
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Electronic configuration of the following metals has to be written –
Concept Introduction:
Electronic configuration of an atom represents the arrangement of electrons in various energy levels. The electrons are arranged in increasing order of energy levels according to Aufbau principle. It is pictorially represented as –
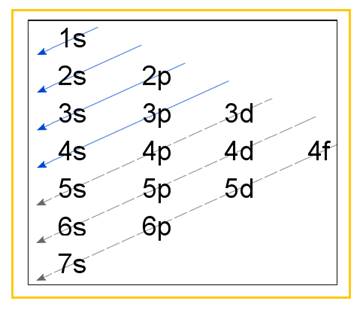
Figure 1
The terms
(a)
Answer to Problem 22E
Electronic configuration of
Explanation of Solution
The above electronic configuration corresponds to that of Argon till
(b)
Interpretation:
Electronic configuration of the following metals has to be written –
Concept Introduction:
Electronic configuration of an atom represents the arrangement of electrons in various energy levels. The electrons are arranged in increasing order of energy levels according to Aufbau principle. It is pictorially represented as –

Figure 1
The terms
(b)
Answer to Problem 22E
Electronic configuration of
Explanation of Solution
Atomic number of Cadmium is
The above electronic configuration corresponds to that of Argon till
(c)
Interpretation:
Electronic configuration of the following metals has to be written –
Concept Introduction:
Electronic configuration of an atom represents the arrangement of electrons in various energy levels. The electrons are arranged in increasing order of energy levels according to Aufbau principle. It is pictorially represented as –
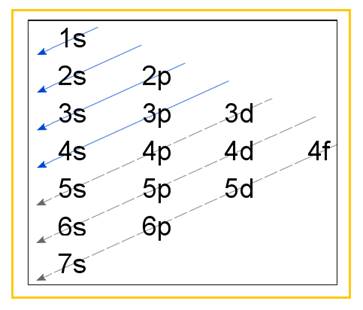
Figure 1
The terms
(c)
Answer to Problem 22E
Electronic configuration of
Explanation of Solution
Atomic number of Zirconium is
The electronic configuration of
The above electronic configurations correspond to that of Argon till
(d)
Interpretation:
Electronic configuration of the following metals has to be written –
Concept Introduction:
Electronic configuration of an atom represents the arrangement of electrons in various energy levels. The electrons are arranged in increasing order of energy levels according to Aufbau principle. It is pictorially represented as –
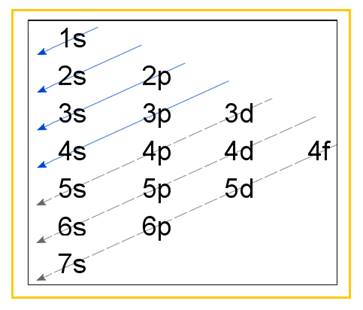
Figure 1
The terms
(d)
Answer to Problem 22E
Electronic configuration of
Explanation of Solution
Atomic number of Osmium is
Os2+ and Os3+ are formed when Osmium loses two electrons and three electrons respectively. Accordingly the electronic configuration of Os2+ is –
The above electronic configuration corresponds to that of Xenon till
The electronic configuration of
The above electronic configuration corresponds to that of Xenon till
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
Chemistry
- At pil below about 35 woon (Fe) oxidizes in streams according to the following Water in a reservoir at 20°C has a pH of 7.7 and contains the following constituents: Constituent (g) + Conc. (mg/L) Ca2+ 38 HCO3 abiotic oxid 183 HO Ferrous iron under these conditions and at 20°Cis Estimate the activities of Ca2+ and HCO3-, using an appropriate equation to compute the activity coefficients. (atomic weight: Ca 40)arrow_forwarddraw the diagram pleasearrow_forwardShow work with explanation. Don't give Ai generated solutionarrow_forward
- Draw the structure of the acetal derived from 2,2-dimethyl-1,3-propanediol and butanal. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. X G Parrow_forwardPredict the major products of the following reaction. 田 Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds to show the stereochemistry of the products when it's important, for example to distinguish between two different major products. 口 + X C₁₂ Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forwardH C-OCH H-C=C÷CH₂ IV Questi Predict the correct splitting tree for circled hydrogen in the structure below. A B C III D IVarrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER
Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER





