
Concept explainers
A transmission tower is held by three guy wires attached to a pin at A and anchored by bolts at B, C, and D. If the tension in wire AC is 590 lb, determine the vertical force P exerted by the tower on the pin at
The vertical force P exerted by the tower on the pin at A , if the tension in the wire AC is 590 lb.
Answer to Problem 2.112P
The vertical force P exerted by the tower on the pin at A is 2000 lb_.
Explanation of Solution
Free body diagram at A is shown in figure1.
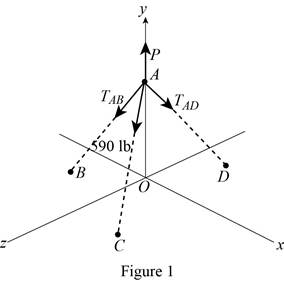
Here, TAB is the magnitude of tension in cable AB, TAC is the magnitude of tension in cable AC, TAD is the magnitude of tension in the cable AD , p is the magnitude of force P exerted by the tower on the pin at A.
The tension in the cable AB is 840 lb.
The sketch of plate supported by three cables is shown in figure2.
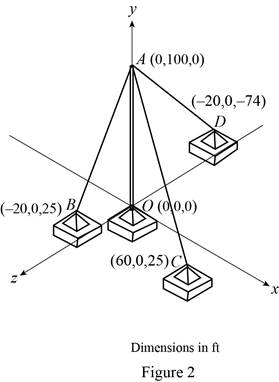
Let TAB, TAC,TAD and P are the tension vector in cable AB, AC, AD and force exerted by the tower at A in the upward direction
Let i , j and k are the unit vectors along the of x,y and z direction.
Write the equation of vector distance AB.
→AB=(x2−x1)i+(y2−y1)j+(z2−z1)k (I)
Here, →AB is the vector distance of the cable AB, the variables x1,y1 and z1 are the coordinates of point A and x2,y2 and z2 are the coordinates of point B.
Write the vector distance of the cable AC.
→AC=(x3−x1)i+(y3−y1)j+(z3−z1)k (II)
Here, →AC is the vector distance of the cable AC, the variables x1,y1 and z1 are the coordinates of point A and x3,y3 and z3 are the coordinates of point C.
Write the vector distance of the cable AD.
→AD=(x4−x1)i+(y4−y1)j+(z4−z1)k (III)
Here, →AD is the vector distance of the cable AD, the variables x1,y1 and z1 are the coordinates of point A and x4,y4 and z4 are the coordinates of point D.
Write the equation of tension in the cable AB.
TAB=λABTAB (IV)
Here, TAB is the tension in the cable AB , TAB is the magnitude of the tension in the cable AB and λAB is the unit vector in the direction of AB.
Write the equation of λAB.
λAB=→ABAB (V)
Write the equation of tension in the cable AC.
TAC=λACTAC (VI)
Here, TAC is the tension in the cable AC , TAC is the magnitude of the tension in the cable AC and λAC is the unit vector in the direction of AC.
Write the equation of λAC.
λAC=→ACAC (VII)
Write the equation of tension in the cable AD.
TAD=λADTAD (VIII)
Here, TAD is the tension in the cable AD , TAD is the magnitude of the tension in the cable AD and λAD is the unit vector in the direction of AD.
Write the equation of λAD.
λAD=→ADAD (IX)
Write the equation of force exerting at point A along y direction.
P=P j (X)
Here, P is the force exerted at by the tower at pin at point A.
Write the equilibrium condition for the forces at A.
∑F=0
Here, F is the force
The above equation implies that at equilibrium, total force acting on the cable at A is zero.
Refer figure 2 and write the equation of equilibrium of forces at A.
TAB+TAC+TAD+P=0
Conclusion:
Substitute 0 ft for x1 , 100 ft for y1 , 0 ft for z1 , −20 ft for x2 , 0 ft for y2 and 25 ft for z2 in equation (I) to get →AB.
→AB=−(20 ft)i−(100 ft)j+(25 ft)k
Calculate the magnitude of →AB.
AB=√(−20 ft)2+(−100 ft)2+(25 ft)2= 105 ft
Substitute 0 ft for x1 , 100 ft for y1 , 0 ft for z1 , 60 ft for x3 , 0 ft for y3 and 25 ft for z3 in equation (II) to get →AC.
→AC=(60 ft)i−(100 ft)j+(18 ft)k
Calculate the magnitude of →AC.
AC=√(60 ft)2+(−100 ft)2+(18 ft)2=118 ft
Substitute 0 ft for x1 , 100 ft for y1 , 0 ft for z1 , −20 ft for x4 , 0 ft for y4 and −74 ft for z4 in equation (III) to get →AD.
→AD=(−20 ft)i−(100 ft)j−(74 ft)k
Calculate the magnitude of →AD.
AD=√(−20 ft)2+(−100 ft)2+(−74 ft)2=126 ft
Substitute −(20 ft)i−(100 ft)j+(25 ft)k for →AB and 105 ft for AB in equation (V) to get λAB.
λAB=−(20 ft)i−(100 ft)j+(25 ft)k105 ft=−421i−2021j+521k
Substitute −421i−2021j+521k for λAB in equation (IV) to get TAB.
TAB=(−421i−2021j+521k)TAB
Substitute (60 ft)i−(100 ft)j+(18 ft)k for →AC and 118 ft for AC in equation
(VII) to get λAC.
λAC=(60 ft)i−(100 ft)j+(18 ft)k118 ft=3059i−5059j+959k
Substitute 3059i−5059j+959k for λAC in equation (VI) to get TAC.
TAC=(3059i−5059j+959k)TAC
Substitute (−20 ft)i−(100 ft)j−(74 ft)k for →AD and 126 ft for AD in equation (IX) to get λAD.
λAD=(−20 ft)i−(100 ft)j−(74 ft)k126 ft=−1063i−5063j−3763k
Substitute −1063i−5063j−3763k for λAD in equation (VIII) to get TAD.
TAD=(−1063i−5063j−3763k)TAD
Substitute (−421i−2021j+521k)TAB for TAB , (3059i−5059j+959k)TAC for TAC , (−1063i−5063j−3763k)TAD, Pj for P in the in equation (XI) to get force P exerted at point A.
(−421i−2021j+521k)TAB+(3059i−5059j+959k)TAC+(−1063i−5063j−3763k)TAD+Pj=0(−421TAB+3059TAC−1063TAD)i+(−2021TAB−5059TAC−5063TAD+P)j+(+521TAB+959TAC−3763TAD)k=0
Since total force is zero. Equate force along each direction as zero.
−421TAB+3059TAC−1063TAD=0 (XII)
−2021TAB−5059TAC−5063TAD+P=0 (XIII)
+521TAB+959TAC−3763TAD= 0 (XIV)
Substitute 590 lb for TAC in equation (XII) and (XIV) to modify the equation.
−421TAB+3059(590 lb)−1063TAD=0
−421TAB+300 lb−1063TAD=0 (XV)
+521TAB+959(590 lb)−3763TAD= 0
+521TAB+90 lb−3763TAD= 0 (XVI)
Multiply equation (XV) by 5 and XVI by −10 and add to get TAC.
−2021TAB+1500 lb−5063TAD+2021TAB+360 lb−14863TAD= 01860 lb−19863TAD= 0TAD= 591.82 lb
Substitute 591.82 lb for TAD in equation (XVI) to get TAB.
+521TAB+90 lb−3763(591.82 lb)= 0TAB= 1081.82 lb
Substitute 1081.82 lb for TAB, 590 lb for TAC and 591.82 lb for TAD in equation (XIII) to get P.
−2021(1081.82 lb)−5059(590 lb)−5063(591.82 lb)+P=0P= 2000 lb
Therefore, the force P exerted by the tower at the pin positioned at A is equal to 2000 lb_.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: STATICS
- The sketch below gives some details of the human heart at rest. What is the total power requirement (work/time) for an artificial heart pump if we use a safety factor of 5 to allow for inefficiencies, the need to operate the heart under stress, etc.? Assume blood has the properties of water. p pressure above atmosphere blood going to the lungs for a fresh charge of oxygen p = 2.9 kPa 25v pulmonary artery d = 25mm fresh oxygenated blood from the lungs p = 1.0 kPa vena cava d=30mm right auricle pulmonary vein, d = 28mm aorta, d=20mm spent blood returning from left auricle the body p = 0.66 kPa right left ventricle ventricle blood to feed the body, p 13 kPa normal blood flow = 90 ml/sarrow_forward4- A horizontal Venturi meter is used to measure the flow rate of water through the piping system of 20 cm I.D, where the diameter of throat in the meter is d₂ = 10 cm. The pressure at inlet is 17.658 N/cm2 gauge and the vacuum pressure of 35 cm Hg at throat. Find the discharge of water. Take Cd = 0.98.arrow_forward10arrow_forward
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
