
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations and Connections
1st Edition
ISBN: 9781133939146
Author: Katz, Debora M.
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 35, Problem 4PQ
You are seated on a couch equidistant between two speakers. The speakers are 2.0 m apart and you are seated 4.0 m away from the point between the speakers as shown in Figure P35.4. Both speakers play an A note (a constant frequency of 440 Hz) in phase and at the same volume. As you move left and right along the couch, you notice that the volume alternates between minimum and maximum due to interference effects. Assume the speed of sound is 343 m/s.
- a. When you are seated at the center of the couch, is the sound a maximum or minimum in volume?
- b. If you slide along the couch to the left or right, approximately how far do you need to move until you reach the next location that has the same volume? (Hint: You may wish to obtain an exact expression and then use a spreadsheet or trial and error to find an approximate solution.)
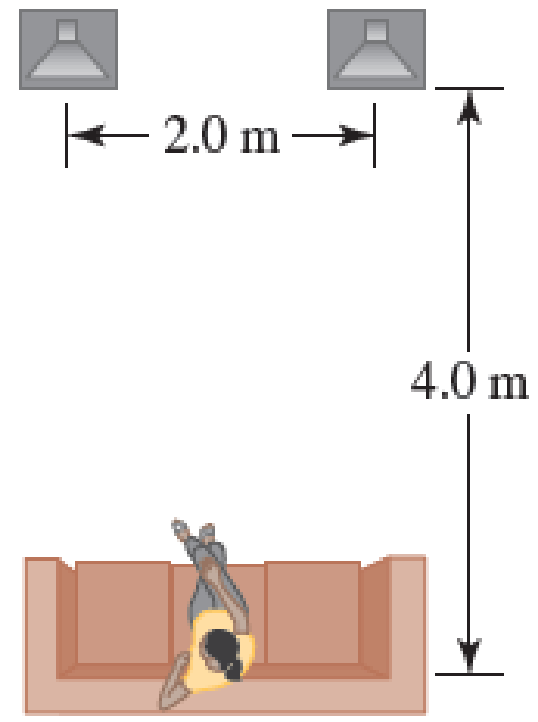
FIGURE P35.4
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
air is pushed steadily though a forced air pipe at a steady speed of 4.0 m/s. the pipe measures 56 cm by 22 cm. how fast will air move though a narrower portion of the pipe that is also rectangular and measures 32 cm by 22 cm
No chatgpt pls will upvote
13.87 ... Interplanetary Navigation. The most efficient way
to send a spacecraft from the earth to another planet is by using a
Hohmann transfer orbit (Fig. P13.87). If the orbits of the departure
and destination planets are circular, the Hohmann transfer orbit is an
elliptical orbit whose perihelion and aphelion are tangent to the
orbits of the two planets. The rockets are fired briefly at the depar-
ture planet to put the spacecraft into the transfer orbit; the spacecraft
then coasts until it reaches the destination planet. The rockets are
then fired again to put the spacecraft into the same orbit about the
sun as the destination planet. (a) For a flight from earth to Mars, in
what direction must the rockets be fired at the earth and at Mars: in
the direction of motion, or opposite the direction of motion? What
about for a flight from Mars to the earth? (b) How long does a one-
way trip from the the earth to Mars take, between the firings of the
rockets? (c) To reach Mars from the…
Chapter 35 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations and Connections
Ch. 35.1 - Perhaps Newton never observed a diffraction...Ch. 35.1 - Prob. 35.2CECh. 35.2 - Prob. 35.3CECh. 35.3 - Prob. 35.4CECh. 35.4 - When we studied Youngs double-slit experiment, we...Ch. 35.6 - Prob. 35.6CECh. 35 - Light Is a Wave C As shown in Figure P35.1, spray...Ch. 35 - Sound Wave Interference Revisited Draw two...Ch. 35 - Prob. 3PQCh. 35 - You are seated on a couch equidistant between two...
Ch. 35 - Prob. 5PQCh. 35 - Prob. 6PQCh. 35 - A student shines a red laser pointer with a...Ch. 35 - Monochromatic light is incident on a pair of slits...Ch. 35 - Prob. 9PQCh. 35 - In a Youngs double-slit experiment with microwaves...Ch. 35 - A beam from a helium-neon laser with wavelength...Ch. 35 - Prob. 12PQCh. 35 - Prob. 13PQCh. 35 - Prob. 14PQCh. 35 - Light from a sodium vapor lamp ( = 589 nm) forms...Ch. 35 - Prob. 16PQCh. 35 - Prob. 17PQCh. 35 - Prob. 18PQCh. 35 - Prob. 19PQCh. 35 - Prob. 20PQCh. 35 - Prob. 21PQCh. 35 - Prob. 22PQCh. 35 - Prob. 23PQCh. 35 - Figure P35.24 shows the diffraction patterns...Ch. 35 - Prob. 25PQCh. 35 - Prob. 26PQCh. 35 - A thread must have a uniform thickness of 0.525...Ch. 35 - Prob. 28PQCh. 35 - Prob. 29PQCh. 35 - A radio wave of wavelength 21.5 cm passes through...Ch. 35 - Prob. 31PQCh. 35 - Prob. 32PQCh. 35 - A single slit is illuminated by light consisting...Ch. 35 - Prob. 34PQCh. 35 - Prob. 35PQCh. 35 - Prob. 36PQCh. 35 - Prob. 37PQCh. 35 - Prob. 38PQCh. 35 - Prob. 39PQCh. 35 - Prob. 40PQCh. 35 - Prob. 41PQCh. 35 - Prob. 42PQCh. 35 - Prob. 43PQCh. 35 - Prob. 44PQCh. 35 - Prob. 45PQCh. 35 - Prob. 46PQCh. 35 - Prob. 47PQCh. 35 - Prob. 48PQCh. 35 - Figure P35.49 shows the intensity of the...Ch. 35 - Prob. 50PQCh. 35 - Prob. 51PQCh. 35 - Prob. 52PQCh. 35 - Light of wavelength 750.0 nm passes through a...Ch. 35 - Prob. 54PQCh. 35 - Prob. 55PQCh. 35 - Prob. 56PQCh. 35 - Light of wavelength 515 nm is incident on two...Ch. 35 - Light of wavelength 515 nm is incident on two...Ch. 35 - A Two slits are separated by distance d and each...Ch. 35 - Prob. 60PQCh. 35 - Prob. 61PQCh. 35 - If you spray paint through two slits, what pattern...Ch. 35 - Prob. 63PQCh. 35 - Prob. 64PQCh. 35 - Prob. 65PQCh. 35 - Prob. 66PQCh. 35 - Prob. 67PQCh. 35 - Prob. 68PQCh. 35 - Prob. 69PQCh. 35 - Prob. 70PQCh. 35 - Prob. 71PQCh. 35 - Prob. 72PQCh. 35 - Prob. 73PQCh. 35 - Prob. 74PQCh. 35 - Prob. 75PQCh. 35 - Prob. 76PQCh. 35 - Prob. 77PQCh. 35 - Another way to construct a double-slit experiment...Ch. 35 - Prob. 79PQCh. 35 - Prob. 80PQCh. 35 - Table P35.80 presents data gathered by students...Ch. 35 - Prob. 82PQCh. 35 - Prob. 83PQCh. 35 - Prob. 84PQCh. 35 - Prob. 85PQCh. 35 - Prob. 86PQCh. 35 - Prob. 87PQCh. 35 - Prob. 88PQCh. 35 - A One of the slits in a Youngs double-slit...Ch. 35 - Prob. 90PQ
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwarda cubic foot of argon at 20 degrees celsius is isentropically compressed from 1 atm to 425 KPa. What is the new temperature and density?arrow_forwardCalculate the variance of the calculated accelerations. The free fall height was 1753 mm. The measured release and catch times were: 222.22 800.00 61.11 641.67 0.00 588.89 11.11 588.89 8.33 588.89 11.11 588.89 5.56 586.11 2.78 583.33 Give in the answer window the calculated repeated experiment variance in m/s2.arrow_forward
- How can i solve this if n1 (refractive index of gas) and n2 (refractive index of plastic) is not known. And the brewsters angle isn't knownarrow_forward2. Consider the situation described in problem 1 where light emerges horizontally from ground level. Take k = 0.0020 m' and no = 1.0001 and find at which horizontal distance, x, the ray reaches a height of y = 1.5 m.arrow_forward2-3. Consider the situation of the reflection of a pulse at the interface of two string described in the previous problem. In addition to the net disturbances being equal at the junction, the slope of the net disturbances must also be equal at the junction at all times. Given that p1 = 4.0 g/m, H2 = 9.0 g/m and Aj = 0.50 cm find 2. A, (Answer: -0.10 cm) and 3. Ay. (Answer: 0.40 cm)please I need to show all work step by step problems 2 and 3arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Spectra Interference: Crash Course Physics #40; Author: CrashCourse;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-ob7foUzXaY;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY