
College Physics
2nd Edition
ISBN: 9780134601823
Author: ETKINA, Eugenia, Planinšič, G. (gorazd), Van Heuvelen, Alan
Publisher: Pearson,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 4, Problem 3P
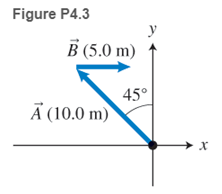
* Determine the x- and y-components of each displacement shown in Figure P4.3.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
No chatgpt pls will upvote
No chatgpt pls will upvote
No chatgpt pls will upvote
Chapter 4 Solutions
College Physics
Ch. 4 - Review Question 4.1 When does a vector have a...Ch. 4 - Review Question 4.2 The x- and y-components of...Ch. 4 - Review Question 4.3 What is the force of friction...Ch. 4 - Review Question 4.4 For problems involving objects...Ch. 4 - Review Question 4.5 Why do we need to resolve the...Ch. 4 - Review Question 4.6
You read in this section that...Ch. 4 - 1. A car accelerates along a road. Identify the...Ch. 4 - 2. A person pushes a 10-kg crate exerting a 200-N...Ch. 4 - Compare the ease of pulling a lawn mower and...Ch. 4 - 4. You simultaneously release two balls: one you...
Ch. 4 - You shoot an arrow with a bow. The following is...Ch. 4 - In what reference frame does a projectile launched...Ch. 4 - In Table 4.6 we found that the two balls touched...Ch. 4 - 8. While running at constant velocity, how should...Ch. 4 - 9. You hold a block on a horizontal, frictionless...Ch. 4 - 10. In the process described in the previous...Ch. 4 - Suppose that two blocks are positioned on an...Ch. 4 - 12. A box containing some stones is resting on a...Ch. 4 - For the following two questions, the answer...Ch. 4 - 14. A block is resting on a rough inclined...Ch. 4 -
15. A box with a heavy television set in it...Ch. 4 - 16. How can an Atwood machine be used to determine...Ch. 4 - 17. Your friend is on Rollerblades holding a...Ch. 4 - Explain why a car starts skidding when a driver...Ch. 4 - 19. Explain why old tires need to be replaced.
Ch. 4 - 20. Explain how friction helps you to walk.
Ch. 4 - 21. Explain why you might fall forward when you...Ch. 4 - Explain why you might fall backward when you slip.Ch. 4 - Explain why the tires of your car can spin out...Ch. 4 - You throw two identical balls simultaneously at...Ch. 4 - 25. Your friend says that the vertical force...Ch. 4 - Your friend says that a projectile launched at an...Ch. 4 - An object of mass m1 placed on an inclined plane...Ch. 4 - 28 An object of mass m1 placed on an inclined...Ch. 4 - 29. A horse is pulling a sled. If the force...Ch. 4 - 30. If you kick a block so that it starts moving...Ch. 4 - Determine the x- and y-components of each force...Ch. 4 - 2. Determine the x- and y-components of each force...Ch. 4 - * Determine the x- and y-components of each...Ch. 4 - 4 * The x- and y-components of several unknown...Ch. 4 - * The x- and y-scalar components of several...Ch. 4 - 6. * Three ropes pull on a knot shown in Figure...Ch. 4 - * Figure P4.7 shows an unlabeled force diagram for...Ch. 4 - For each of the following situations, draw the...Ch. 4 - * Write Newtons second law in component form for...Ch. 4 - For the situations described here, construct a...Ch. 4 - * Write Newtons second law in component form for...Ch. 4 - Apply Newtons second law in component form for the...Ch. 4 - Apply Newtons second law in component form for the...Ch. 4 - 14. * Equation Jeopardy 1 The three sets of...Ch. 4 - * You exert a force of 100 N on a rope that pulls...Ch. 4 - 16. * You exert a force of a known magnitude F on...Ch. 4 - * Olympic 100-m dash start At the start of his...Ch. 4 - 18. * Your own accelerometer A train has an...Ch. 4 - * EST Finn and Hazel are using a battery-powered...Ch. 4 - A 91.0-kg refrigerator sits on the floor. The...Ch. 4 - A 60-kg student sitting on a hardwood floor does...Ch. 4 - Car stopping distance and friction A car traveling...Ch. 4 - 23. * A 50-kg box rests on the floor. The...Ch. 4 - 24. * Marsha is pushing down and to the right on a...Ch. 4 - * You want to determine the coefficient of kinetic...Ch. 4 - * A wagon is accelerating to the right. A book is...Ch. 4 - s. Determine an expression for the minimum...Ch. 4 - * A car has a mass of 1520 kg. While traveling at...Ch. 4 - m/s2 when pulled by a rope exerting a 120-N force...Ch. 4 - 30. ** A crate of mass m sitting on a horizontal...Ch. 4 - * EST You absentmindedly leave your book bag on...Ch. 4 - 32. * Block 1 is on a horizontal surface with a...Ch. 4 - 33. * You want to use a rope to pull a 10-kg box...Ch. 4 - 34. * A car with its wheels locked rests on a...Ch. 4 - 35. Olympic skier Olympic skier Tina Maze skis...Ch. 4 - * Another Olympic skier Bode Miller. 80-kg...Ch. 4 - * A book slides off a desk that is tilted 15...Ch. 4 - * Helge, Steve, and Heidi are sitting on a sled on...Ch. 4 - 40. * When traveling on an airplane you get meals...Ch. 4 - 41. Skier A 52-kg skier starts at rest and slides...Ch. 4 - 42. * Ski rope tow You agree to build a backyard...Ch. 4 - 43. * Soapbox racecar A soapbox derby racecar...Ch. 4 - 44. * A person is pushing two carts that are...Ch. 4 - 45. * BIO Whiplash Experience A car sitting at...Ch. 4 - Iditarod race practice The dogs of four-time...Ch. 4 - angle above the horizontal. The other end of the...Ch. 4 - * Rope 1 pulls horizontally, exerting a force of...Ch. 4 - * Three sleds of masses m1,m2,m3 are on a smooth...Ch. 4 - 50. ** Repeat Problem 4.49 , only this time with...Ch. 4 - 51. * A skier is moving down a snowy hill with an...Ch. 4 - ** A person holds a 200-g block that is connected...Ch. 4 - 53. ** Two blocks of masses are connected to each...Ch. 4 - 54. ** The 20-kg block shown in Figure P4.54 ...Ch. 4 - * A squirrel jumps of a roof in the horizontal...Ch. 4 - * A frog jumps at an angle 30 above the...Ch. 4 - 57. A bowling ball rolls off a table. Draw a force...Ch. 4 - 58 * A tennis ball is served from the back line of...Ch. 4 - 59. * Equation Jeopardy 3 The equations below...Ch. 4 - 60 * EST An airplane is delivering food to a small...Ch. 4 - A ball moves in an arc through the air (see Figure...Ch. 4 - A marble is thrown as a projectile at an angle...Ch. 4 - 63 * Marbles are exiting a container through a...Ch. 4 - * Robbie Knievel ride On May 20, 1999, Robbie...Ch. 4 - 65. * Daring Darless wishes to cross the Grand...Ch. 4 - * A football punter wants to kick the ball so that...Ch. 4 - 67. * If you shoot a cannonball from the same...Ch. 4 - 68. When you actually perform the experiment...Ch. 4 - 69. * You can shoot an arrow straight up so that...Ch. 4 - 70. * Robin Hood wishes to split an arrow already...Ch. 4 - 71. * Three force diagrams for a car on a road are...Ch. 4 - * A minivan of mass 1560 kg starts at rest and...Ch. 4 - 74. * Emily pulls a 5-kg block across a rough...Ch. 4 - 75. * EST You abruptly push a 1.7-kg book along a...Ch. 4 - 76 ** EST In the situation of Problem 4.75,...Ch. 4 - 78. * Two blocks of masses and hang at the ends...Ch. 4 - 79. * A 3.5-kg object placed on an Inclined plane...Ch. 4 - above the horizontal) is connected by a string...Ch. 4 - above the horizontal) is connected by a string...Ch. 4 - 82 ** You are driving at a reasonable constant...Ch. 4 - 84. * In the situation of Problem 2.71 (Chapter 2...Ch. 4 - 87. * Your friend has a pie on the roof of his...Ch. 4 - * A ledge on a building is 20 m above the ground....Ch. 4 - 89. * You are hired to devise a method to...Ch. 4 - The mass of a spacecraft is about 480 kg. An...Ch. 4 - incline When she reaches the level floor at the...Ch. 4 - * Tell all A sled starts at the top of the hill...Ch. 4 - Professor tests airplane takeoff speed D. A....Ch. 4 - Professor tests airplane takeoff speed D A Wardle,...Ch. 4 - Professor tests airplane takeoff speed D A Wardle,...Ch. 4 - Professor tests airplane takeoff speed D. A....Ch. 4 - Choose the best velocity-versus-time graph below...Ch. 4 - Ski jumping in Vancouver The 2010 Olympic ski...Ch. 4 - Ski jumping in Vancouver The 2010 Olympic ski...Ch. 4 - Ski jumping in Vancouver The 2010 Olympic ski...Ch. 4 - Assume that the skier left the ramp moving...Ch. 4 - Ski jumping in Vancouver The 2010 Olympic ski...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Which one of the following is not a fuel produced by microorganisms? a. algal oil b. ethanol c. hydrogen d. met...
Microbiology: An Introduction
Plants use the process of photosynthesis to convert the energy in sunlight to chemical energy in the form of su...
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
Explain all answers clearly, with complete sentences and proper essay structure if needed. An asterisk (*) desi...
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Which compound is more easily decarboxylated?
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
10.71 Identify each of the following as an acid or a base: (10.1)
H2SO4
RbOH
Ca(OH)2
HI
...
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
13.2 Describe and give an example (real or hypothetical) of each of the following:
upstream activator sequence...
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- air is pushed steadily though a forced air pipe at a steady speed of 4.0 m/s. the pipe measures 56 cm by 22 cm. how fast will air move though a narrower portion of the pipe that is also rectangular and measures 32 cm by 22 cmarrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward13.87 ... Interplanetary Navigation. The most efficient way to send a spacecraft from the earth to another planet is by using a Hohmann transfer orbit (Fig. P13.87). If the orbits of the departure and destination planets are circular, the Hohmann transfer orbit is an elliptical orbit whose perihelion and aphelion are tangent to the orbits of the two planets. The rockets are fired briefly at the depar- ture planet to put the spacecraft into the transfer orbit; the spacecraft then coasts until it reaches the destination planet. The rockets are then fired again to put the spacecraft into the same orbit about the sun as the destination planet. (a) For a flight from earth to Mars, in what direction must the rockets be fired at the earth and at Mars: in the direction of motion, or opposite the direction of motion? What about for a flight from Mars to the earth? (b) How long does a one- way trip from the the earth to Mars take, between the firings of the rockets? (c) To reach Mars from the…arrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwarda cubic foot of argon at 20 degrees celsius is isentropically compressed from 1 atm to 425 KPa. What is the new temperature and density?arrow_forwardCalculate the variance of the calculated accelerations. The free fall height was 1753 mm. The measured release and catch times were: 222.22 800.00 61.11 641.67 0.00 588.89 11.11 588.89 8.33 588.89 11.11 588.89 5.56 586.11 2.78 583.33 Give in the answer window the calculated repeated experiment variance in m/s2.arrow_forward
- How can i solve this if n1 (refractive index of gas) and n2 (refractive index of plastic) is not known. And the brewsters angle isn't knownarrow_forward2. Consider the situation described in problem 1 where light emerges horizontally from ground level. Take k = 0.0020 m' and no = 1.0001 and find at which horizontal distance, x, the ray reaches a height of y = 1.5 m.arrow_forward2-3. Consider the situation of the reflection of a pulse at the interface of two string described in the previous problem. In addition to the net disturbances being equal at the junction, the slope of the net disturbances must also be equal at the junction at all times. Given that p1 = 4.0 g/m, H2 = 9.0 g/m and Aj = 0.50 cm find 2. A, (Answer: -0.10 cm) and 3. Ay. (Answer: 0.40 cm)please I need to show all work step by step problems 2 and 3arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Newton's First Law of Motion: Mass and Inertia; Author: Professor Dave explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1XSyyjcEHo0;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY