
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The pro-R or pro-S hydrogen removed from citrate during the dehydration in step 2 of the citric acid cycle.
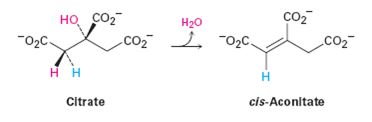
Concept introduction:
A molecule is said to be pro chiral, if it can be converted from achiral to chiral a single chemical step.
For instance, an unsymmetrical
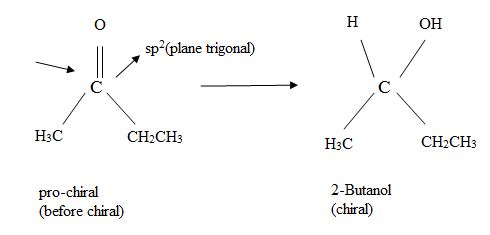
Which enantiomer of 2-butanol is produced depends on which face of the planar carbonyl undergoes reaction to distinguish between the possibilities, the stereo chemical description Re and Si (announced ‘ray’ and ‘sigh’) are used.
The concept of this designation is as follows: Rank the three groups attached to the trigonal, sp2 hybridized carbon according to the conventional Cahn-In gold-Prelog (CIP) system and imagine curved among from the highest to second highest, to third highest ranked substituents.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 29 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- The dehydration of citrate to yield cis-aconitate, a step in the citric acid cycle, involves the pro-R “arm’’ of citrate rather than the pro-S arm. Which of the following two products is formed?arrow_forwardLinoleic acid is shown below. What makes this fatty acid particularly susceptible to autoxidation? 1. The red CH bond has a low bond dissociation energy because it is doubly allylic. 2. The red CH bond has a high bond dissociation energy because it is doubly allylic. 3. The red CH bond is the most accessible to reaction with O2 because it is the least sterically crowded CH bond. 4. Both 2 and 3.arrow_forwardCan 4-methylcyclohexanoic acid be reduced by NABH4?arrow_forward
- ADH н он + NAD* + NADH + H* A B In the reaction scheme above, compound A is converted to compound B by alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH). Give the IUPAC name of the compound that is being oxidized. Answer:arrow_forwardOxaloacetic acid (or 2‑ketosuccinic acid) is a very important intermediate in metabolism. The compound is involved in the citric acid cycle for energy production within the cell. However, the compound is unstable and slowly decomposes spontaneously. Draw the decomposition products.arrow_forwardOne step in the gluconeogenesis pathway for the biosynthesis of glucose is the partial reduction of 3-phosphoglycerate to give glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate. The process occurs by phosphorylation with ATP to give 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate, reaction with a thiol group on the enzyme to give an enzyme-bound thioester, and reduction with NADH. -OPO3²- Enz-SH H-C-OH ATP CH₂OPO3²- 3-phosphoglycerate O 0-0--0 O ADP CH₂CH3 substitute for 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate C H-C-OH CH₂OPO3²- 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate O=C CH3-SH substitute for Enz-SH H H-C-OH | CH₂OPO3²- PO4³- O. S-Enz H-C-OH glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate Propose a structure for the first intermediates in the reaction of 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate with a thiol group on the enzyme to form an enzyme-bound thioester. Assume a basic group on the enzyme catalyzes the formation of this intermediate. To simplify the drawing process, substitute the structures below for the 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate and Enz-SH. CH₂OPO3²- (Enzyme-bound thioester) NADH/H* NAD*,…arrow_forward
- a. Draw a three-dimensional structure for the following steroid. b. What is the structure of the single stereoisomer formed by reduction of this ketone wrth H2, Pd-C? Explain why only one stereoisomer is formed.arrow_forwarda) The D-aldopentose A, C5H1005, reacts with HNO3 to yield an optically active aldaric acid B. Kiliani-Fischer chain extension of A produces a pair of D-aldohexoses C and D. C is converted by HNO3 to an optically active aldaric acid, but D is converted by HNO3 to an optically inactive aldaric acid. Write acyclic Fischer projections for A, B, C, D. b) Disaccharide E is a reducing sugar. It is hydrolyzed by an α-glycosidase enzyme, which means it contains an α- glycoside link. Treatment of E with Ag2O and excess Mel gives an octamethyl derivative F. Hydrolysis of F in dilute aqueous acid gives the pair of molecules shown below. Write the structures of E and F. (If the stereochemistry at a particular carbon is not determined by the above data, indicate this with a wavy line as shown below.) HO OMe OMe MeO MeO MOH OMe mOH OMe OMearrow_forwarda) The D-aldopentose A, C5H1005, reacts with HNO3 to yield an optically active aldaric acid B. Kiliani-Fischer chain extension of A produces a pair of D-aldohexoses C and D. C is converted by HNO3 to an optically active aldaric acid, but D is converted by HNO3 to an optically inactive aldaric acid. Write acyclic Fischer projections for A, B, C, D.arrow_forward
- Digitalis is a preparation made from the dried seeds and leaves of the purple foxglove, Digitalis purpurea, a plant native to southern and central Europe and cultivated in the United States. The preparation is a mixture of several active components, including digitalin. Digi- talis is used in medicine to increase the force of myocardial contraction and as a conduction depressant to decrease heart rate (the heart pumps more forcefully but less often). HC OH H,C H CH3 H. H. (a) Describe this glycosidic bond OCH, H A (b) Draw an open-chain Fischer projection of this monosaccharide CH3 H. (e) Describe this glycosidic bond OCH, HA H. HO H) H. OH НО (d) Name this monosaccharide unit H. OH Digitalinarrow_forwardDraw the organic products formed in attached reaction, and indicate the stereochemistry of products that contain stereogenic centers.arrow_forwardGive the major organic product that is formed when the primary hydroxyl group of the following monosaccharide undergo nucleophilic substitution reaction with acetic anhydridearrow_forward

 EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning



