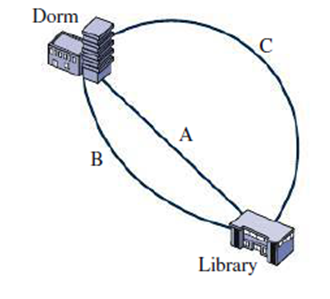
Problem 1FTD: Under what conditions is the magnitude of the vector sum A + B equal to the sum of the magnitudes of... Problem 2FTD: Can two vectors of equal magnitude sum to zero? How about two vectors of unequal magnitude? Problem 3FTD: Repeat Question 2 for three vectors. 2. Can two vectors of equal magnitude sum to zero? How about... Problem 4FTD: Can an object have a southward acceleration while moving northward? A westward acceleration while... Problem 5FTD: Youre a passenger in a car rounding a curve. The driver claims the car isnt accelerating because the... Problem 6FTD: In what sense is Equation 3.8 really two (or three) equations? Problem 7FTD: Is a projectiles speed constant throughout its parabolic trajectory? Problem 8FTD: Is there any point on a projectiles trajectory where velocity and acceleration are perpendicular? Problem 9FTD: How is it possible for an object to be moving in one direction but accelerating in another? Problem 10FTD: Youre in a bus moving with constant velocity on a level road when you throw a ball straight up. When... Problem 11FTD: Which of the following are legitimate mathematical equations? Explain, (a) v = 5 m/s; (b) v = 5 m/s;... Problem 12FTD: You would probably reject as unscientific any claim that Earth is flat. Yet the assumption of... Problem 13E: You walk west 220 m, then north 150 m. What are the magnitude and direction of your displacement... Problem 14E: An ion in a mass spectrometer follows a semicircular path of radius 15.2 cm. What are (a) the... Problem 15E: A migrating whale follows the west coast of Mexico and North America toward its summer home in... Problem 16E: Vector A has magnitude 3.0 m and points to the right; vector B has magnitude 4.0 m and points... Problem 17E: Use unit vectors to express a displacement of 120 km at 29 counterclockwise from the x-axis. Problem 18E: Find the magnitude of the vector 34 + 13 m and determine its angle to the x-axis. Problem 19E: (a) Whats the magnitude of + ? (b) What angle does it make with the x-axis? Problem 20E: Youre leading an international effort to save Earth from an asteroid heading toward us at 15 km/s.... Problem 21E: An object is moving at 18 m/s at 220 counterclockwise from the x-axis. Find the x- and y-components... Problem 22E: A car drives north at 40 mi/h for 10 min, then turns east and goes 5.0 mi at 60 mi/h. Finally, it... Problem 23E: An objects velocity is v = ct3 + d, where t is time and c and d are positive constants with... Problem 24E: A car, initially going eastward, rounds a 90 curve and ends up heading southward. If the speedometer... Problem 25E: What are (a) the average velocity and (b) the average acceleration of the tip of the 2.4-cm-long... Problem 26E: An ice skater is gliding along at 2.4 m/s, when she undergoes an acceleration of magnitude 1.1 m/s2... Problem 27E: An object is moving in the x-direction at 1.3 m/s when it undergoes an acceleration a = 0.52 m/s2.... Problem 28E: Youre a pilot beginning a 1500-km flight. Your planes speed is 1000 km/h, and air traffic control... Problem 29E: You wish to row straight across a 63-m-wide river. You can row at a steady 1.3 m/s relative to the... Problem 30E: A plane with airspeed 370 km/h flies perpendicularly across the jet stream, its nose pointed into... Problem 31E: A flock of geese is attempting to migrate due south, but the wind is blowing from the west at 5.1... Problem 32E: The position of an object as a function of time is given by r = (3.2t + 1.8t2) + (1.7t 2.4t2) m,... Problem 33E: Youre sailboarding at 6.5 m/s when a wind gust hits, lasting 6.3 s accelerating your board at 0.48... Problem 34E: You toss an apple horizontally at 8.7 m/s from a height of 2.6 m. Simultaneously, you drop a peach... Problem 35E: A carpenter tosses a shingle horizontally off an 8.8-m-high roof at 11 m/s. (a) How long does it... Problem 36E: An arrow fired horizontally at 41 m/s travels 23 m horizontally. From what height was it fired? Problem 37E: Droplets in an ink-jet printer are ejected horizontally at 12 m/s and travel a horizontal distance... Problem 38E: Protons drop 1.2 m over the 1.7-km length of a particle accelerator. Whats their approximate average... Problem 39E: If you can hit a golf ball 180 m on Earth, how far can you hit it on the Moon? (Your answer will be... Problem 40E: Chinas high-speed rail network calls for a minimum turn radius of 7.0 km for 350-km/h trains. Whats... Problem 41E: The minute hand of a clock is 7.50 cm long. Find the magnitude of the acceleration of its tip. Problem 42E: How fast would a car have to round a 75-m-radius turn for its acceleration to be numerically equal... Problem 43E: Estimate the acceleration of the Moon, which completes a nearly circular orbit of 384.4 Mm radius in... Problem 44E: Global Positioning System (GPS) satellites circle Earth at altitudes of approximately 20,000 km,... Problem 45P: Two vectors A and B have the same magnitude A and are at right angles. Find the magnitudes of (a) A... Problem 46P Problem 47P: Let A = 15 40 and B = 31 + 18k. Find C such that A + B + C = 0. Problem 48P: A biologist looking through a microscope sees a bacterium at r1 = 2.2 + 3.7 1.2k pm. After 6.2 s,... Problem 49P: A particles position is r = (ct2 2dt3) + (2ct2 dt3), where c and d are positive constants. Find... Problem 50P: For the particle in Problem 49, is there any time t 0 when the particle is (a) at rest and (b)... Problem 51P: Youre designing a cloverleaf highway interchange. Vehicles will exit the highway and slow to a... Problem 52P: An object undergoes acceleration 2.3 + 3.6 m/s2 for 10 s. At the end of this time, its velocity is... Problem 53P: The New York Wheel is the worlds largest Ferris wheel. Its 183 meters in diameter and rotates once... Problem 54P: A ferryboat sails between towns directly opposite each other on a river, moving at speed v relative... Problem 55P: The sum of two vectors, A + B, is perpendicular to their difference, A B. How do the vectors... Problem 56P: Write an expression for a unit vector at 45 clockwise from the x-axis. Problem 57P: An object is initially moving in the .x-direction at 4.5 m/s, when it undergoes an acceleration in... Problem 58P: A particle leaves the origin with its initial velocity given by v0 = 11 + 14 m/s, undergoing... Problem 59P: A kid fires a squirt gun horizontally from 1.6 m above the ground. It hits another kid 2.1 m away... Problem 60P: A projectile has horizontal range R on level ground and reaches maximum height h. Find an expression... Problem 61P: You throw a baseball at a 45 angle to the horizontal, aiming at a friend whos sitting in a tree a... Problem 62P: In a chase scene, a movie stuntman runs horizontally off the flat roof of one building and lands on... Problem 63P: Standing on the ground 3.0 m from a building, you want to throw a package from your 1.5-m shoulder... Problem 64P: Derive a general formula for the horizontal distance covered by a projectile launched horizontally... Problem 65P: Consider two projectiles launched on level ground with the same speed, at angles 45 . Show that the... Problem 66P: You toss a protein bar to your hiking companion located 8.6 m up a 39 slope, as shown in Fig. 3.24.... Problem 67P: The table below lists position versus time for an object moving in the x-y plane, which is... Problem 68P: A projectile launched at angle to the horizontal reaches mum height h. Show that its horizontal... Problem 69P: As an expert witness, youre testifying in a case involving a motorcycle accident. A motorcyclist... Problem 70P: Show that, for a given initial speed, the horizontal range of a projectile is the same for launch... Problem 71P: A basketball player is 15 ft horizontally front the center of the basket, which is 10 ft off the... Problem 72P: Two projectiles are launched simultaneously from the same point, with different launch speeds and... Problem 73P: Consider the two projectiles in GOT IT? 3.5. Suppose the 45 projectile is launched with speed v and... Problem 74P: The portion of a projectiles parabolic trajectory in the vicinity of the peak can be approximated as... Problem 75P: A jet is diving vertically downward at 1200 km/h. If the pilot can withstand a maximum acceleration... Problem 76P: Your alpine rescue team is using a slingshot to send an emergency medical packet to climbers... Problem 77P: If you can throw a stone straight up to height h. whats the maximum horizontal distance you could... Problem 78P: In a conversion from military to peacetime use, a missile with maximum horizontal range 180 km is... Problem 79P: A soccer player can kick the ball 28 m on level ground, with its initial velocity at 40 to the... Problem 80P: A diver leaves a 3-m board on a trajectory that takes her 2.5 m above the board and then into the... Problem 81P Problem 82P: You're a consulting engineer specializing in athletic facilities, and youve been asked to help... Problem 83P: Differentiate the trajectory Equation 3.14 to find its slope, tan = dy/dx, and show that the slope... Problem 84P: Your medieval history class is constructing a trebuchet, a catapult-like weapon for hurling stones... Problem 85P: Generalize Problem 84 to find an expression for the angle that will maximize the range of a... Problem 86P: (a) Show that the position of a particle on a circle of radius R with its center at the origin is r... Problem 87P: In dealing with nonuniform circular motion, as shown in Fig. 3.23, we should write Equation 3.16 as... Problem 88P: Repeat Problem 87, now generalizing to the case where not only the speed but also the radius may be... Problem 89PP: Alice (A), Bob (B), and Carrie (C) all start from their dorm and head for the library for an evening... Problem 90PP: Alice (A), Bob (B), and Carrie (C) all start from their dorm and head for the library for an evening... Problem 91PP: Alice (A), Bob (B), and Carrie (C) all start from their dorm and head for the library for an evening... Problem 92PP: Alice (A), Bob (B), and Carrie (C) all start from their dorm and head for the library for an evening... format_list_bulleted


 Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill