
Loose Leaf for Engineering Circuit Analysis Format: Loose-leaf
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781259989452
Author: Hayt
Publisher: Mcgraw Hill Publishers
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 3, Problem 12E
For the circuit of Fig. 3.55 (which employs a model for the dc operation of a bipolar junction transistor biased in active region), IC is measured to be 1.5 mA. Calculate IB and IE.
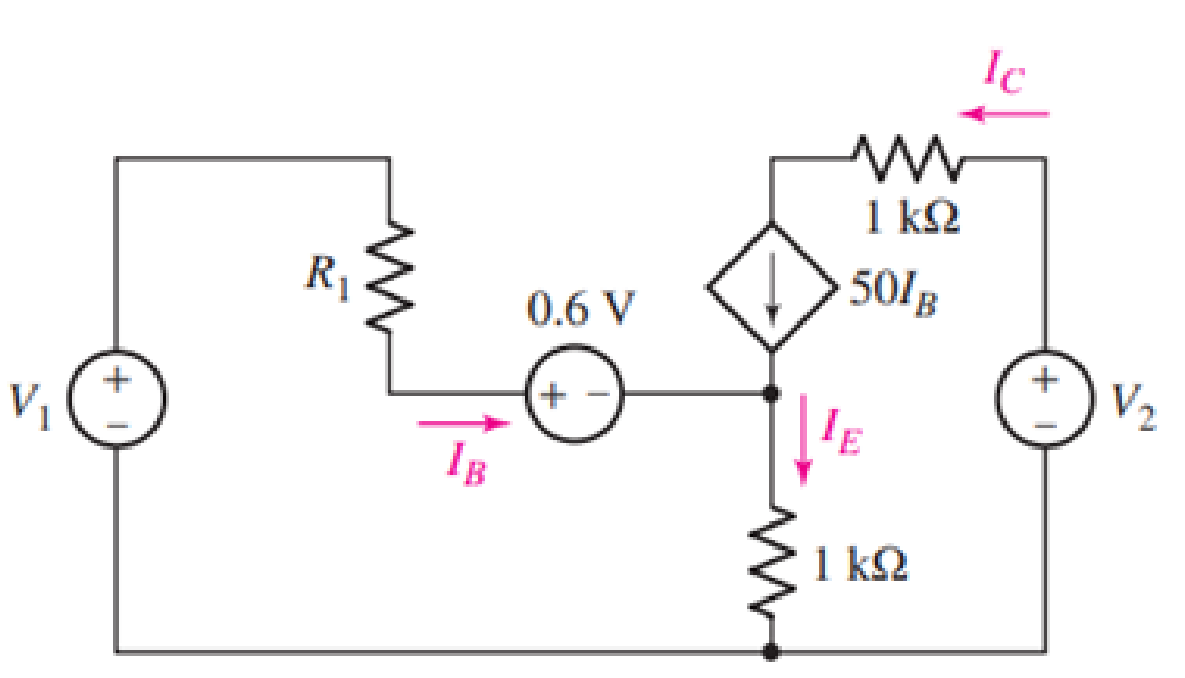
FIGURE 3.55
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
I need a drawing on how to connect the function generator, oscilliscope, and both multimeters. It is hard for me to follow text instructions. The function generator has a postive,common and negative. The oscilliscope has chanell A and B, both channels have a postive and a negative. I know you can provide text instruction but a little sketch would be very helpful thank you.
Don't use ai to answer I will report you answer
Q1/ A three phase, 500 kVA, 6600 V, 50 Hz, 6 pole, star connected synchronous motor has synchronous
impedance of J 70 ohm per phase at its normal rating, the motor is excited to give unity power factor at the input
terminals. Find
a) The rated current and power factor.
b) The emf behind the synchronous impedance.
c) The developed torque.
d) The pull out torque.
e) The increase in excitation which will just permit an increase of 30% of rated torque before pulling out of
synchronism.
(45 M.)
Chapter 3 Solutions
Loose Leaf for Engineering Circuit Analysis Format: Loose-leaf
Ch. 3.2 - 3.1 (a) Count the number of branches and nodes in...Ch. 3.3 - Determine ix and vx in the circuit of Fig. 3.7....Ch. 3.3 - For the circuit of Fig. 3.9, if vR1=1V, determine...Ch. 3.3 - Determine vx in the circuit of Fig. 3.11.Ch. 3.4 - In the circuit of Fig. 3.12b, vs1 = 120 V, vs2 =...Ch. 3.4 - 3.6 In the circuit of Fig. 3.14, find the power...Ch. 3.5 - Determine v in the circuit of Fig. 3.16.Ch. 3.5 - For the single-node-pair circuit of Fig. 3.18,...Ch. 3.6 - Determine the current i in the circuit of Fig....Ch. 3.6 - Determine the voltage v in the circuit of Fig....
Ch. 3.6 - Determine whether the circuit of Fig. 3.25...Ch. 3.7 - 3.12 Determine a single-value equivalent...Ch. 3.7 - 3.13 Determine i in the circuit of Fig. 3.29....Ch. 3.7 - Determine v in the circuit of Fig. 3.31 by first...Ch. 3.7 - 3.15 For the circuit of Fig. 3.33, calculate the...Ch. 3.8 - 3.16 Use voltage division to determine vx in the...Ch. 3.8 - In the circuit of Fig. 3.40, use resistance...Ch. 3 - Referring to the circuit depicted in Fig. 3.45,...Ch. 3 - Referring to the circuit depicted in Fig. 3.46,...Ch. 3 - For the circuit of Fig. 3.47: (a) Count the number...Ch. 3 - For the circuit of Fig. 3.47: (a) Count the number...Ch. 3 - Refer to the circuit of Fig. 3.48, and answer the...Ch. 3 - A local restaurant has a neon sign constructed...Ch. 3 - Referring to the single-node diagram of Fig. 3.50,...Ch. 3 - Determine the current labeled I in each of the...Ch. 3 - In the circuit shown in Fig. 3.52, the resistor...Ch. 3 - The circuit of Fig. 3.53 represents a system...Ch. 3 - In the circuit depicted in Fig. 3.54, ix is...Ch. 3 - For the circuit of Fig. 3.55 (which employs a...Ch. 3 - Determine the current labeled I3 in the circuit of...Ch. 3 - Study the circuit depicted in Fig. 3.57, and...Ch. 3 - Prob. 15ECh. 3 - For the circuit of Fig. 3.58: (a) Determine the...Ch. 3 - For each of the circuits in Fig. 3.59, determine...Ch. 3 - Use KVL to obtain a numerical value for the...Ch. 3 - Prob. 19ECh. 3 - In the circuit of Fig. 3.55, calculate the voltage...Ch. 3 - Determine the value of vx as labeled in the...Ch. 3 - Consider the simple circuit shown in Fig. 3.63....Ch. 3 - (a) Determine a numerical value for each current...Ch. 3 - The circuit shown in Fig. 3.65 includes a device...Ch. 3 - The circuit of Fig. 3.12b is constructed with the...Ch. 3 - Obtain a numerical value for the power absorbed by...Ch. 3 - Compute the power absorbed by each element of the...Ch. 3 - Compute the power absorbed by each element in the...Ch. 3 - Kirchhoffs laws apply whether or not Ohms law...Ch. 3 - Referring to the circuit of Fig. 3.70, (a)...Ch. 3 - Determine a value for the voltage v as labeled in...Ch. 3 - Referring to the circuit depicted in Fig. 3.72,...Ch. 3 - Determine the voltage v as labeled in Fig. 3.73,...Ch. 3 - Although drawn so that it may not appear obvious...Ch. 3 - Determine the numerical value for veq in Fig....Ch. 3 - Determine the numerical value for ieq in Fig....Ch. 3 - For the circuit presented in Fig. 3.76. determine...Ch. 3 - Determine the value of v1 required to obtain a...Ch. 3 - (a) For the circuit of Fig. 3.78, determine the...Ch. 3 - What value of IS in the circuit of Fig. 3.79 will...Ch. 3 - (a) Determine the values for IX and VY in the...Ch. 3 - Determine the equivalent resistance of each of the...Ch. 3 - For each network depicted in Fig. 3.82, determine...Ch. 3 - (a) Simplify the circuit of Fig. 3.83 as much as...Ch. 3 - (a) Simplify the circuit of Fig. 3.84, using...Ch. 3 - Making appropriate use of resistor combination...Ch. 3 - Calculate the voltage labeled vx in the circuit of...Ch. 3 - Determine the power absorbed by the 15 resistor...Ch. 3 - Calculate the equivalent resistance Req of the...Ch. 3 - Show how to combine four 100 resistors to obtain...Ch. 3 - Prob. 51ECh. 3 - Prob. 52ECh. 3 - Prob. 53ECh. 3 - Prob. 54ECh. 3 - Prob. 55ECh. 3 - Prob. 56ECh. 3 - Prob. 57ECh. 3 - Prob. 58ECh. 3 - Prob. 59ECh. 3 - Prob. 60ECh. 3 - With regard to the circuit shown in Fig. 3.98,...Ch. 3 - Delete the leftmost 10 resistor in the circuit of...Ch. 3 - Consider the seven-element circuit depicted in...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- can you fin Vds and Vgs of all transistors and specify te operating region off all transistors and prove it. 58V 5.8 V 1.8V M2 0.9V 22222 と A 4852 m 3 01 A Voy = 0.2 V V4)=0.SV λ=0.1 V-1arrow_forwardNeed a aolarrow_forward2 Find Inverse Fourier transform of F(jw) = 2w -16+w2, and plot the f(t).arrow_forward
- 5.25. Determine the corner frequency resulting from Cin in Fig. 5.47(d). For simplicity, assume C₁ is a short circuit. TVDD C₁ M2 RF Vin H w - Vout Cin M₁arrow_forwardIn the below circuit, find out the value of equivalent Thevenin's voltage and Thevenin's resistance at the terminal. 2000 0.25 A 400 2 800 2 0.1 Aarrow_forwardQ1: For the circuit shown in Figure-1, (a) Calculate the equivalent resistance of the circuit, RAB at the terminals A and B. [10] (b) When 50V dc source is switched at terminals A-B, solve for the voltage V₁ at the location shown. [10] 50V www 12Ω 10Ω 5Ω www www A + B 200 Figure-1 www 10Ω ww 25Ω 100arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Current Divider Rule; Author: Neso Academy;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hRU1mKWUehY;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY