
Concept explainers
A. (1)
Prepare
A. (1)
Explanation of Solution
Equivalents units for production
The activity of a processing department in terms of fully completed units is known as equivalent units. It includes the completed units of direct materials and conversion cost of beginning work in process, units completed and transferred out, and ending work in process.
Cost per unit
Total unit cost is the cost incurred by the company to produce one unit of product. The unit cost is calculated by dividing the units produced with the total cost.
Prepare the journal entry to record material charged to production for casting department of Incorporation AC as shown below:
| Account title and Explanation | Debit | Credit |
| work in process - Casting Department | $350,000 | |
| Materials - Alloy | $350,000 | |
| (To record the materials used in production) |
Table (1)
- • Work in process inventory – Casting department is a current asset, and increased. Therefore, debit work in process inventory – casting department account for $350,000.
- • Materials – Alloy is a current asset, and decreased. Therefore, credit materials – Alloy account for $350,000.
A. (2)
Prepare journal entry to record conversion costs charged to production for casting department of Incorporation AC.
A. (2)
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the journal entry to record conversion costs charged to production for casting department of Incorporation AC as shown below:
| Account title and Explanation | Debit | Credit |
| work in process - Casting Department | $49,600 | |
| Wages payable | $19,840 | |
| Factory | $29,760 | |
| (To record the conversion costs used in production) |
Table (2)
- • Work in process inventory – Casting department is a current asset, and increased. Therefore, debit work in process inventory – casting department account for $49,600.
- • Wages payable is a current liability and increased. Therefore, credit wages payable account for $19,840.
- • Factory overhead is a component of
stockholders’ equity and decreased it. Therefore, credit factory overhead account for $29,760.
Working note (1):
Calculate
A. (3)
Prepare journal entry to record transferred out to Machining department of Incorporation AC.
A. (3)
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the journal entry to record transferred out to Machining department of Incorporation AC as shown below:
| Account title and Explanation | Debit | Credit |
| Work in process – Machining Department | $402,684 | |
| Work in process – Casting department (5) | $402,684 | |
| (To record completed production transferred from casting department to Machining department ) |
Table (3)
- • Work in process inventory – Machining department is a current asset, and increased. Therefore, debit work in process inventory – machining department account for $402,684.
- • Work in process inventory – Casting department is a current asset, and decreased. Therefore, credit work in process inventory – Casting department account for $402,684.
Working note (2):
Calculate equivalent units for production of casting department as shown below:
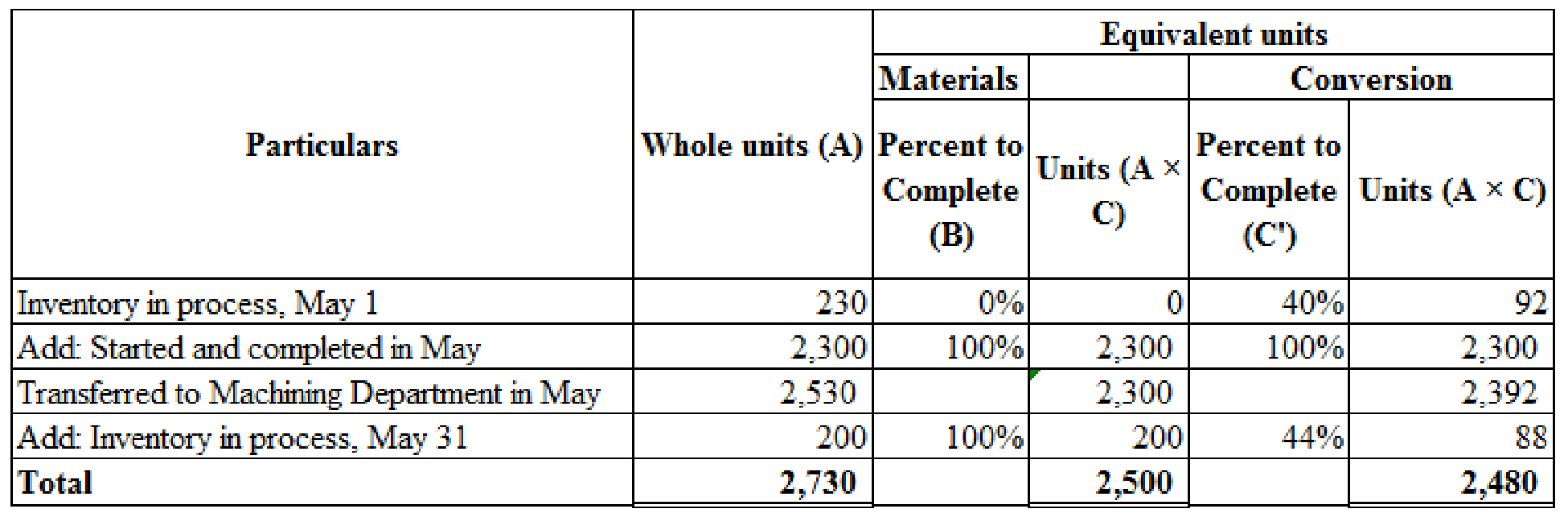
Figure (1)
Hints:
- 1. Opening work in process inventory units for conversion costs is calculated by multiplying whole units of opening work in process inventory with percent to complete.
- 2. A started and completed unit in May is calculated by deducting opening work in process inventory whole units from Transferred units to machining department.
- 3. Ending work in process inventory whole units is calculated by adding units produced during the period of May, and opening work in process inventory whole units and then deduct with transferred to machining department in May.
- 4. Ending work in process inventory units for conversion costs is calculated by multiplying whole units of ending work in process inventory with percentage completed during the period of May.
Working note (3):
Calculate equivalent cost per unit for direct materials as shown below:
Working note (4):
Calculate equivalent cost per unit for conversion costs as shown below:
Working note (5):
Calculate cost transferred out costs to Machining department as shown below:
| Particulars | Pounds (A) | Per pound (B) | Amount (A × B) |
| Cost of 2,530 transferred out pounds: | |||
| Materials | 230 | $132 | $30,360 |
| Conversion | 138 | $18 | $2,484 |
| Add: Cost to complete, May 1: | |||
| Materials | 0 | $140 | $0 |
| Conversion | 92 | $20 | $1,840 |
| Add: Pounds started and completed in May: | |||
| Materials | 2,300 | $140 | $322,000 |
| Conversion | 2,300 | $20 | $46,000 |
| Transferred costs to Machining Department | $402,684 |
Table (4)
B.
Calculate the ending work in process balance for casting department of Incorporation AC.
B.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the ending work in process balance for casting department of Incorporation AC as shown below:
| Particulars | Pounds (A) | Per pound (B) | Amount (A × B) |
| Ending work in process inventory: | |||
| Direct materials | 200 | $140 | $28,000 |
| Conversion costs | 88 | $20 | $1,760 |
| Total ending work in process inventory | $29,760 |
Table (5)
Therefore, ending work in process inventory balance for casting department of Incorporation AC is $29,760.
C.
Evaluate the changes in equivalent cost per unit of direct materials and conversion costs comparing with previous month.
C.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the changes in equivalent cost per unit of direct materials and conversion costs comparing with previous month as shown below:
| Particulars | Per pound |
| Cost per unit for May | $140 |
| Less: Cost per unit for April | $132 |
| Increase in Direct material cost per unit | $8 |
Table (6)
| Particulars | Per pound |
| Cost per unit for May | $20 |
| Less: Cost per unit for April | $18 |
| Increase in Conversion cost per unit | $2 |
Table (7)
Change in equivalent cost per unit for direct material is $8 per pound ($140 – $132). Hence, equivalent cost per unit for direct materials is increased by $8 per pound. A change in equivalent cost per unit for conversion cost is $2 per pound ($20 – $18). Hence, equivalent cost per unit for conversion cost is increased by $2 per pound. Incorporation AC might to scrutinize the reasons for increasing in direct material cost per unit and conversion cost per unit.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Managerial Accounting
 Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning



