
Concept explainers
a)

Interpretation:
Whether trimethylacetaldehyde undergoes aldol self-condensation reaction or not is to be stated. The product formed, if the reaction is successful, is also to be shown.
Concept introduction:
To state:
Whether trimethylacetaldehyde undergoes aldol self-condensation reaction or not.
To show:
The product formed, if the reaction is successful.
Answer to Problem 48AP
Trimethylacetaldehyde does not undergo aldol self-condensation reaction. The reaction is not successful.
Explanation of Solution
The requirement of aldol reaction is the aldehyde or ketone should have α-hydrogen atom. Trimethylacetaldehyde does not possess α-hydrogen atom. Hence the reaction is not successful.
Trimethylacetaldehyde does not undergo aldol self-condensation reaction. The reaction is not successful.
b)
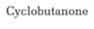
Interpretation:
Whether cyclobutanone undergoes aldol self-condensation reaction or not is to be stated. The product formed, if the reaction is successful, is also to be shown.
Concept introduction:
Aldehydes and ketones with α-hydrogen undergo a base catalyzed carbonyl condensation reaction in aldol condensation. In this reaction two molecules of the reactant combine by forming a bond between α-carbon of one molecule and the carbonyl carbon within the same molecule or of the second molecule.
To state:
Whether cyclobutanone undergoes aldol self-condensation reaction or not.
To show:
The product formed, if the reaction is successful.
Answer to Problem 48AP
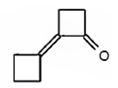
Cyclobutanone undergoes aldol self-condensation reaction. The product formed is
Explanation of Solution
The requirement of aldol reaction is the aldehyde or ketone should have α-hydrogen atom. Cyclobutanone has α-hydrogen atoms. Hence the reaction is successful. Two molecules of cyclobutanone condense in the presence of a base to yield an aldol which dehydrates to give α, β-unsaturated ketone.
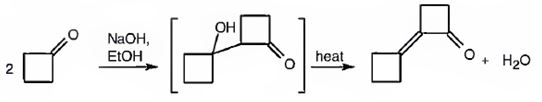
Cyclobutanone undergoes aldol self-condensation reaction. The product formed is
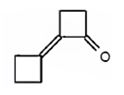
c)
Interpretation:
Whether benzophenone undergoes aldol self-condensation reaction or not is to be stated. The product formed, if the reaction is successful, is also to be shown.
Concept introduction:
Aldehydes and ketones with α-hydrogen undergo a base catalyzed carbonyl condensation reaction in aldol condensation. In this reaction two molecules of the reactant combine by forming a bond between α-carbon of one molecule and the carbonyl carbon within the same molecule or of the second molecule.
To state:
Whether benzophenone undergoes aldol self-condensation reaction or not.
To show:
The product formed, if the reaction is successful.
Answer to Problem 48AP
Benzophenone does not undergo self aldol condensation reaction. The reaction is not successful.
Explanation of Solution
The requirement of aldol reaction is the aldehyde or ketone should have α-hydrogen atom. Benzophenone does not possess α-hydrogen atom. Hence the reaction is not successful.
Benzophenone does not undergo self aldol condensation reaction. Theb reaction is not successful.
d)

Interpretation:
Whether 3-pentanone undergoes aldol self-condensation reaction or not is to be stated. The product formed, if the reaction is successful, is also to be shown.
Concept introduction:
Aldehydes and ketones with α-hydrogen undergo a base catalyzed carbonyl condensation reaction in aldol condensation. In this reaction two molecules of the reactant combine by forming a bond between α-carbon of one molecule and the carbonyl carbon within the same molecule or of the second molecule.
To state:
Whether 3-pentanone undergoes aldol self-condensation reaction or not.
To show:
The product formed, if the reaction is successful.
Answer to Problem 48AP
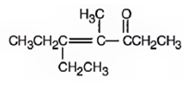
3-pentanone undergoes aldol self-condensation reaction. The product formed is
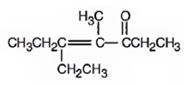
Explanation of Solution
The requirement of aldol reaction is the aldehyde or ketone should have α-hydrogen atom. 3-Pentanone has α-hydrogen atom. Hence the reaction is successful. Two molecules of 3-pentanone condense in the presence of a base to yield an aldol which dehydrates to give the α, β-unsaturated ketone.
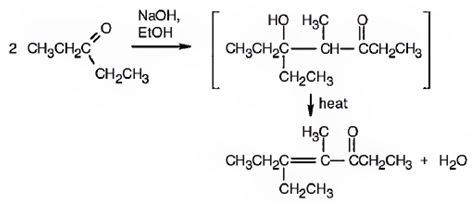
3-pentanone undergoes aldol self-condensation reaction. The product formed is
e)

Interpretation:
Whether decanal undergoes aldol self-condensation reaction or not is to be stated. The product formed, if the reaction is successful, is also to be shown.
Concept introduction:
Aldehydes and ketones with α-hydrogen undergo a base catalyzed carbonyl condensation reaction in aldol condensation. In this reaction two molecules of the reactant combine by forming a bond between α-carbon of one molecule and the carbonyl carbon within the same molecule or of the second molecule.
To state:
Whether decanal undergoes aldol self-condensation reaction or not.
To show:
The product formed, if the reaction is successful.
Answer to Problem 48AP
Decanal undergoes aldol self-condensation reaction. The product formed is
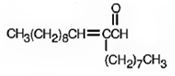
Explanation of Solution
The requirement of aldol reaction is the aldehyde or ketone should have α-hydrogen atom. Decanal has α-hydrogen atom. Hence the reaction is successful. Two molecules of decanal condense in the presence of a base to yield an aldol which dehydrates to give an α, β-unsaturated aldehyde.
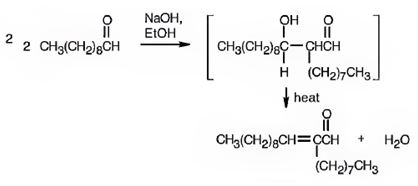
Decanal undergoes aldol self-condensation reaction. The product formed is
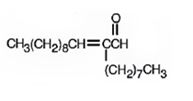
f)
Interpretation:
Whether 3-phenyl-2-propenal undergoes aldol self-condensation reaction or not is to be stated. The product formed, if the reaction is successful, is also to be shown.
Concept introduction:
Aldehydes and ketones with α-hydrogen undergo a base catalyzed carbonyl condensation reaction in aldol condensation. In this reaction two molecules of the reactant combine by forming a bond between α-carbon of one molecule and the carbonyl carbon within the same molecule or of the second molecule.
To state:
Whether 3-phenyl-2-propenal undergoes aldol self-condensation reaction or not.
To show:
The product formed, if the reaction is successful.
Answer to Problem 48AP
3-Phenyl-2-propenal does not undergo aldol self-condensation reaction. The reaction is not successful.
Explanation of Solution
The requirement of aldol reaction is the aldehyde or ketone should have α-hydrogen atom. 3-Phenyl-2-propenal does not possess α-hydrogen atom. Hence the reaction is not successful.
3-Phenyl-2-propenal does not undergo aldol self-condensation reaction. The reaction is not successful.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 23 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Pleasssssseeee solve this question in cheeemsirty, thankss sirarrow_forwardThe Ksp for lead iodide ( Pbl₂) is 1.4 × 10-8. Calculate the solubility of lead iodide in each of the following. a. water Solubility = mol/L b. 0.17 M Pb(NO3)2 Solubility = c. 0.017 M NaI mol/L Solubility = mol/Larrow_forwardPleasssssseeee solve this question in cheeemsirty, thankss sirarrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

