
Concept explainers
(a)
The magnitude of contact force between the two masses.
(a)
Answer to Problem 79P
The magnitude of contact force between the two masses is
Explanation of Solution
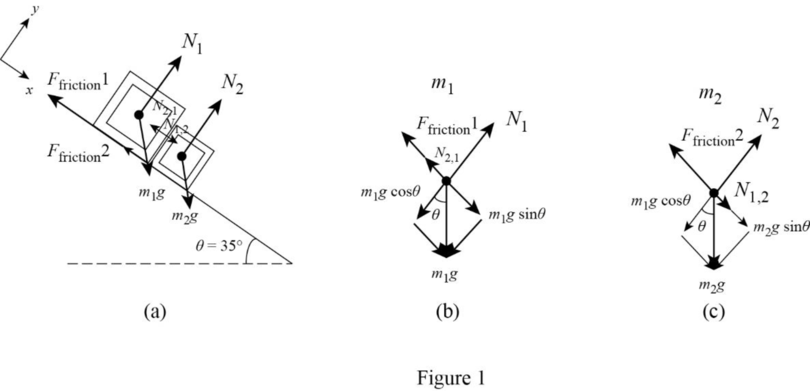
Write the expression for the Newton’s second law of motion.
Here,
If the plane is frictionless, then the only force on the two masses are the normal forces and the weight with the frictional forces equalling zero. Since there is no force directed up the incline, the normal force between the two blocks must be zero.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the magnitude of contact force between the two masses is
(b)
The magnitude of contact force between two masses if the coefficient of kinetic friction between the masses and the plane are equal.
(b)
Answer to Problem 79P
The magnitude of contact force between two masses if the coefficient of kinetic friction between the masses and the plane are equal is
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for the Newton’s law for the mass
Here,
Write the expression for the Newton’s law for the mass
Here,
Use equation (III) to write the expression for
Here,
Use equation (III) in (II) to solve for
Write the expression for the Newton’s law for the mass
Here,
Write the expression for the Newton’s law for the mass
Here,
Use equation (VI) to write the expression for
Here,
Use equation (VII) in (V) to solve for
Write the expression for the Newton’s third law of motion.
If the normal force is non-zero, then the acceleration must be equal.
Use equation (VIII) and (IV) in (X) and it becomes,
The coefficient of kinetic friction between the masses and the plane are equal.
Use equation (XII) in (XI) to solve for the contact forces between the two masses.
The only way this can be true with
Conclusion:
Therefore, the magnitude of contact force between two masses if the coefficient of kinetic friction between the masses and the plane are equal is
(c)
If
(c)
Answer to Problem 79P
The magnitude of contact force between the two blocks is
Explanation of Solution
Use equation (IX) and (XI) to solve for
Conclusion:
Substitute
Therefore, the magnitude of contact force between the two blocks is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
College Physics, Volume 1
- A small sphere with a mass of 3.00×10−3 g and carrying a charge of 4.80×10−8 C hangs from a thread near a very large, charged insulating sheet, as shown in the figure (Figure 1). The charge density on the sheet is −2.20×10−9 C/m2 . Find the angle of the thread.arrow_forwardA small conducting spherical shell with inner radius aa and outer radius bb is concentric with a larger conducting spherical shell with inner radius c and outer radius d (Figure 1). The inner shell has total charge +2q, and the outer shell has charge −2q. Calculate the magnitude of the electric field in terms of q and the distance rr from the common center of the two shells for r<a. Calculate the magnitude of the electric field for a<r<b. Calculate the magnitude of the electric field for b<r<c.arrow_forwardA cube has sides of length L = 0.800 m . It is placed with one corner at the origin as shown in the figure. The electric field is not uniform but is given by E→=αxi^+βzk^, where α=−3.90 and β= 7.10. What is the sum of the flux through the surface S5 and S6? What is the sum of the flux through the surface S2 and S4? Find the total electric charge inside the cube.arrow_forward
- In the figure, a proton is projected horizontally midway between two parallel plates that are separated by 0.6 cm. The electrical field due to the plates has magnitude 450000 N/C between the plates away from the edges. If the plates are 3 cm long, find the minimum speed of the proton if it just misses the lower plate as it emerges from the field.arrow_forwardA point charge of magnitude q is at the center of a cube with sides of length L. What is the electric flux Φ through each of the six faces of the cube? What would be the flux Φ1 through a face of the cube if its sides were of length L1? Please explain everything.arrow_forwardIf a 1/2 inch diameter drill bit spins at 3000 rotations per minute, how fast is the outer edge moving as it contacts a piece of metal while drilling a machine part?arrow_forward
- Need help with the third question (C)A gymnast weighing 68 kg attempts a handstand using only one arm. He plants his hand at an angl reesulting in the reaction force shown.arrow_forwardQ: What is the direction of the force on the current carrying conductor in the magnetic field in each of the cases 1 to 8 shown below? (1) B B B into page X X X x X X X X (2) B 11 -10° B x I B I out of page (3) I into page (4) B out of page out of page I N N S x X X X I X X X X I (5) (6) (7) (8) Sarrow_forwardQ: What is the direction of the magnetic field at point A, due to the current I in a wire, in each of the cases 1 to 6 shown below? Note: point A is in the plane of the page. ▪A I I ▪A (1) (2) ▪A • I (out of page) (3) ▪A I x I (into page) ▪A ▪A I (4) (5) (6)arrow_forward
- A tennis ball is thrown into the air with initial speed vo=46 m/s and angle (theta) 38 degrees from the ground. Find the distance it travels (x) when it hits the ground.arrow_forwardProblem 04.08 (17 points). Answer the following questions related to the figure below. ථි R₁ www R₂ E R₁ www ли R₁ A Use Kirchhoff's laws to calculate the currents through each battery and resistor in terms of R1, R2, E1, & E2. B Given that all the resistances and EMFs have positive values, if E₁ > E2 and R₁ > R2, which direction is the current flowing through E₁? Through R₂? C If E1 E2 and R₁ > R2, which direction is the current flowing through E₁? Through R2?arrow_forwardA 105- and a 45.0-Q resistor are connected in parallel. When this combination is connected across a battery, the current delivered by the battery is 0.268 A. When the 45.0-resistor is disconnected, the current from the battery drops to 0.0840 A. Determine (a) the emf and (b) the internal resistance of the battery. 10 R2 R₁ ww R₁ Emf 14 Emf Final circuit Initial circuitarrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





