
Organic Chemistry, Loose-leaf Version
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781305865549
Author: William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 3, Problem 3.24P
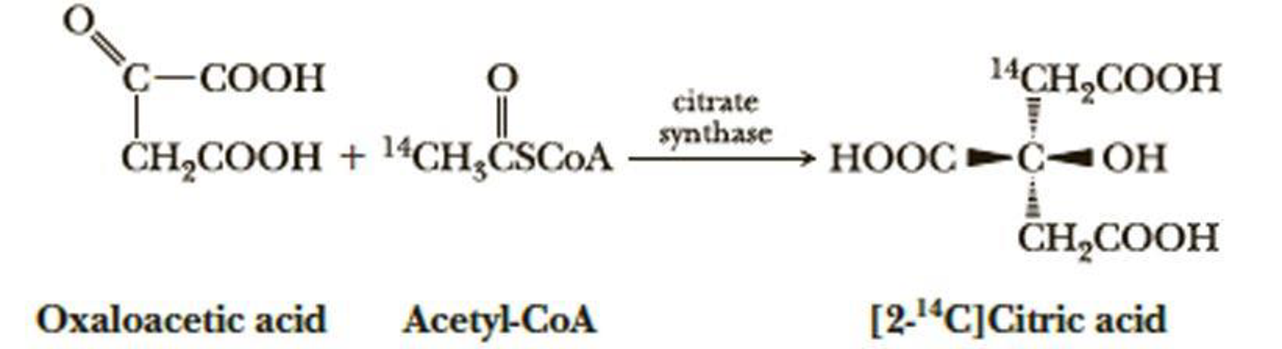
When oxaloacetic acid and acetyl-coenzyme A (acetyl-CoA) labeled with radioactive carbon-14 in position 2 are incubated with citrate synthase, an enzyme of the tricarboxylic acid cycle, only the following enantiomer of [2-l4C]citric acid is formed stereoselectively. Note that citric acid containing only 12C is achiral. Assign an R or S configuration to this enantiomer of [2-14C]citric acid. (Note: Carbon-14 has a higher priority than carbon-12.)
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
When oxaloacetic acid and acetyl-coenzyme A (acetyl-CoA) labeled with radioactive
carbon-14 in position 2 are incubated with citrate synthase, an enzyme of the tricarboxylic
acid cycle, only the following enantiomer of [2-14C]citric acid is formed stereoselectively.
Note that citric acid containing only 12C is achiral. Assign an R or S configuration to this
enantiomer of [2-14C]citric acid. (Note: Carbon-14 has a higher priority than carbon-12.)
C-COOH
14CH,COOH
citrate
synthase
ČH,COOH + 14CH,CSCOA
НООС
-COH
CH,COOH
Oxaloacetic acid
Acetyl-CoA
[2-14C]Citric acid
Heating D-altrose with dilute acid produces a nonreducing anhydro sugar (C6H1005). Methylation of the anhydro sugar followed by
acid hydrolysis yields 2,3,4-tri-O-methyl-D-altrose. The formation of the anhydro sugar takes place through a chair conformation of ẞ-
D-altropyranose in which the -CH2OH group is axial.
What is the structure of the anhydro sugar?
CH3
OH
HO
OH
I
H₂C
CH3
0.
0
H
H
H
H
HO
OH
OH
I
CH3
H₂C
H
H
H
H
CH₂
-OH
OH
HO
eTextbook and Media
Explain how is it formed.
The anhydro sugar is formed when the axial -CH2OH group reacts with C
to form a cyclic
SUPF
Because the anhydro sugar is
(i.e., an internal glycoside), it is a
sugar.
Methylation followed by acid hydrolysis converts the anhydro sugar to 2,3,4-tri-O-methyl-D-altrose.
When pure (S)-lactic acid is esterified by racemic butan-2-ol, the product is 2-butyl lactate, with the following structure:H+CH3 CH COOH CH3 CH CH3 CH CHOH OHCH2CH3 CH2CH3lactic acidC OOH CH O 3butan-2-ol 2-butyl lactate+(a) Draw three-dimensional structures of the two stereoisomers formed, specifying the configuration at each asymmetriccarbon atom. (Using your models may be helpful.)(b) Determine the relationship between the two stereoisomers you have drawn
Chapter 3 Solutions
Organic Chemistry, Loose-leaf Version
Ch. 3.2 - Prob. 3.1PCh. 3.3 - Assign priorities to the groups in each set. (a)...Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 3.3PCh. 3.4 - Following are stereorepresentations for the four...Ch. 3.4 - Prob. 3.5PCh. 3.4 - Prob. 3.6PCh. 3.5 - How many stereoisomers exist for...Ch. 3.5 - How many stereoisomers exist for...Ch. 3.7 - Prob. 3.9PCh. 3.7 - Prob. 3.10P
Ch. 3.8 - If the side chain of the amino add is a methyl...Ch. 3.8 - Prob. BQCh. 3.8 - The amino acids cysteine and serine are shown....Ch. 3.8 - Prob. DQCh. 3.8 - As stated, proteins are stereochemically pure...Ch. 3.8 - As stated, proteins are stereochemically pure...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.11PCh. 3 - One reason we can be sure that sp3-hybridized...Ch. 3 - Which compounds contain chiral centers? (a)...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.15PCh. 3 - Prob. 3.16PCh. 3 - Prob. 3.17PCh. 3 - Mark each chiral center in the following molecules...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.19PCh. 3 - Assign priorities to the groups in each set. (a) H...Ch. 3 - Following are structural formulas for the...Ch. 3 - Following is a staggered conformation for one of...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.23PCh. 3 - When oxaloacetic acid and acetyl-coenzyme A...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.25PCh. 3 - Mark each chiral center in the following molecules...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.27PCh. 3 - Prob. 3.28PCh. 3 - Prob. 3.29PCh. 3 - Prob. 3.30PCh. 3 - Which of the following are meso compounds?Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.32PCh. 3 - Prob. 3.33PCh. 3 - Which of the following compounds are chiral?...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.35PCh. 3 - Prob. 3.36PCh. 3 - Prob. 3.37PCh. 3 - The chiral catalyst (R)-BINAP-Ru is used to...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.39P
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The first step in the metabolism of glycerol, formed by digestion of fats, is phosphorylation of the pro-R—CH2OH group by reaction with adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to give the corresponding glycerol phosphate plus adenosine diphosphate (ADP). Show the stereochemistry of the product.arrow_forwardTreatment of -D-glucose with methanol in the presence of an acid catalyst converts it into a mixture of two compounds called methyl glucosides (Section 25.3A). In these representations, the six-membered rings are drawn as planar hexagons. (a) Propose a mechanism for this conversion and account for the fact that only the OH on carbon 1 is transformed into an OCH3 group. (b) Draw the more stable chair conformation for each product. (c) Which of the two products has the chair conformation of greater stability? Explain.arrow_forwardFollowing is a retrosynthesis for the coronary vasodilator ganglefene. (a) Propose a synthesis for ganglefene from 4-hydroxybenzoic acid and 3-methyl-3-buten-2-one. (b) Is ganglefene chiral? If so, which of the possible stereoisomers are formed in this synthesis?arrow_forward
- The lactic acid that builds up in tired muscles is formed from pyruvate. If the reaction occurs with addition of hydrogen to the Re face of pyruvate, what is the stereochemistry of the product?arrow_forwardOne of the following molecules (a)–(d) is d-erythrose 4-phosphate, an intermediate in the Calvin photosynthetic cycle by which plants incorporate CO2 into carbohydrates. If d-erythrose 4-phosphate has R stereochemistry at both chirality centers, which of the structures is it? Which of the remaining three structures is the enantiomer of d-erythrose 4-phosphate, and which are diastereomers?arrow_forwardIn the conversion of acetone to aceto-cyanohydrin, the effect of electron-donating substituents on the tetrahedral intermediate is to: stabilize the charge on oxygen destabilize the carbocation formed destabilize the ch charge on oxygen make the intermediate more crowded Which of the following is not indicated by this reaction? KI, H;PO4 ether, 25° C The reaction occurs in solution. It occurs at room conditions. The reaction is carried out with an acid catalyst. The solvent is KI. Predict the increasing rate of reaction of the following alkenes with HCI. 1. 2-butene II. 2-methyl-2-butene II. ethene (A I, II, II B II, I, II II, III, I III, I, IIarrow_forward
- Treatment of cholesterol with MCPBA results in formation of a single epoxide A, with the stereochemistry drawn. Why isn't the isomeric epoxide B formed to any extent? H HO Но A HIarrow_forward2305032118517 CHO H-C-OH H-C-OH H₂C₂OH CHO Ho-C-tt A D-aldotetrose yields a mixture of the two compounds shown below when subjected to Kiliani - Fischer Chain extension synthesis. What is the Structure of the aldotetrose? 3 CH₂OH Compound I H-C-OH CHO HO-C-H Ho C-H сно HO-C-H WOO Н-С-он H-C-OH CH ₂ OH Compound II CHO H² C-OH HO-C-H CH₂OH CH ₂ OH CH₂OH CA) (B) (D) (E) Both choices (B) and (C) could be the correct structure of D-erythrose. CHO H₂C-OH HC OH CH ₂ OH ctrl MAND optionarrow_forwardMyo-inositol, the most prominent naturally occurring form of inositols, is a carbocyclic polyol that plays an important role as the structural basis for a number of secondary messengers in eukaryotic cells. It is generated in vivo from the aldol cyclization of glucose-6-phosphate to myo-inositol-1-phosphatearrow_forward
- Draw the organic products formed in the attached reactionarrow_forwardNonearrow_forwardCitrate synthase, one of the enzymes in the series of enzyme-catalyzed reactions known as the citric acid cycle, catalyzes the synthesis of citric acid from oxaloacetic acid and acetyl-CoA. If the synthesis is carried out with acetyl-CoA that contains radioactive carbon (14C) in the indicated position , the isomer shown here is obtained. a. Which stereoisomer of citric acid is synthesized: R or S? b. If the acetyl-CoA used in the synthesis contains 12C instead of 14C, will the product of the reaction be chiral or achiral?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Enzymes - Effect of cofactors on enzyme; Author: Tutorials Point (India) Ltd;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AkAbIwxyUs4;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Enzyme Catalysis Part-I; Author: NPTEL-NOC IITM;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aZE740JWZuQ;License: Standard Youtube License