
(a)
Interpretation:
The pH at which the zwitter ion [Z] and the cationic form [C+] of the amino acid alanine become equal needs to be calculated.
Concept introduction:
- Amino acids are organic compounds composed of C, H, N and O. The two main
functional groups include the amino −NH2 and carboxyl −COOH group in addition to a side chain each with a characteristic pKa value. - Isoelectric point (pI) is the pH at which the net charge on the amino acid is zero. For amino acid with one −COOH and one −NH2, the pI is given as:
Answer to Problem 30QAP
pH = 2.29
Explanation of Solution
The given amino acid is alanine which has the following structure:
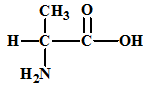
The structures of the respective cationic form (C+), zwitter ion (Z) and the anionic form (A-) are:
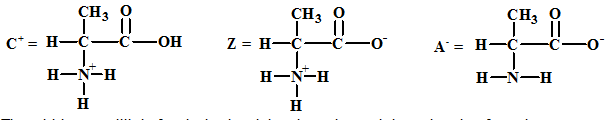
The acid-base equilibria for alanine involving the cation and the zwitter ion forms is:
(b)
Interpretation:
The pH at which the zwitter ion [Z] and the anionic form [A-] of the amino acid alanine become equal needs to be calculated
Concept introduction:
- Amino acids are organic compounds composed of C, H, N and O. The two main functional groups include the amino −NH2 and carboxyl −COOH group in addition to a side chain each with a characteristic pKa value.
- Isoelectric point (pI) is the pH at which the net charge on the amino acid is zero. For amino acid with one −COOH and one −NH2, the pI is given as:
Answer to Problem 30QAP
pH = 9.74
Explanation of Solution
The given amino acid is alanine which has the following structure:
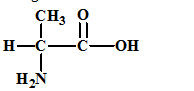
The structures of the respective cationic form (C+), zwitter ion (Z) and the anionic form (A-) are:
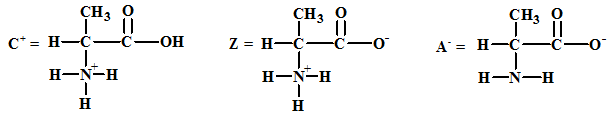
The acid-base equilibria for alanine involving the anion and the zwitter ion forms is:
(c)
Interpretation:
The pH at the isoelectric point needs to be calculated
Concept introduction:
- Amino acids are organic compounds composed of C, H, N and O. The two main functional groups include the amino −NH2 and carboxyl −COOH group in addition to a side chain each with a characteristic pKa value.
- Isoelectric point (pI) is the pH at which the net charge on the amino acid is zero. For amino acid with one −COOH and one −NH2, the pI is given as:
Answer to Problem 30QAP
pH = 6.02
Explanation of Solution
For alanine at the isoelectric point:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 23 Solutions
Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
- A weak acid, HA, has a pKa = 6.2. If a solution of NaA(aq) is prepared, what does the pH of the solution need to be adjusted to in order to achieve the following ratios of deprotonated to protonated species? 1) [A-] / [HA] = 0.01 2) [A-] / [HA] = 10 3) [A-] / [HA] = 1 4) [A-] / [HA] = 106 Note: NaA is the sodium salt of , the conjugate base of HA. Assume NaA completely dissociates in water.arrow_forwardWrite the equilibrium constant expression of the reaction.arrow_forwardPredict the products from the following chemical reactions. (a) HNO3 + Ba(OH)2 ⟶ (b) CaCl2 + CsOH ⟶ (c) Ammonium Phosphate + Magnesium Sulfate ⟶arrow_forward
- A monoprotic weak acid,HA, dissociates in water according to the reaction HA(aq)+H2O equilibrium arrows H3O+(aq)+A-(aq) The equilibrium concentrations of the reactants and products are [HA]=0.230M, [H3O+]=4.00•10^-4 and [A-]=4.00•10^-4. Calculate the Ka value for the acid HA.arrow_forwardIdentify one of the conjugate acid-base pairs in the reactionarrow_forwardUsing the law of mass action, write the equilibrium expression for each of the following reactions. (a) Zn(s) + 2 Ag*(aq) 2 Zn²*(aq) + 2 Ag(s) (b) VO-(aq) + H2O(€)2 VO3(OH)²-(aq) + OH¯(aq) (c) 2 As(OH);¯(aq) + 6 CO2(g) 6 HCO, (aq) + 3 H20(€) 2 As2O3(s) +arrow_forward
- 56. Write balanced net ionic equations for the following reactions in basic medium. (a) Ca(s) + VO,3-(aq)→C22+(aq) + V²+(aq) (b) C,H4(g) + BiO³-(aq) → CO2(g) + Bi³+(aq) (c) PbO2(s) + H,O→02(g) + Pb²+ (b) IO,-(aq) + CI-(aq) → Cl2(g) + I;¬(aq)arrow_forwardWhat are the speactor ions in the following reaction?arrow_forwardWrite short hand notation for each reaction: (a) Fe + Ag+ → Fe2+ + Ag (b) VO2+ + O2 + H2O(l) → VO2+ + H+arrow_forward
- Write the expression Kc for the following reactions. (a) Fe2+(aq) + Ce4+(aq) ⇋ Fe3+(aq) + Ce3+(aq) (b) CaCO3(s) ⇋ CaO(s) + CO3(g)arrow_forwardThe pH of a 0.10 M solution of Ni(NO3)2 is 5.0. Calculate the acid ionization constant of Ni(H 2O) 62+(aq).arrow_forwardA monoprotic weak acid, HA, dissociates in water according to the reaction HA(aq) + H,O(1) =H,0*(aq) + A¯(aq) The equilibrium concentrations of the reactants and products are [HA] = 0.140 M, [H,O*] = 4.00 × 10-4 M, and [A = 4.00 x 10-4 M. Calculate the Ka value for the acid HA. K =arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning

