
The Cosmic Perspective (9th Edition)
9th Edition
ISBN: 9780134874364
Author: Jeffrey O. Bennett, Megan O. Donahue, Nicholas Schneider, Mark Voit
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 3, Problem 3VSC
Use the following questions to check your understanding of some of the many types of visual information used in astronomy. For additional practice, try the Chapter 3 Visual Quiz at MasteringAstronomy®.
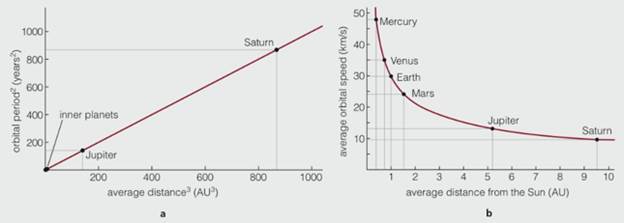
Study the two graphs above, based on Figure 3.19. Use the information in the graphs to answer the following questions.
3. Uranus, not shown on graph b, orbits about 19 AU from the Sun. Based on the graph, its approximate orbital speed is between about
a. 20 and 25 km/s.
b. 15 and 20 km/s.
c. 10 and 15 km/s.
d. 5 and 10 km/s.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Let's use Kepler's laws for the inner planets. Use the following distances from the sun to calculate the orbital period for each of these planets. Express your answer in terms of Earth years to two significant figures. Answer for the highlighted planet in each question.
Note: Use Kepler's law directly. Don't just Google the answers, as they will be a little bit different.
When you have calculated them, only submit the value for Earth.
Planet
Distance from the sun
Period of orbit around the sun
Earth
150 million km
___ Earth years
Mercury
58 million km
___ Earth years
Venus
108 million km
___ Earth years
Mars
228 million km
___ Earth years
Question 1 (Total: 30 points)
a. What is a repeat ground-track orbit?
b. Explain why repeat ground-track and Sun-synchronous orbits are typically used for Earth observation missions.
c. The constraint for a Sun-synchronous and repeat ground-track orbit is given by T = 286, 400, where I is the orbital period in seconds, m the number of days and k
the number of revolutions. Explain why this is, in fact, a constraint on the semi-major axis of the orbit.
Delay time for communication between GEO satellites and Earth.
Use the relationship between distance (d), time (t) and speed (v),
d = vt
to repeat the calculation we did in class, but this time using the English units. Use the fact that
GEO satellites orbit at 22,236 miles above Earth's equator, and that the speed of light is
1.86 x 105 mi/s. (Note that both of these values are equivalent to those used in class.) You
may want to write this calculation on paper and insert a photo here.
Chapter 3 Solutions
The Cosmic Perspective (9th Edition)
Ch. 3 - Prob. 1VSCCh. 3 - Use the following questions to check your...Ch. 3 - Use the following questions to check your...Ch. 3 - Use the following questions to check your...Ch. 3 - Use the following questions to check your...Ch. 3 - Prob. 6VSCCh. 3 - Prob. 7VSCCh. 3 - Prob. 1EAPCh. 3 - Why did ancient peoples study astronomy? Describe...Ch. 3 - Describe the astronomical origins of our day,...
Ch. 3 - What is a lunar calendar? How can it be kept...Ch. 3 - What do we mean by a model in science?Ch. 3 - Summarize the development of the Greek geocentric...Ch. 3 - What was the Copernican revolution, and how did it...Ch. 3 - 8. What is an ellipse? Define its foci, semimajor...Ch. 3 - 9. State and explain the meaning of each of...Ch. 3 - Describe the three hallmarks of science and how we...Ch. 3 - 11. What is the difference between a hypothesis...Ch. 3 - What is the basic idea behind astrology? Explain...Ch. 3 - Science or Nonscience? Each of the following...Ch. 3 - Science or Nonscience? Each of the following...Ch. 3 - Science or Nonscience?
Each of the following...Ch. 3 - Science or Nonscience?
Each of the following...Ch. 3 - Science or Nonscience?
Each of the following...Ch. 3 - Science or Nonscience? Each of the following...Ch. 3 - Science or Nonscience? Each of the following...Ch. 3 - Science or Nonscience?
Each of the following...Ch. 3 - Science or Nonscience?
Each of the following...Ch. 3 - Science or Nonscience? Each of the following...Ch. 3 - In the Greek geocentric model, the retrograde...Ch. 3 - Which of the following was not a major advantage...Ch. 3 - When we say that a planet has a highly eccentric...Ch. 3 - Earth is closer to the Sun in January than in...Ch. 3 - According to Kepler’s third law, (a) Mercury...Ch. 3 - Tycho Brahe’s contribution to astronomy included...Ch. 3 - Galileo’s contribution to astronomy included (a)...Ch. 3 - Which of the following is not true about...Ch. 3 - Which of the following is not true about a...Ch. 3 - When Einstein’s theory of gravity (general...Ch. 3 - What Makes It Science? Choose a single idea in the...Ch. 3 - Prob. 35EAPCh. 3 - Prob. 36EAPCh. 3 - Prob. 37EAPCh. 3 - Earth’s Shape. It took thousands of years for...Ch. 3 - Prob. 40EAPCh. 3 - Copernican Players. Using a bulleted-list format,...Ch. 3 - Prob. 44EAPCh. 3 - The Metonic Cycle. The length of our calendar year...Ch. 3 - Chinese Calendar. The traditional Chinese lunar...Ch. 3 - Method of Eratosthenes I. You are an astronomer on...Ch. 3 - Method of Eratosthenes II. You are an astronomer...Ch. 3 - Mars Orbit. Find the perihelion and aphelion...Ch. 3 - Eris Orbit. The dwarf planet Eris orbits the Sun...Ch. 3 - New Planet Orbit. A newly discovered planet orbits...Ch. 3 - Halley Orbit. Halley’s Comet orbits the Sun every...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- As discussed in class, the moon is receding from the Earth due to tides at a rate of ~4 cm/year. Let’s assume that rate has been constant throughout time (it wasn’t, but we can use it to illustrate some key points). Its current semi-major axis is 384,400 km.a) If the moon formed 4.5 billion years ago and has been receding from the Earth ever since, what was its original semi-major axis? What was its original orbital period?b) What would the apparent size of the Moon have been in the sky as viewed from Earth? That is, in Hmwk 2, you were told the diameter of the Moon spans about 0.5o when viewed from Earth today. What would it have been when the Moon first formed? Reletive Numbers Relevant Numbers1 AU = 150,000,000 km = 1.5x108 kmEccentricity of Earth’s Orbit: 0.0167Radius of Earth: 6371 kmMass of Earth: 5.96x1024 kgRadius of the Moon: 1737 kmMass of Moon: 7.34x1022 kgRadius of Mars: 3390 kmMass of Mars: 6.4x1023 kgRadius of the Sun: R⦿=696,300 kmMass of the Sun: M⦿=2x1030…arrow_forwardbetween a planet and its moon. Procedure/Analysis: Go to: https://www.physicsclassroom.com/Physics-Interactives/Circular-and-Satellite- Motion/Gravitational-Fields/Gravitational-Fields-Interactive Use the program to answer the following questions. 1. A planet and its moon are shown in the simulation window. Click and drag the moon to various positions about the planet and observe the gravitational force vector. In the diagram below, draw a force vector (arrow with arrowhead) to depict the direction and relative magnitude of the force acting upon the moon at the designated locations. Note: the size of the arrow should be representative of the strength of the force.arrow_forwardUnit 3: Final Assessment Use your Digital Interactive Notebook, Peardeck Notes, and Science Weekly Reading for assistance. Question #1: Which evidence first supported the heliocentric model of the solar system? A. mapping of stars using the unaided eye B. taking pictures of distant galaxies with satellite-based cameras C. determining that planets orbit in elliptical paths with telescopes D. observing the surface features of nearby planets and moons with telescopesarrow_forward
- Use Kepler's 3rd Law and the small angle approximation. a) An object is located in the solar system at a distance from the Sun equal to 41 AU's . What is the objects orbital period? b) An object seen in a telescope has an angular diameter equivalent to 41 (in units of arc seconds). What is its linear diameter if the object is 250 million km from you? Draw a labeled diagram of this situation.arrow_forwardThis is Pre-Calc! Please help and Thank you! Please click the pics for the background info Directions: Answer questions 1-8 based on the information on Table 1. Round all answers to the nearest thousandth and label with the appropriate units. 1. According to Table 1, what is the closest distance between Earth and Mars? 2. According to Table 1, what is the farthest distance between Earth and Mars? 3. Based on your answers from #2 and #3, what is the average distance between the two planets? 4. Based on your answers from #2 and #3, what is the amplitude of the distances? 5. The distance has a period of 772 days. Write a sinusoidal equation relating the number of days and distance from Earth to Mars. 6. Based on the equation from #5, what is the distance between our planets on Mr. Schutt’s birthday (day 187)? 7. Write a sinusoidal equation relating the number of days and the one-waycommunication between Earth to Mars. 8. What is the one-way communication time delay between our planets on…arrow_forwardSolve for ALL four questions using PROPER EXPLANATIONS, DETAILED DIAGRAMS AND EXPLAINING HOW THE ANSWER WAS JUSTIFIED. Use proper physics terminology, don't repeat the same questions, and double check answers for clarity.arrow_forward
- Using the GUFSA Template. Round off your final answer to the nearest hundredths. As we already know, rockets travel at very high speeds. How much time will it take a rocket (in seconds) to reach the moon if the moon is 238,900 miles away from the Earth, and the rocket is travelling 1,800,000 centimeters per minute? (express your answer in meters per second)arrow_forward1. If people on Earth were viewing a total lunar eclipse, what would you see from your home on the Moon? Draw a diagram. 2. Why were the main reasons why the idea that the Earth was at the center of the universe lasted so long? 3. Discuss in 2 paragraphs the observations made by Galileo that disproved Geocentrism. Which one do you think was the most important? 4. Write down a hypothesis and observational experiment to test one of Newton’s laws of motion. EXPLAIN YOUR REASONING! 5. One of the first exoplanets discovered orbits the star 51 Pegasi with a period of just 4.2 days. 51 Pegasi is very similar to the Sun. Use Kepler’s laws to find the distance (in astronomical units) between the planet (unofficially named Bellerophon) and its star. SHOW YOUR WORK! 6. How does halving the distance between two objects affect the gravitational force between them? 7. Suppose the Sun were somehow replaced by a star with five times as much mass. What would happen to the gravitational force between…arrow_forwardAstronomy question: PLEASE ANSWER the questions correlty and please answer all the questions with what it regards in saying exactly, please and thank you take your time. Ive read the guide lines and honor code that i can have up to Submit only one question at a time under the appropriate subject. A question can have up to 3 subparts (i.e. part a, b, and c). If you dont belive me here is the link of barthleby saying exactly that thanks: https://bartleby.zendesk.com/hc/en-us/articles/360017462394-How-can-I-ensure-my-questions-get-answered-as-quickly-as-possible-arrow_forward
- The table below presents the semi-major axis (a) and Actual orbital period for all of the major planets in the solar system. Cube for each planet the semi-major axis in Astronomical Units. Then take the square root of this number to get the Calculated orbital period of each planet. Fill in the final row of data for each planet. Table of Data for Kepler’s Third Law: Table of Data for Kepler’s Third Law: Planet aau = Semi-Major Axis (AU) Actual Planet Calculated Planet Period (Yr) Period (Yr) __________ ______________________ ___________ ________________ Mercury 0.39 0.24 Venus 0.72 0.62 Earth 1.00 1.00 Mars 1.52 1.88 Jupiter…arrow_forwardPLEASE MAKE SURE THAT YOU ARE ANSWERING THE QUESTIONS USING YOUR OWN THOUGHTS. STRICTLY NO COPY PASTE PLEASE! Answer each questions in not less than 2 paragraphs: 3. What is astronomy? 4. What is Geocentric Model?arrow_forwardParallax from Jupiter. Suppose you could observe stellar parallax from the orbit of Jupiter. How would it differ from the stellar parallax we observe from Earth? Would it be easier or more difficult to measure stellar distances? Explain.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON
Kepler's Three Laws Explained; Author: PhysicsHigh;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kyR6EO_RMKE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY