
PEARSON ETEXT ENGINEERING MECH & STATS
15th Edition
ISBN: 9780137514724
Author: HIBBELER
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 5, Problem 40P
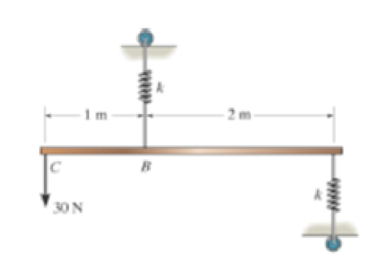
Determine the stiffness k of each spring so that the 30-N force causes the bar to tip θ = 15° when the force is applied. Originally the bar is horizontal and the springs are unstretched. Neglect the weight of the bar.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
A.The bar of negligible weight is supported by two springs, each having a stiffness k = 98 N/m. If the springs are originally unstretched, and the force is vertical as shown, determine the angle the bar makes with the horizontal, when the 31-N force is applied to the bar.
B.Determine the stiffness k of each spring so that the 32-N force causes the bar to tip = 13.6° when the force is applied. Originally the bar is horizontal and the springs are unstretched. Neglect the weight of the bar.
The 250-N block rests upon a level plane for which fk = 0.2. It is pulled by force P = 100N inclined at 20o with the horizontal. If the 100-N pull is then removed, find the distance the block will travel.
The horizontal force P is applied to the handle of the puller. Determine the resulting tension T in the chain in terms of P .
Chapter 5 Solutions
PEARSON ETEXT ENGINEERING MECH & STATS
Ch. 5 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 5 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 5 - The truss is supported by a pin at A and a roller...Ch. 5 - Prob. 4FPCh. 5 - The 25 kg bar has a center of mass at G. If it is...Ch. 5 - Prob. 6FPCh. 5 - Determine the reactions at the supports. Prob....Ch. 5 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 5 - Determine the reactions at the supports. Prob....Ch. 5 - A uniform glass rod having a length L is placed in...
Ch. 5 - If the intensity of the distributed load acting on...Ch. 5 - Prob. 23PCh. 5 - Prob. 24PCh. 5 - Prob. 25PCh. 5 - Prob. 27PCh. 5 - Prob. 30PCh. 5 - Prob. 35PCh. 5 - The cantilevered jib crane is used to support the...Ch. 5 - Prob. 38PCh. 5 - Prob. 39PCh. 5 - Determine the stiffness k of each spring so that...Ch. 5 - The boom supports the two vertical loads. Neglect...Ch. 5 - Prob. 43PCh. 5 - The 10-kg uniform rod is pinned at end A. If It is...Ch. 5 - Prob. 46PCh. 5 - Prob. 47PCh. 5 - Prob. 48PCh. 5 - Prob. 53PCh. 5 - The uniform rod has a length I and weight W. It is...Ch. 5 - Prob. 7FPCh. 5 - Prob. 8FPCh. 5 - Prob. 9FPCh. 5 - Determine the support reactions at the smooth...Ch. 5 - Prob. 11FPCh. 5 - Determine the components of reaction that the...Ch. 5 - The uniform loads has a mass of 600 kg and is...Ch. 5 - The 100-lb door has its center of gravity at G....Ch. 5 - Determine me tension in each cable and the...Ch. 5 - The bent rod is supported at A, B, and C by smooth...Ch. 5 - The bent rod is supported at A, B, and C by smooth...Ch. 5 - Prob. 77PCh. 5 - Prob. 78PCh. 5 - Prob. 80PCh. 5 - Prob. 82PCh. 5 - The bar AB is supported by two smooth collars. At...Ch. 5 - Prob. 84PCh. 5 - Prob. 85PCh. 5 - Prob. 86PCh. 5 - Both pulleys are fixed to the shaft and as the...Ch. 5 - Member AB is supported by a cable BC and at A by a...Ch. 5 - Prob. 2RPCh. 5 - Prob. 4RP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The spring has a stiffness of 830 N/m and is undisturbed and measures 400 mm. Determine the forces on the BC and BD cables when the spring is stretched in the position shown in the figure.arrow_forward30°- 50 mm -20 mm- 10 mm The operation of the fuel pump for an automobile depends on the reciprocating action of the rocker arm ABC, which is pinned at B and is spring loaded at A and D. The vertical force acting on the rocker arm at A is FA = 50N, and at C it is Fc = 150N. When the smooth cam C is in the position shown, determine the magnitude of the force at B wwwwarrow_forwardThe uniform links AB and BC each weigh 2 lb and the cylinder weighs 20 lb. Determine the horizontal force P required to hold the mechanism in the position when θ = 45°. The spring has an unstretched length of 6 in.arrow_forward
- Determine the n- and t-components of the force F which is exerted by the rod AB on the crank OA. Evaluate your general expression for F = 118 N and (a) e = 30°, B = 25° and (b) e = 21°, B = 29° Answers: (a) Fn= i N, F: = i N (b) Fn = i N. F:= Narrow_forwardDetermine the n- and t-components of the force F which is exerted by the rod AB on the crank OA. Evaluate your general expression for F = 90 N and (a) 0 = 29°, 3= 25° and (b) = 14°, 3 = 37° Answers: (a) Fn = (b) Fn = i i B BI A N, Ft= N, Ft= i N Narrow_forwardThe homogeneous box has mass m. The magnitude of force P is slowly increased until motion occurs. Motion could occur as slipping or tipping and you must decide which occurs first. Find the value of P which first causes motion. P А 36° d He = 0.50 2.1 d Answer: P = i mgarrow_forward
- Both pulleys are fixed to the shaft and as the shaft turns with constant angular velocity, the power of pulley A is transmitted to pulley B. Determine the horizontal tension T in the belt on pulley B and the x, y, z components ofreaction at the journal bearing C and thrust bearing D if θ = 0°. The bearings are in proper alignment and exert only force reactions on the shaft.arrow_forwardthe uniform concrete pole has a mass of 25 tons and is slowly being lifted to a vertical position through the tension P in the cable. for position theta=60° calculate the tension T in the horizontal anchor cable 6 m 6 m 8 2m T Barrow_forwardEach spring has an unstretched length of 2 mm and a stiffness of k = 350 N/m. Determine the stretch in OA spring required to hold the 25-kg crate in the equilibrium position shown. Determine the stretch in OB spring required to hold the 25-kg crate in the equilibrium position shown.arrow_forward
- The homogeneous box has mass m. The magnitude of force P is slowly increased until motion occurs. Motion could occur as slipping or tipping and you must decide which occurs first. Find the value of P which first causes motion. 34° H = 0.45 1.6 darrow_forwardThe homogeneous box has mass m. The magnitude of force Pis slowly increased until motion occurs. Motion could occur as slipping or tipping and you must decide which occurs first. Find the value of P which first causes motion. A 33° = 0.40 B 2.0 darrow_forwardDetermine the reactions at the wheels at the moment a worker applies a force of 350 N. P The mass of the hand truck is 65Kg. 60° 0.5 m Go 0.2 m -0.3 m 0.2 m- 0.4 marrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:CENGAGE L
Dynamics - Lesson 1: Introduction and Constant Acceleration Equations; Author: Jeff Hanson;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7aMiZ3b0Ieg;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY