
Organic Chemistry (9th Edition)
9th Edition
ISBN: 9780321971371
Author: Leroy G. Wade, Jan W. Simek
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 21, Problem 21.45SP
Predict the products of the following reactions.
- a. phenol + acetic anhydride
- b. phenol + acetic formic anhydride
- c. aniline + phthalic anhydride
- d. anisole + succinic anhydride and aluminum chloride
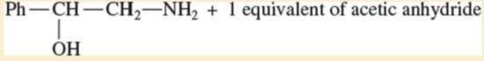
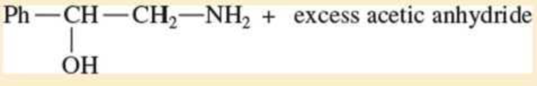
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
What are the products of the following reactions? (A trace amount of acid is present in each case.)
a. cyclopentanone + ethylamine c. acetophenone + hexylamine
b. cyclopentanone + diethylamine d. acetophenone + cyclohexylamine
Phosgene (COCl2) was used as a poison gas in World War I. What product would be formed from the reaction of phosgene with each of the following reagents? a. one equivalent of methanol b. excess methanol c. excess propylamine d. excess water
What is the first step in the general mechanism for electrophilic aromatic substitution?
a. aromatic ring protonation
b.loss of the electrophilic aromatic ring
c. deprotonation of the aromatic ring
d.addition of the electrophilic to the aromatic ring.
Chapter 21 Solutions
Organic Chemistry (9th Edition)
Ch. 21.2F - Name the following carboxylic acid derivatives,...Ch. 21.4A - Prob. 21.2PCh. 21.4A - Prob. 21.3PCh. 21.4A - Prob. 21.4PCh. 21.5C - Prob. 21.7PCh. 21.6 - When ethyl 4-hydroxybutyrate is heated in the...Ch. 21.6 - Propose a mechanism for the following ring-opening...Ch. 21.6 - Prob. 21.15PCh. 21.7B - Prob. 21.16PCh. 21.7C - Prob. 21.19P
Ch. 21.7C - Prob. 21.20PCh. 21.7C - Prob. 21.21PCh. 21.7D - Prob. 21.22PCh. 21.7D - The mechanism for acidic hydrolysis of a nitrile...Ch. 21.8A - Prob. 21.24PCh. 21.8C - Prob. 21.25PCh. 21.9 - Prob. 21.26PCh. 21.9 - Prob. 21.27PCh. 21.9 - Prob. 21.28PCh. 21.10 - Draw a mechanism for the acylation of anisole by...Ch. 21.10 - Prob. 21.30PCh. 21.11 - Prob. 21.31PCh. 21.11 - Prob. 21.32PCh. 21.12 - Problem 21-33 Propose a mechanism for the...Ch. 21.12 - Suggest the most appropriate reagent for each...Ch. 21.12 - Show how you would synthesize each compound,...Ch. 21.13 - Prob. 21.36PCh. 21.13 - Prob. 21.37PCh. 21.14 - Prob. 21.38PCh. 21.14 - Prob. 21.39PCh. 21.16 - Prob. 21.40PCh. 21.16 - Prob. 21.41PCh. 21 - Prob. 21.42SPCh. 21 - Give appropriate names for the following...Ch. 21 - Predict the major products formed when benzoyl...Ch. 21 - Predict the products of the following reactions....Ch. 21 - Prob. 21.46SPCh. 21 - Prob. 21.47SPCh. 21 - Prob. 21.48SPCh. 21 - Propose mechanisms for the following reactions.Ch. 21 - Prob. 21.51SPCh. 21 - An ether extraction of nutmeg gives large...Ch. 21 - Prob. 21.53SPCh. 21 - Show how you would accomplish the following...Ch. 21 - Prob. 21.55SPCh. 21 - Prob. 21.56SPCh. 21 - Prob. 21.57SPCh. 21 - Prob. 21.58SPCh. 21 - Prob. 21.59SPCh. 21 - Explain this curious result. What does this...Ch. 21 - Prob. 21.61SPCh. 21 - Prob. 21.62SPCh. 21 - Prob. 21.63SPCh. 21 - A chemist was called to an abandoned aspirin...Ch. 21 - Prob. 21.67SPCh. 21 - The IR spectrum, 13ONTVTR spectrum, and 1HNMR...Ch. 21 - Prob. 21.69SPCh. 21 - Prob. 21.70SPCh. 21 - Prob. 21.71SP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Under basic reaction conditions, two molecules of benzaldehyde condense to give: a. Benzyl alcohol and Benzoic acid b. Benzyl alcohol and sodium benzoate c. Benzoic acid and phenol d. Benzyl alcohol and benzylic acid Under which reaction conditions, Benzil rearrange to benzilate? a. Strongly acidic conditions b. Neutral conditions c. Strongly basic conditions d. Mild acidic conditions In benzoin experiment two traps where used, one in the first step and another in the second step, in order to prevent the escape of (respectively) a. NaOH aq, hydrocyanic acid b. Nitrogen oxides, hydrocyanic acid C. HBr gas, N20 gas d. Hydrocyanic acid, Nitrogen oxidesarrow_forwardBy means of a suitable reaction, show how each of the compounds can be prepared from propionic acid. More than one step may be required. a. methyl propylamine (CH3NHCH2CH2CH3)b. propionyl chloridec. ethyl propionated. propionic anhydridee. N-methyl propionamidearrow_forward1. Give the product of the reaction of the cyclic anhydride shown below when treated with the following reagents. a. aquous NaOH b. aqueous HCI c. methanol d. sodium methoxide in methanol e. ethylaminearrow_forward
- 27. What reaction converts the C=O bond to the C=C bond? a. Witten Reaction b. Wittig Reaction c. Winding Reaction d. Whinging Reaction 28. What reagent can reduce imines to primary amines? a. Lithium aluminiumhydride b. Phosphorous pentachloride c. Pyridinium chlorochromate d. Sodium cyanoborohydride 29. What are the steps that can convert imines to amino acids? a. 1. LiAlH₄; Water b. 1. NaCN; 2. Water c. 1. LiAlH₄; 2. Ammonia d. 1. NaCN; 2. Ammonia 30. Cyclohexanone reacts with NaCN to form a.The S-isomer b.The R-isomer c.A racemic mixture d.None of the abovearrow_forwardCreate 3-methyl-1-butanamine using the four different methods below. a. Gabriel synthesis b. Using sodium azide c. Using a carboxylic acid d. Using an alkyl bromidearrow_forwardPredict the products (if any) of the reaction of each of the ff. reagents with benzoic acid. a. NaOH b. LiAlH4 c. PCl5 d. conc. HClarrow_forward
- Hh.10.arrow_forwardStarting with an alkyl halide, how could the following compounds be prepared? a. 2-methoxybutane b. 1-methoxybutane c. butylmethylaminearrow_forwardName and Draw the structures of all possible chemical (Electrophilic aromatic substitution) reactions of p- Chloroaniline a. Halogenation (Chlorination or Bromination) b. Nitration c. Sulphonation d. Friedal Craft Alkylation e. Friedal Craft Acylationarrow_forward
- Which of the following is expected to be the MOST reactive towards electrophilic aromatic substitution? a. p-Cresol b. p-Toluidine c. p-Chlorophenol d.p-Chloroaniline 2. Which of the following is expected to be the LEAST reactive towards electrophilic aromatic substitution? a. p-Hydroxybenzoic acid b. p-Methoxybenzoic acid c. p-Aminophenyl acetate d. p-Methoxyphenyl acetatearrow_forwardWhich of the following molecules gives a disproportionation reaction in a basic medium? A. benzyl alcohol B. benzamide C. benzonitrile D. benzaldehyde E. benzoic acidarrow_forwardd. 12. What is the simplest fused aromatic hydrocarbon? a. Naphthalene b. 1,2-Benzylpyrene c. Methylbenzene d. Cyclobenzene 13. In electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions, a phenyl substituent on the aromatic ring is a. a deactivator and a m-director b. a deactivator and an o,p-director c. an activator and an o,p-director d. none of the above 14. Acetylide ion formation requires a strong base like NaNH2 which in turn is made using ammonia and Na. The catalyst used in this reaction is a. Cu b. Fe C. Pt d. Pd 15. Hydroboration-Oxidation of terminal alkyne results in the formation of an a. Aldehyde by Markovnikov mechanism b. Ketone by anti-Markovnikov mechanism c. Enol by Markovnikov mechanism d. Aldehyde by anti-Markovnikov mechanism 16.p-Methoxybenzaldehyde can be prepared from anisole using the Gatterman- Koch formylation. What mixture of reagents is necessary for this process? a. CO, HCI, AICI3, CuCI b. CO, SO3, H2SO4 CO2, HCI, AICI3 d. CO2, SO3, H2SO4 e. CO2, HNO3, H2SO4 C.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY
Lipids - Fatty Acids, Triglycerides, Phospholipids, Terpenes, Waxes, Eicosanoids; Author: The Organic Chemistry Tutor;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7dmoH5dAvpY;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY