
Consider the simple circuit shown in Fig. 3.63. (a) Using KVL, derive the expressions
(b) Under what conditions is it possible to find that |v2| < |vs|?
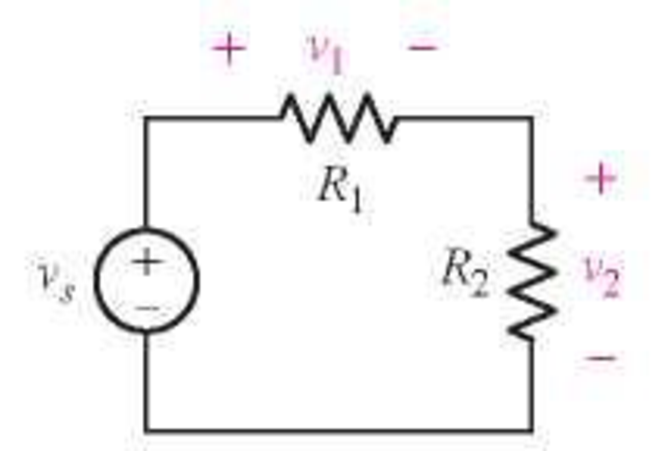
FIGURE 3.63
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 3 Solutions
Loose Leaf for Engineering Circuit Analysis Format: Loose-leaf
- The efficiency of a motor is always low when it operates at 10 percent of its nominal power rating. Explain.arrow_forwardA dc motor connected to a 240 V line pro- duces a mechanical output of 160 hp. Knowing that the losses are 12 kW, calculate the input power and the line current.arrow_forwardA 115 V dc generator delivers 120 A to a load. If the generator has an efficiency of 81 percent, calculate the mechanical power needed to drive it [hp].arrow_forward
- A machine having class B insulation attains a temperature of 208°C (by resistance) in a torrid ambient temperature of 180°C. a. What is the temperature rise? b. Is the machine running too hot and, if so, by how much?arrow_forward1 Name the losses in a dc motor. 2 What causes iron losses and how can they be reduced? -3 Explain why the temperature of a machine increases as the load increases.arrow_forward20. A tractor weighing 14 kN with a wheel base of 3m carries an 8 kN load on its rear wheel. Compute the maximum bending moment and shear when crossing a 4.5 span. Consider the load only at the wheels.arrow_forward
- A 110-V, three-phase, Y-connected, 8 pole, 48-slot, 6000-rpm, double-layer wound chronoun anı vonorotor boo 10 +1 urn or oilarrow_forward-7 Name some of the factors that contribute to the deterioration of organic insulators. -8 A motor is built with class H insulation. What maximum hot-spot temperature can it withstand?arrow_forwardCalculate the full-load current of a 250 hp, 230 V dc motor having an efficiency of 92 percent.arrow_forward
- Assignment #2 A 110-V, three-phase, Y-connected, 8 pole, 48-slot, 6000-rpm, double-layer wound, synchronous generator has 12 turns per coil. If one side of the coil is in slot 1, the other side is in slot 6. There are 4 parallel paths. When the generator delivers the rated load at a line voltage of 110 V, the voltage regulation is 5%. What is the flux per pole? Draw two consecutive phasegroups of one of the phase windings and connect them (a) in series and (b) in parallel showing the Start (S) and Finish (F) of both connections. (A separate drawing for each connection)arrow_forward3-4 Transmissiva Live of 120km has R= 0.2 ~2/15 X= 0.8 -2/km Y = 15H/6 5/km The line is supplies a load of 45 kV, SOMW, 0.8 lead p.f find sending voltage, Sending Current p.f. Sanding Voltage Regulation ⑨Voltage 5 Ⓒ charching coming! изу usy π cct लेarrow_forwardA (medium) single phase transmission line 100 km long has the following constants : Resistance/km = 0.25 Q; Susceptance/km = 14 × 10° siemen ; Reactance/km = 0.8 Receiving end line voltage = 66,000 V Assuming that the total capacitance of the line is localised at the receiving end alone, determine (i) the sending end current (ii) the sending end voltage (iii) regulation and (iv) supply power factor. The line is delivering 15,000 kW at 0.8 power factor Lead Draw the phasor diagram to illustrate your calculations.arrow_forward
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,





