
Concept explainers
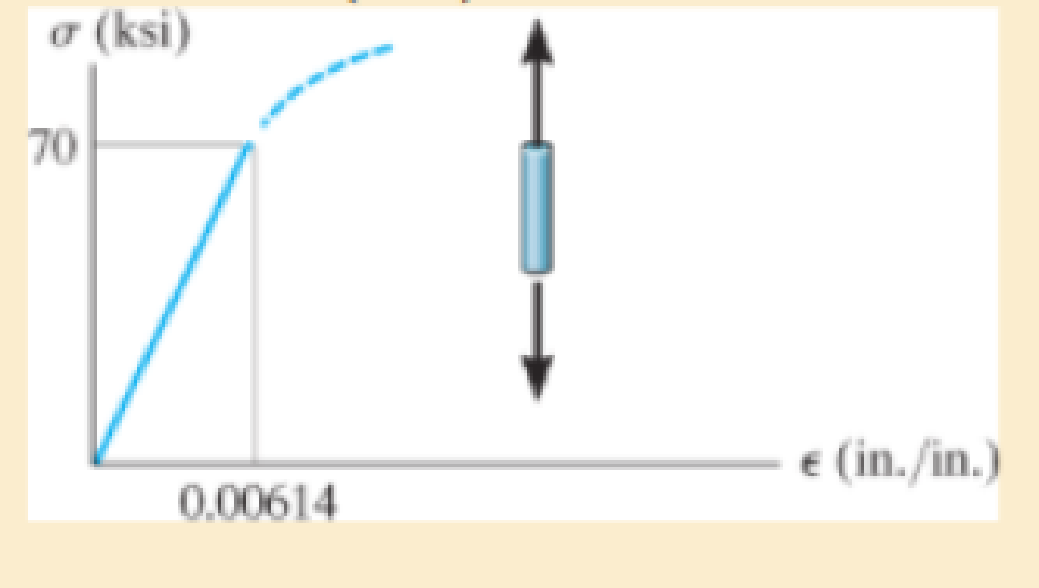
The elastic portion of the tension stress-strain diagram for an aluminum alloy is shown in the figure. The specimen used for the test has a gage length of 2 in. and a diameter of 0.5 in. When the applied load is 9 kip, the new diameter of the specimen is 0.49935 in. Calculate the shear modulus Gal for the aluminum.
The shear modulus for an aluminum alloy
Answer to Problem 3.1RP
The shear modulus for an aluminum alloy is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Gage length is
The diameter of the specimen is
The axial load acts on the specimen is
The new diameter of the specimen is
Calculation:
Calculate the modulus of elasticity for aluminum
Here, the stress is
Refer the stress-strain diagram.
The value of stress is 70 ksi and the value of strain is
Substitute 70 ksi for
The expression to find the cross-sectional area of the specimen
Here, the diameter of the specimen is
Substitute
Find the value of stress when the specimen is loaded with a 9 kip load using the relation:
Here, the load is P.
Substitute 9 kip for P and
The expression to find the strain in the longitudinal or axial direction
Here, the Young’s modulus of the aluminum is
Substitute
Find the strain in lateral direction
Here, the new diameter is
Substitute
Find the Poisson’s ratio
Substitute
Calculate the modulus of rigidity for the specimen
Substitute
Therefore, the shear modulus for an aluminum alloy is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Starting Out with Programming Logic and Design (5th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Degarmo's Materials And Processes In Manufacturing
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
Java How to Program, Early Objects (11th Edition) (Deitel: How to Program)
Thinking Like an Engineer: An Active Learning Approach (4th Edition)
Computer Science: An Overview (13th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
- A vertical true centrifugal casting process is used to produce bushings that are 250 mm long and 200 mm in outside diameter. If the rotational speed during solidification is 500 rev/min, determine the inside radii at the top and bottom of the bushing if R-2Rb. Take: 8-9.81 m/sarrow_forwardIn conventional drawing of a stainless steel wire, the original diameter D.-3mm, the area reduction at each die stand r-40%, and the proposed final diameter D₁-0.5mm, how many die stands are required to complete this process.arrow_forwardA vertical true centrifugal casting process is used to produce bushings that are 250 mm long and 200 mm in outside diameter. If the rotational speed during solidification is 500 rev/min, determine the inside radii at the top and bottom of the bushing if R-2Rb. Take: 8-9.81 m/sarrow_forward
- In non-continuous dieless drawing process for copper tube as shown in Fig. (1), take the following data: Do-20mm, to=3mm, D=12mm, ti/to=0.6 and vo-15mm/s. Calculate: (1) area reduction RA, (2) drawing velocity v. Knowing that: t₁: final thickness D₁ V. Fig. (1) Darrow_forward-6- 8 من 8 Mechanical vibration HW-prob-1 lecture 8 By: Lecturer Mohammed O. attea The 8-lb body is released from rest a distance xo to the right of the equilibrium position. Determine the displacement x as a function of time t, where t = 0 is the time of release. c=2.5 lb-sec/ft wwwww k-3 lb/in. 8 lb Prob. -2 Find the value of (c) if the system is critically damping. Prob-3 Find Meq and Ceq at point B, Drive eq. of motion for the system below. Ш H -7~ + 目 T T & T тт +arrow_forwardQ For the following plan of building foundation, Determine immediate settlement at points (A) and (B) knowing that: E,-25MPa, u=0.3, Depth of foundation (D) =1m, Depth of layer below base level of foundation (H)=10m. 3m 2m 100kPa A 2m 150kPa 5m 200kPa Barrow_forward
- W PE 2 43 R² 80 + 10 + kr³ Ø8=0 +0 R²+J+ kr200 R² + J-) + k r² = 0 kr20 kr20 8+ W₁ = = 0 R²+1) R²+J+) 4 lec 8.pdf Mechanical vibration lecture 6 By: Lecturer Mohammed C. Attea HW1 (Energy method) Find equation of motion and natural frequency for the system shown in fig. by energy method. m. Jo 000 HW2// For the system Fig below find 1-F.B.D 2Eq.of motion 8 wn 4-0 (1) -5- marrow_forwardThe hose supplying the cylinder operating the bucket of a large excavator has fluid at 1000 psi flowing at 5 gpm. What is theavailable power in the line?arrow_forwardQ For the following plan of building foundation, Determine immediate settlement at points (A) and (B) knowing that: E,-25MPa, u=0.3, Depth of foundation (D) =1m, Depth of layer below base level of foundation (H)=10m. 3m 2m 100kPa A 2m 150kPa 5m 200kPa Barrow_forward
- Given the following data for crack rocker mechanism. If θ2 = 4π/3 and ω2 = 1 rad/s, Determine all possible values of ω4 and ω3 analytically. The lengths of links are a = 2, b = 8, c = 7 and d = 9 in cm.arrow_forwardQ6] (20 Marks) Select the most suitable choice for the following statements: modo digi -1A 10 af5 1 -The copper-based alloy which is responded to age hardening is a) copper-nickel b) aluminum bronze c) copper - beryllium d) brass besincaluy 2- Highly elastic polymers may experience elongations to greater than.... b) 500% bromsia-P c) 1000%. d) 1200% 15m or -2 a)100% 3- The cooling rate of quenching the steel in saltwater will be ......the cooling rate of quenching ir c) faster than sold) none of them a) slower than 4- Adding of a) Cr b) the same as ...... Will lead to stabilize the b) Mo 10 austenite in steel. c) Nimble avolls 1d) Sized loloin nl 5- The adjacent linear chains of crosslinked polymers are joined one to another at various positic DIR... by.........bonds c) covalent noisqo gd) ionic lg 120M 6- For the ceramic with coordination number 6 the cation to anion radius ratio will be a) Van der Waals a) 0.155-0.225 a) linear b) hydrogen (b) 0.225-0.414 c) 0.414 0.732 ..polymers.…arrow_forwardExamine Notes: Attempt Six Questions Only. rever necessa , Q1] (20 Marks) Answer with true (T) or false (F), corrects the wrong phrases, and gives sho reasons for correct and corrected statements: 1- High chromium irons are basically grey cast irons alloyed with 12 to 30 % Cr. yous board-19qgo orT-1 2- The drawbacks of Al- Li alloys are their high young modulus and high density.&M 0) (0 3- Vulcanized rubbers are classified under thermoplastic polymers. 4- Diamond is a stable carbon polymorph at room temperature and atmospheric pressure. ( 5- The metallic ions of ceramic are called anions, and they are positively charged. yldgiH-S 69001(6arrow_forward
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
