
Concept explainers
The following four structures are naturally occurring optically active compounds. Star (*) the asymmetric carbon atoms in these structures.
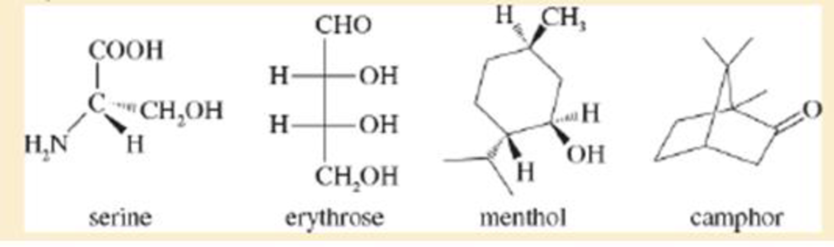
Interpretation: The asymmetric carbon atoms in the given structures are to be marked by star.
Concept introduction: A chiral carbon atom is attached to four different atoms or group of atoms and shows a tetrahedral geometry. The mirror image of a chiral compound is non-super imposable. The two different forms in which a single chiral carbon can exist are referred as enantiomers. The number of enantiomers of a molecule depends on the number of chiral centers.
To determine: The asymmetric carbon atoms in the given structures marked by star.
Answer to Problem 5.25SP
The asymmetric carbon atoms in the given structure have been marked by star.
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is serine. It is attached to
The asymmetric carbon atom present in it is marked by star as shown below.
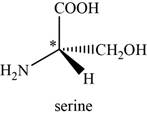
Figure 1
The given compound is erythrose. There are two chiral centres present in it.
The asymmetric carbon atoms present in it are marked by star as shown below.
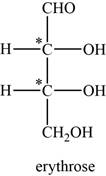
Figure 2
The given compound is menthol. There are three chiral centres present in it.
The asymmetric carbon atoms present in it are marked by star as shown below.
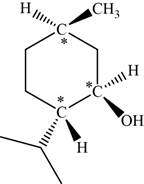
Figure 3
The given compound is camphor. There are two chiral centres present in it.
The asymmetric carbon atoms present in it are marked by star as shown below.
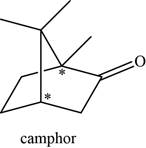
Figure 4
The asymmetric carbon atoms in the given structure have been marked by star.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Organic Chemistry, Books a la Carte Edition (9th Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Chemistry For Changing Times (14th Edition)
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
Chemistry (7th Edition)
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (3rd Edition)
Chemistry In Context
General Chemistry: Principles and Modern Applications (11th Edition)
- (c) There is one (1) other positional isomer of X missing for reaction II. Draw the structural formula of this isomer.arrow_forward1. Although there is only one alkene with the formula C2H4 (ethene) and only one with the formula C3H6 (propene), there are several alkenes with the formula C4H8. Draw all of the possible bond line structures for alkenes with the formula C4H3 including all possible structural and stereoisomers.arrow_forwardDraw the structure of [C6H5SO³]¯. Include all lone pairs and charges as appropriate.arrow_forward
- Draw the skeletal (line-bond) structure of [CH3CH2CH2CH2O]-. Include all lone pairs and charges as appropriate.arrow_forwardc) The first molecule: trans-2-butene. The second molecule is a mirror image of trans-2-butene. Both molecules are shown on the right. Are the molecules superimposable (identical)? Are the molecules optical isomers (enantiomers)?arrow_forwardCompounds X and Y both have the formula C7H₁4. Both X and Y react with one molar equivalent of hydrogen in the presence of a palladium catalyst to form 2-methylhexane. The heat of hydrogenation of X is greater than that of Y. Both X and Y react with HCI to give the same single C7H15Cl compound as the major product. What is the structure of X? • In cases where there is more than one answer, just draw one. 23 ▾ Sn [F ChemDoodleⓇ 146arrow_forward
- Which of the following substances exist as can cis–trans isomers? Draw both isomers for those that do.(a) 2,3-Dimethylpent-2-ene (condensed structures only)(b) 2-Methylhex-2-ene (both condensed and line structures)(c) Hex-2-ene (line structures only)arrow_forwardHow many cyclic compounds (constitutional isomers only) have the molecular formula C3H7N?arrow_forwardThe molar heat of combustion of gaseous cyclopropaneis -2089 kJ/mol; that for gaseous cyclopentane is-3317 kJ/mol. Calculate the heat of combustion per CH2group in the two cases, and account for the difference.arrow_forward
- 12. Write bond-line structural formulas for (a.) two primary alcohols, (b.) a secondary alcohol, and (c.) a tertiary alcohol-all having the molecular formula CaH100.arrow_forwardatoms have the unique ability to form strong bonds with each other in compounds have carbon as a contain only hydrogen and carbon atoms are open-chain (1) different ways. Therefore, all (2) constituent element. (1) and are the simplest organic compounds. (3) hydrocarbons with single covalent bons between the carbon atoms, (4) open- chain hydrocarbons with at least one double bond between carbon atoms, and (5) between two carbon atoms. (6) four or more carbons in the molecule. A (7) atoms the presence of which confers characteristic properties to the compound. are are open- chain hydrocarbons with at least one triple bond is shown by hydrocarbons with at least is an atom or a group of A reaction is characterized by the joining of two molecules and the while in this reaction, (8) elimination of a small molecule, usually water. (9) an ester reacts with aqueous NaOH solution to produce back the carboxylic acid and the alcohol. This reaction originates from soap making. (10).arrow_forwardHow do you draw in bond line form. An octane chain with two iso-propyl groups attached so the octane is still the longest linear carbon chain and the compound is MESO.arrow_forward
- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning  Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning World of ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780618562763Author:Steven S. ZumdahlPublisher:Houghton Mifflin College Div
World of ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780618562763Author:Steven S. ZumdahlPublisher:Houghton Mifflin College Div





