
(a)
Interpretation:
The anticipated output of the circuit is to be stated.
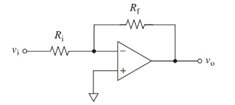
Concept introduction:
The sine wave voltage is a type of voltage that can be represented with the sine function. The average value of the sine wave over a complete cycle is zero, as both the positive and negative half the wave cancel out each other.
(b)
Interpretation:
The anticipated output of the circuit is to be stated.
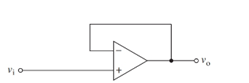
Concept introduction:
The sine wave voltage is a type of voltage that can be represented with the sine function. The average value of the sine wave over a complete cycle is zero, as both the positive and negative half the wave cancel out each other.
(c)
Interpretation:
The anticipated output of the circuit is to be stated.
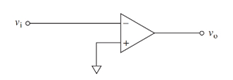
Concept introduction:
The sine wave voltage is a type of voltage that can be represented with the sine function. The average value of the sine wave over a complete cycle is zero, as both the positive and negative half the wave cancel out each other.
(d)
Interpretation:
The anticipated output of the circuit is to be stated.
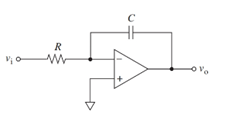
Concept introduction:
The sine wave voltage is a type of voltage that can be represented with the sine function. The average value of the sine wave over a complete cycle is zero, as both the positive and negative half the wave cancel out each other.
(e)
Interpretation:
The anticipated output of the circuit is to be stated.
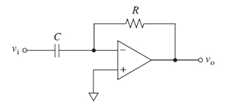
Concept introduction:
The sine wave voltage is a type of voltage that can be represented with the sine function. The average value of the sine wave over a complete cycle is zero, as both the positive and negative half the wave cancel out each other.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 3 Solutions
Principles of Instrumental Analysis
- Don't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardIndicate the correct option.a) Graphite conducts electricity, being an isotropic materialb) Graphite is not a conductor of electricityc) Both are falsearrow_forward(f) SO: Best Lewis Structure 3 e group geometry:_ shape/molecular geometry:, (g) CF2CF2 Best Lewis Structure polarity: e group arrangement:_ shape/molecular geometry: (h) (NH4)2SO4 Best Lewis Structure polarity: e group arrangement: shape/molecular geometry: polarity: Sketch (with angles): Sketch (with angles): Sketch (with angles):arrow_forward
- 1. Problem Set 3b Chem 141 For each of the following compounds draw the BEST Lewis Structure then sketch the molecule (showing bond angles). Identify (i) electron group geometry (ii) shape around EACH central atom (iii) whether the molecule is polar or non-polar (iv) (a) SeF4 Best Lewis Structure e group arrangement:_ shape/molecular geometry: polarity: (b) AsOBr3 Best Lewis Structure e group arrangement:_ shape/molecular geometry: polarity: Sketch (with angles): Sketch (with angles):arrow_forward(c) SOCI Best Lewis Structure 2 e group arrangement: shape/molecular geometry:_ (d) PCls Best Lewis Structure polarity: e group geometry:_ shape/molecular geometry:_ (e) Ba(BrO2): Best Lewis Structure polarity: e group arrangement: shape/molecular geometry: polarity: Sketch (with angles): Sketch (with angles): Sketch (with angles):arrow_forwardDon't used Ai solutionarrow_forward
 Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
