
Concept explainers
Reece Financial Services Co., which specializes in appliance repair services, is owned and operated by Joni Reece. Reece Financial Services’ accounting clerk prepared the following unadjusted
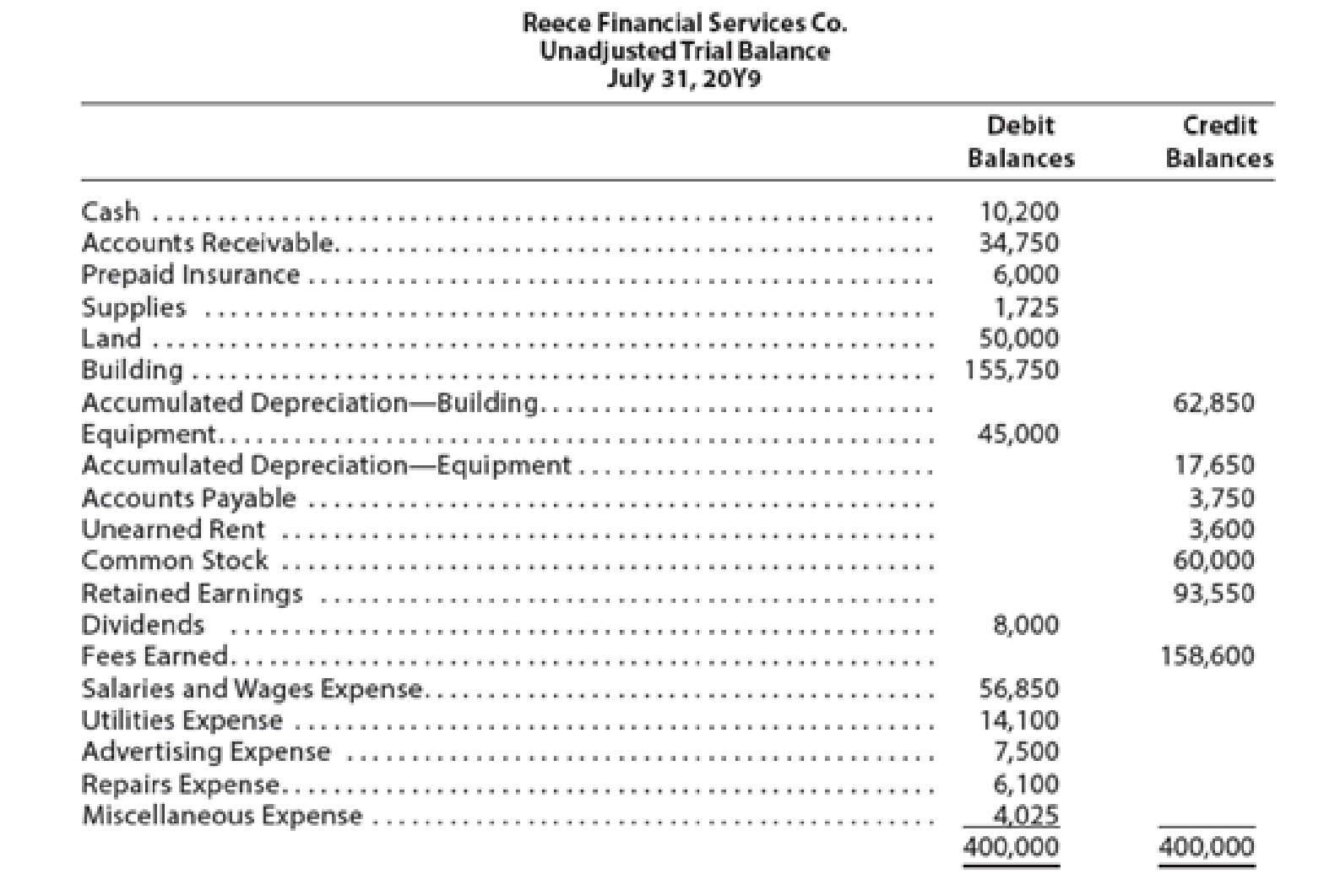
The data needed to determine year-end adjustments are as follows:
•
• Depreciation of equipment for the year, $2,800.
• Accrued salaries and wages at July 31, $900.
• Unexpired insurance at July 31, $1,500.
• Fees earned but unbilled on July 31, $10,200.
• Supplies on hand at July 31, $615.
• Rent unearned at July 31, $300.
Instructions
1. Journalize the adjusting entries using the following additional accounts: Salaries and Wages Payable; Rent Revenue; Insurance Expense; Depreciation Expense—Building; Depreciation Expense— Equipment; and Supplies Expense.
2. Determine the balances of the accounts affected by the adjusting entries, and prepare an adjusted trial balance.
1.
Prepare the adjusting entries on July 31, 20Y9 of Company RFS.
Explanation of Solution
Adjusting Entries:
Adjusting entries indicates those entries, which are passed in the books of accounts at the end of one accounting period. These entries are passed in the books of accounts as per the revenue recognition principle and the expenses recognition principle to adjust the revenue, and the expenses of a business in the period of their occurrence.
Rule of Debit and Credit:
Debit - Increase in all assets, expenses & dividends, and decrease in all liabilities and stockholders’ equity.
Credit - Increase in all liabilities and stockholders’ equity, and decrease in all assets & expenses.
The adjusting entry for recording depreciation for building is as follows:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| July 31 | Depreciation expense | 6,400 | |
| Accumulated Depreciation- building | 6,400 | ||
| (To record the depreciation on building for the current year.) |
Table (1)
- Depreciation expense is component of stockholders’ equity and decreased it, so debit depreciation expense by $6,400.
- Accumulated depreciation is a contra asset account, and it decreases the asset value by $6,400. So credit accumulated depreciation by $6,400.
The adjusting entry for recording depreciation for equipment is as follows:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| July 31 | Depreciation expense | 2,800 | |
| Accumulated Depreciation- equipment | 2,800 | ||
| (To record the depreciation on equipment for the current year.) |
Table (2)
- Depreciation expense is component of stockholders’ equity and decreased it, so debit depreciation expense by $2,800.
- Accumulated depreciation is a contra asset account, and it decreases the asset value by $2,800. So credit accumulated depreciation by $2,800.
The following entry shows the adjusting entry for Salary and wages expense on July 31.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| July 31 | Salary and wages expense | 900 | |
| Wages Payable | 900 | ||
| (To record the salary and wages accrued but not paid at the end of the accounting period.) |
Table (3)
- Salary and wages expense is a component of Stockholders ‘equity, and it decreased it by $900. So debit wage expense by $900.
- Salary and wages payable is a liability, and it is increased by $900. So credit Salary and wages payable by $900.
The following entry shows the adjusting entry for unexpired insurance on July 31.
| Date | Description |
Post. Ref |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| July 31 | Insurance expense (1) | 4,500 | ||
| Prepaid insurance | 4,500 | |||
| (To record the insurance expense incurred at the end of the year) |
Table (4)
Working note (1):
Calculate the value of insurance expense at the end of the year:
- Insurance expense is a component of owners’ equity, and decreased it by $4,500 hence debit the insurance expense for $4,500.
- Prepaid insurance is an asset, and it decreases the value of asset by $4,500, hence credit the prepaid insurance for $4,500.
The following entry shows the adjusting entry for accrued fees unearned on July 31.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| July 31 | Accounts Receivable | 10,200 | |
| Fees earned | 10,200 | ||
| (To record the accounts receivable at the end of the year.) |
Table (5)
- Accounts Receivable is an asset, and it is increased by $10,200. So debit Accounts receivable by $10,200.
- Fees earned are component of stockholders’ equity, and it increased it by $10,200. So credit fees earned by $10,200.
The following entry shows the adjusting entry for supplies on July 31.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| July 31 | Supplies Expense (2) | 1,110 | |
| Supplies | 1,110 | ||
| (To record the supplies expense at the end of the accounting period) |
Table (6)
- Supplies expense is a component of stockholders’ equity, and it decreased the stockholders’ equity by $1,110. So debit supplies expense by $1,110.
- Supplies are an asset for the business, and it is decreased by $1,110. So credit supplies by $1,110.
Working Note (2):
Calculation of Supplies expense for the accounting period
The following entry shows the adjusting entry for unearned Rent on July 31.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| July 31 | Unearned Rent | 3,300 | |
| Rent revenue (3) | 3,300 | ||
| (To record the Rent revenue from services at the end of the accounting period.) |
Table (7)
- Unearned Rent is a liability, and it is decreased by $3,300. So debit unearned rent by $3,300.
- Rent revenue is a component of Stockholders’ equity, and it is increased by $3,300. So credit rent revenue by $3,300.
Working Notes (3):
Calculation of Rent Revenue for the accounting period
2.
Prepare the adjusted trial balance of the Company RFS on July 31, 20Y9.
Explanation of Solution
Adjusted Trial Balance
Adjusted trial balance is a trial balance prepared at the end of a financial period, after all the adjusting entries are journalized and posted. It is prepared to prove the equality of the total debit and credit balances.
The adjusted trial balance of the Company RFS is as follows:
| Company RFS | ||
| Trial Balance after Adjustments | ||
| July 31, 20Y9 | ||
| Particulars | Debit $ | Credit $ |
| Cash | 10,200 | |
| Accounts Receivable(5) | 44,950 | |
| Prepaid Insurance | 1,500 | |
| Supplies | 615 | |
| Land | 50,000 | |
| Building | 155,750 | |
| Accumulated Depreciation - Building(1) | 69,250 | |
| Equipment | 45,000 | |
| Accumulated Depreciation - Equipment(2) | 20,450 | |
| Accounts Payable | 3,750 | |
| Unearned Rent | 300 | |
| Salaries and Wages Payable | 900 | |
| Capital | 153,550 | |
| Drawing | 8,000 | |
| Fees earned | 168,800 | |
| Rent Revenue (7) | 3,300 | |
| Salaries and Wages Expense (3) | 57,750 | |
| Utilities Expense | 14,100 | |
| Advertising Expense | 7,500 | |
| Repairs Expense | 6,100 | |
| Depreciation Expense - building | 6,400 | |
| Depreciation Expense - equipment | 2,800 | |
| Insurance Expense (4) | 4,500 | |
| Supplies Expense (6) | 1,110 | |
| Miscellaneous Expense | 4,025 | |
| 420,300 | 420,300 | |
Table (8)
1. Calculation of accumulated depreciation- building
2. Calculation of accumulated depreciation- equipment
3. Calculation of Salaries and Wages expenses
4. Calculate the value of insurance expense at the end of the year
5. Calculation of accounts receivable
6. Calculation of Supplies expense for the accounting period
7. Calculation of rent revenue:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Financial And Managerial Accounting
- Degregorio Corporation makes a product that uses a material with the following direct material standards: Standard quantity 4 kilos per unit Standard price $9 per kilo The company produced 7,200 units in November using 29,290 kilos of the material. During the month. the company purchased 31,480 kilos of the direct material at a total cost of $277,024. The direct materials purchases variance is computed when the materials are purchased. The materials price variance for November is: a. $5,592 F b. $5,592 U c. $6,296 F d. $6,296 Uarrow_forwardNonearrow_forwardSelect the correct equation format for the purchases budget. a. Beginning inventory + expected sales = required purchases b. Expected sales + Desired ending inventory = required purchases c. Beginning inventory + expected sales - desired ending inventory = required purchases d. Expected sales + desired ending inventory - beginning inventory = required purchasesarrow_forward
- Principles of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781337280570Author:Scott, Cathy J.Publisher:South-Western College Pub
College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781337280570Author:Scott, Cathy J.Publisher:South-Western College Pub  Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning




