
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The principal organic product expected when
Concept introduction:
The
Answer to Problem 22.55AP
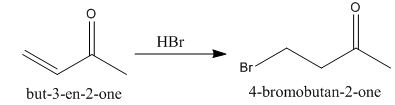
The principal organic product obtained when
Explanation of Solution
The principal organic product obtained when

Figure 1
In this reaction, the addition of
The principal organic product obtained when
(b)
Interpretation:
The principal organic product expected when
Concept introduction:
The
Answer to Problem 22.55AP
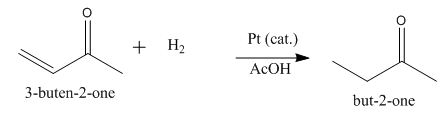
The principal organic product obtained when
Explanation of Solution
The principal organic product obtained when

Figure 2
In this reaction, the addition of
The principal organic product obtained when
(c)
Interpretation:
The principal organic product expected when
Concept introduction:
The
Answer to Problem 22.55AP
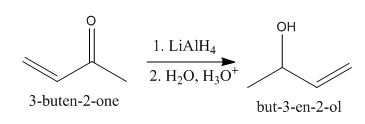
The principal organic product obtained when
Explanation of Solution
The principal organic product obtained when

Figure 3
In this reaction, the addition of
The principal organic product obtained when
(d)
Interpretation:
The principal organic product expected when
Concept introduction:
The
Answer to Problem 22.55AP
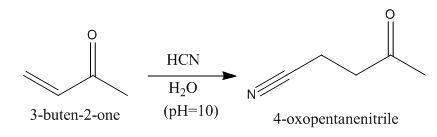
The principal organic product obtained when
Explanation of Solution
The principal organic product obtained when

Figure 4
In this reaction, the addition of
In the product, hydrogen will add to that carbon of the double bond that has the least number of hydrogens.
The principal organic product obtained when
(e)
Interpretation:
The principal organic product expected when
Concept introduction:
The
Answer to Problem 22.55AP
The principal organic product obtained when
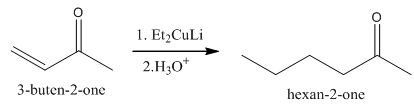
Explanation of Solution
The principal organic product obtained when

Figure 5
The reaction of
The principal organic product obtained when
(f)
Interpretation:
The principal organic product expected when
Concept introduction:
The
Answer to Problem 22.55AP
The principal organic product obtained when
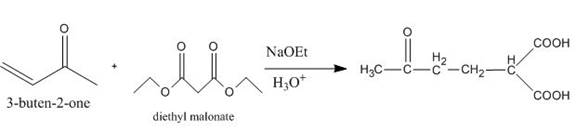
Explanation of Solution
The principal organic product obtained when

Figure 6
The reaction of
The principal organic product obtained when
(g)
Interpretation:
The principal organic product expected when
Concept introduction:
The
Answer to Problem 22.55AP
The principal organic product obtained when
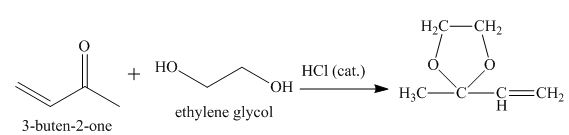
Explanation of Solution
The principal organic product obtained when

Figure 7
The reaction of
The principal organic product obtained when
(h)
Interpretation:
The principal organic product expected when
Concept introduction:
Diels-Alder reaction is a cycloaddition reaction. The reaction is known as a
Answer to Problem 22.55AP
The principal organic product obtained when
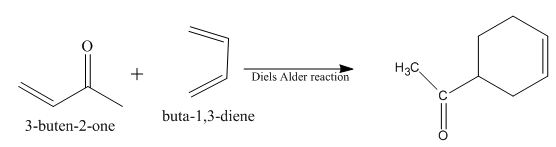
Explanation of Solution
The principal organic product obtained when

Figure 8
The reaction of
The principal organic product obtained when
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 22 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
