781305627734Author:Jeffrey D. Camm, James J. Cochran, Michael J. Fry, Jeffrey W. Ohlmann, David R. AndersonPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,





