
Concept explainers
Two forces P and Q are applied to the lid of a storage bin as shown. Knowing that P = 48 N and Q = 60 N, determine by trigonometry the magnitude and direction of the resultant of the two forces.
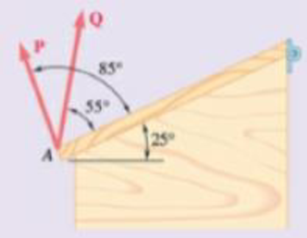
Fig. P2.127
The direction and magnitude of the resultant of two forces.
Answer to Problem 2.127RP
The magnitude of the resultant of two forces is R=104.4 N_, and the direction is ϕ=86.7°_.
Explanation of Solution
The sketch of the triangle formed by the two forces P, Q, and resultant R is shown in figure 1.
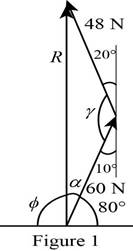
Write the expression for the total angle of a triangle
α+ϕ+γ=180° (I)
Here, α, ϕ, and γ are the three angles of a triangle.
Write the expression for the angle ϕ formed at the base
ϕ=180°−α−80° (II)
The sum of the three angles of a triangle is equal to 180°.
Write the expression for cosine law for finding R in figure
R2=A2+B2−2(ABcosγ) (III)
Here, R is the hypotenuse which is representing resultant of two forces P and Q
Write the expression for law of Sines
Asinα=Bsinϕ=Rsinγ (IV)
Here, A, B, and C are the side lengths of triangle.
Conclusion:
Use equation (I) to obtain the angle γ as shown in figure
γ=180°−(20°+10°)=150°
Substitute 48 N for A, 60 N for B, and 150° for γ to obtain resultant force R
R2=(48 N)2+(60 N)2−2(48 N×60 N×cos150°)=10892.3R=104.366 N
Use the law of sines to find the angle α.
Substitute 48 N for A, 104.366 N for R, and 150° for γ in equation (III) to find α
48 Nsinα=104.366 Nsin150° Nsinα=48 N×sin150° 104.366 N=0.22996α=13.2947°
Substitute 13.2947° for α in equation (II)
ϕ=180°−13.2947°−80°=86.705°
Therefore the magnitude of resultant force is R=104.4 N_, and the direction is ϕ=86.7°_.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: STATICS
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Java: An Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming (8th Edition)
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals and Applications
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
- Calculate the bending moment at the point D on the beam below. Take F=79 and remember that this quantity is to be used to calculate both forces and lengths. 15F 30F A сarrow_forwardShow work on how to obtain P2 and T2. If using any table, please refer to it. If applying interpolation method, please show the work.arrow_forwardcast-iron roller FIGURE P11-3 Shaft Design for Problems 11-17 Chapter 11 BEARINGS AND LUBRICATION 677 gear key P assume bearings act as simple supports 11-18 Problem 7-18 determined the half-width of the contact patch for a 1.575-in-dia steel cylinder, 9.843 in long, rolled against a flat aluminum plate with 900 lb of force to be 0.0064 in. If the cylinder rolls at 800 rpm, determine its lubrication condition with ISO VG 1000 oil at 200°F. R₁ = 64 μin (cylinder); R₁ = 32 μin (plate). 11-19 The shaft shown in Figure P11-4 was designed in Problem 10-19. For the data in the row(s) assigned from Table P11-1, and the corresponding diameter of shaft found in Problem 10-19, design suitable bearings to support the load for at least 5E8 cycles at 1200 rpm. State all assumptions. (a) (b) Using hydrodynamically lubricated bronze sleeve bearings with ON = 40, 1/ d=0.80, and a clearance ratio of 0.002 5. Using deep-groove ball bearings for a 10% failure rate. *11-20 Problem 7-20 determined the…arrow_forward
- Calculate the shear force at the point D on the beam below. Take F=19 and remember that this quantity is to be used to calculate both forces and lengths. 15F A сarrow_forward"II-1 The shaft shown in Figure P11-I was designed in Problem 10-1. For the data in the row(s) assigned from Table P11-1, and the corresponding diameter of shaft found in Problem 10-1, design suitable bearings to support the load for at least 7E7 cycles at 1500 rpm. State all assumptions. (a) Using hydrodynamically lubricated bronze sleeve bearings with Ox = 20, 1/d=1.25, and a clearance ratio of 0.001 5. assume bearings act as simple supports FIGURE P11-1 Shaft Design for Problem 11-1 11-2 The shaft shown in Figure P11-2 was designed in Problem 10-2. For the data in the row(s) assigned from Table P11-1, and the corresponding diameter of shaft found in Problem 10-2, design suitable bearings to support the load for at least 3E8 cycles at 2.500 rpm. State all assumptions. (a) Using hydrodynamically lubricated bronze sleeve bearings with ON=30, 1/d=1.0, and a clearance ratio of 0.002. FIGURE P11-2 Shaft Design for Problem 11-2 Table P11-1 Data for Problems assume bearings act as simple…arrow_forwardFor the frame below, calculate the shear force at point Q. Take P=13 and note that this value is used for both the loads and the lengths of the members of the frame. 1 A Q ✗ 19 KBP 2.5P- B R C 45 degrees ✗ 1 .2P- 4PhN -P→arrow_forward
- Calculate the Bending Moment at point D in the frame below. Leave your answer in Nm (newton-metres) J J A 2m 2m <2m х D 不 1m X E 5m 325 Nm 4x 400N/marrow_forwardIn the beam below, calculate the shear force at point A. Take L=78 and remember that both the loads and the dimensions are expressed in terms of L. 143 1 DX A - Li 4 LhN 14LRN/m Х B 22 3 L.arrow_forwardCalculate the Shear Force at Point F on the beam below. Keep your answer in Newtons and make shear force positive to the right. A х 2m <2m E D 5m 1m Хт 325N1m 400N/m 8arrow_forward
- The normal force at C on the beam below is equal to: A ShN C X 15h N 8 ○ OkN 2.5kN 10kN ○ 12.5kN 1m Im 1m 1m;arrow_forwardCalculate the y coordinate of the of the centroid of the shape below. Take A= 18.5 8 6A 4A X 6Aarrow_forwardIn MATLAB write out a program to integrate the equations of motion of a rigid body. The inertia matrix is given by I = [125 0 0; 0 100 0; 0 0 75] which is a diagonal, where diag operator provides a matrix with given elements placed on its diagonal. Consider three cases where the body rotates 1 rad/sec about each principal axis. Integrate the resulting motion and study the angular rates and the resulting attitude (use any attitude coordinates). For each principal axis case, assume first that a pure spin about the principal axis is performed, and then repeat the simulation where a small 0.1 rad/sec motion is present about another principal axis. Discuss the stability of each motion. The code should produce a total of 6 simulations results when it is ran.arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





