
Essential University Physics (3rd Edition)
3rd Edition
ISBN: 9780134202709
Author: Richard Wolfson
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 3, Problem 82P
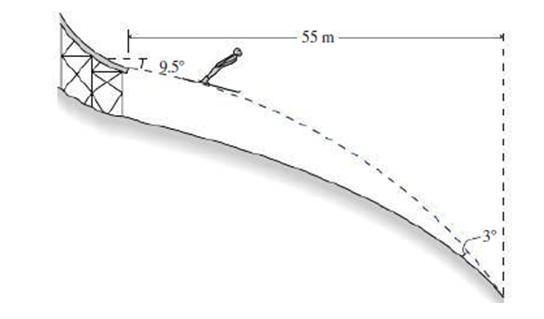
You're a consulting engineer specializing in athletic facilities, and you’ve been asked to help design the Olympic ski jump pictured in Fig. 3.27. Skiers will leave the jump at 28 m/s and 9.5° below the horizontal, and land 55 m horizontally from the end of the jump. Your job is to specify the slope of the ground so skiers’ trajectories make an angle of only 3.0° with the ground on landing, ensuring their safety. What slope do you specify?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
19:39 ·
C
Chegg
1 69%
✓
The compound beam is fixed at Ę and supported by rollers at A and B. There are pins at C and D. Take
F=1700 lb. (Figure 1)
Figure
800 lb
||-5-
F
600 lb
بتا
D
E
C
BO
10 ft 5 ft 4 ft-—— 6 ft — 5 ft-
Solved Part A The compound
beam is fixed at E and...
Hình ảnh có thể có bản quyền. Tìm hiểu thêm
Problem
A-12
% Chia sẻ
kip
800 lb
Truy cập )
D Lưu
of
C
600 lb
|-sa+ 10ft 5ft 4ft6ft
D
E
5 ft-
Trying
Cheaa
Những kết quả này có
hữu ích không?
There are pins at C and D To F-1200 Egue!)
Chegg
Solved The compound b...
Có Không ☑
|||
Chegg
10
וח
No chatgpt pls will upvote
No chatgpt pls will upvote
Chapter 3 Solutions
Essential University Physics (3rd Edition)
Ch. 3.1 - Which vector describes a displacement of 10 units...Ch. 3.2 - An object is accelerating downward. Which, if any,...Ch. 3.3 - An airplane is making a 500-km trip directly north...Ch. 3.4 - An object is moving initially in the +x-direction....Ch. 3.5 - Two projectiles are launched simultaneously from...Ch. 3.6 - An object moves in a horizontal plane with...Ch. 3 - Under what conditions is the magnitude of the...Ch. 3 - Can two vectors of equal magnitude sum to zero?...Ch. 3 - Repeat Question 2 for three vectors. 2. Can two...Ch. 3 - Can an object have a southward acceleration while...
Ch. 3 - Youre a passenger in a car rounding a curve. The...Ch. 3 - In what sense is Equation 3.8 really two (or...Ch. 3 - Is a projectiles speed constant throughout its...Ch. 3 - Is there any point on a projectiles trajectory...Ch. 3 - How is it possible for an object to be moving in...Ch. 3 - Youre in a bus moving with constant velocity on a...Ch. 3 - Which of the following are legitimate mathematical...Ch. 3 - You would probably reject as unscientific any...Ch. 3 - You walk west 220 m, then north 150 m. What are...Ch. 3 - An ion in a mass spectrometer follows a...Ch. 3 - A migrating whale follows the west coast of Mexico...Ch. 3 - Vector A has magnitude 3.0 m and points to the...Ch. 3 - Use unit vectors to express a displacement of 120...Ch. 3 - Find the magnitude of the vector 34 + 13 m and...Ch. 3 - (a) Whats the magnitude of + ? (b) What angle...Ch. 3 - Youre leading an international effort to save...Ch. 3 - An object is moving at 18 m/s at 220...Ch. 3 - A car drives north at 40 mi/h for 10 min, then...Ch. 3 - An objects velocity is v = ct3 + d, where t is...Ch. 3 - A car, initially going eastward, rounds a 90 curve...Ch. 3 - What are (a) the average velocity and (b) the...Ch. 3 - An ice skater is gliding along at 2.4 m/s, when...Ch. 3 - An object is moving in the x-direction at 1.3 m/s...Ch. 3 - Youre a pilot beginning a 1500-km flight. Your...Ch. 3 - You wish to row straight across a 63-m-wide river....Ch. 3 - A plane with airspeed 370 km/h flies...Ch. 3 - A flock of geese is attempting to migrate due...Ch. 3 - The position of an object as a function of time is...Ch. 3 - Youre sailboarding at 6.5 m/s when a wind gust...Ch. 3 - You toss an apple horizontally at 8.7 m/s from a...Ch. 3 - A carpenter tosses a shingle horizontally off an...Ch. 3 - An arrow fired horizontally at 41 m/s travels 23 m...Ch. 3 - Droplets in an ink-jet printer are ejected...Ch. 3 - Protons drop 1.2 m over the 1.7-km length of a...Ch. 3 - If you can hit a golf ball 180 m on Earth, how far...Ch. 3 - Chinas high-speed rail network calls for a minimum...Ch. 3 - The minute hand of a clock is 7.50 cm long. Find...Ch. 3 - How fast would a car have to round a 75-m-radius...Ch. 3 - Estimate the acceleration of the Moon, which...Ch. 3 - Global Positioning System (GPS) satellites circle...Ch. 3 - Two vectors A and B have the same magnitude A and...Ch. 3 - Prob. 46PCh. 3 - Let A = 15 40 and B = 31 + 18k. Find C such that...Ch. 3 - A biologist looking through a microscope sees a...Ch. 3 - A particles position is r = (ct2 2dt3) + (2ct2 ...Ch. 3 - For the particle in Problem 49, is there any time...Ch. 3 - Youre designing a cloverleaf highway interchange....Ch. 3 - An object undergoes acceleration 2.3 + 3.6 m/s2...Ch. 3 - The New York Wheel is the worlds largest Ferris...Ch. 3 - A ferryboat sails between towns directly opposite...Ch. 3 - The sum of two vectors, A + B, is perpendicular to...Ch. 3 - Write an expression for a unit vector at 45...Ch. 3 - An object is initially moving in the .x-direction...Ch. 3 - A particle leaves the origin with its initial...Ch. 3 - A kid fires a squirt gun horizontally from 1.6 m...Ch. 3 - A projectile has horizontal range R on level...Ch. 3 - You throw a baseball at a 45 angle to the...Ch. 3 - In a chase scene, a movie stuntman runs...Ch. 3 - Standing on the ground 3.0 m from a building, you...Ch. 3 - Derive a general formula for the horizontal...Ch. 3 - Consider two projectiles launched on level ground...Ch. 3 - You toss a protein bar to your hiking companion...Ch. 3 - The table below lists position versus time for an...Ch. 3 - A projectile launched at angle to the horizontal...Ch. 3 - As an expert witness, youre testifying in a case...Ch. 3 - Show that, for a given initial speed, the...Ch. 3 - A basketball player is 15 ft horizontally front...Ch. 3 - Two projectiles are launched simultaneously from...Ch. 3 - Consider the two projectiles in GOT IT? 3.5....Ch. 3 - The portion of a projectiles parabolic trajectory...Ch. 3 - A jet is diving vertically downward at 1200 km/h....Ch. 3 - Your alpine rescue team is using a slingshot to...Ch. 3 - If you can throw a stone straight up to height h....Ch. 3 - In a conversion from military to peacetime use, a...Ch. 3 - A soccer player can kick the ball 28 m on level...Ch. 3 - A diver leaves a 3-m board on a trajectory that...Ch. 3 - Prob. 81PCh. 3 - You're a consulting engineer specializing in...Ch. 3 - Differentiate the trajectory Equation 3.14 to find...Ch. 3 - Your medieval history class is constructing a...Ch. 3 - Generalize Problem 84 to find an expression for...Ch. 3 - (a) Show that the position of a particle on a...Ch. 3 - In dealing with nonuniform circular motion, as...Ch. 3 - Repeat Problem 87, now generalizing to the case...Ch. 3 - Alice (A), Bob (B), and Carrie (C) all start from...Ch. 3 - Alice (A), Bob (B), and Carrie (C) all start from...Ch. 3 - Alice (A), Bob (B), and Carrie (C) all start from...Ch. 3 - Alice (A), Bob (B), and Carrie (C) all start from...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Give an example of interspecies H2 transfer. Why can it be said that both organisms benefit from this process?
Brock Biology of Microorganisms (15th Edition)
APPLY 1.2 Express the following quantities in scientific notation
using fundamental SI units of mass and lengt...
Chemistry (7th Edition)
14.19 In Genetic Analysis, we designed a screen to identify conditional mutants of S. cerevisiae in which the s...
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Fibrous connective tissue consists of ground substance and fibers that provide strength, support, and flexibili...
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Calculate the lattice energy of CaCl2 using a Born-Haber cycle and data from Appendices F and L and Table 7.5. ...
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
4. How do gross anatomy and microscopic anatomy differ?
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardair is pushed steadily though a forced air pipe at a steady speed of 4.0 m/s. the pipe measures 56 cm by 22 cm. how fast will air move though a narrower portion of the pipe that is also rectangular and measures 32 cm by 22 cmarrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- 13.87 ... Interplanetary Navigation. The most efficient way to send a spacecraft from the earth to another planet is by using a Hohmann transfer orbit (Fig. P13.87). If the orbits of the departure and destination planets are circular, the Hohmann transfer orbit is an elliptical orbit whose perihelion and aphelion are tangent to the orbits of the two planets. The rockets are fired briefly at the depar- ture planet to put the spacecraft into the transfer orbit; the spacecraft then coasts until it reaches the destination planet. The rockets are then fired again to put the spacecraft into the same orbit about the sun as the destination planet. (a) For a flight from earth to Mars, in what direction must the rockets be fired at the earth and at Mars: in the direction of motion, or opposite the direction of motion? What about for a flight from Mars to the earth? (b) How long does a one- way trip from the the earth to Mars take, between the firings of the rockets? (c) To reach Mars from the…arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwarda cubic foot of argon at 20 degrees celsius is isentropically compressed from 1 atm to 425 KPa. What is the new temperature and density?arrow_forward
- Calculate the variance of the calculated accelerations. The free fall height was 1753 mm. The measured release and catch times were: 222.22 800.00 61.11 641.67 0.00 588.89 11.11 588.89 8.33 588.89 11.11 588.89 5.56 586.11 2.78 583.33 Give in the answer window the calculated repeated experiment variance in m/s2.arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardCan you help me solve the questions pleasearrow_forward
- Can you help me solve these questions please so i can see how to do itarrow_forwardHow can i solve this if n1 (refractive index of gas) and n2 (refractive index of plastic) is not known. And the brewsters angle isn't knownarrow_forward2. Consider the situation described in problem 1 where light emerges horizontally from ground level. Take k = 0.0020 m' and no = 1.0001 and find at which horizontal distance, x, the ray reaches a height of y = 1.5 m.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Kinematics Part 3: Projectile Motion; Author: Professor Dave explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aY8z2qO44WA;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY