
(a)
Interpretation:
The complete, detailed mechanism of a given compound synthesized from an acid chloride and water is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Answer to Problem 21.40P
The complete mechanism is
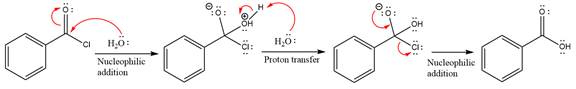
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is
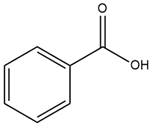
The carboxylic acid formation requires water as a nucleophile in the nucleophilic addition step. In this reaction,
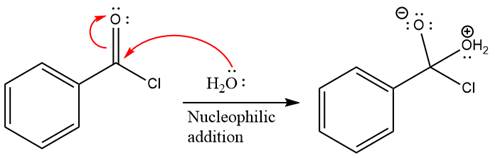
In the first step, water acts as a nucleophile and adds to the carbonyl carbon of the acid chloride to produce a protonated intermediate ion. The
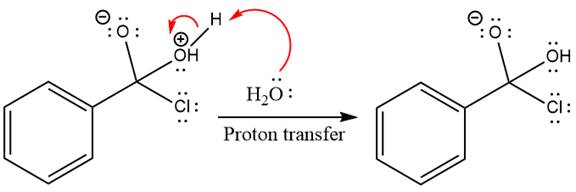
The protonated water is then deprotonated by a second molecule of the water.
Finally, one lone pair on the negatively charged oxygen will move back to reform the carbonyl group, eliminating the chloride and forming the product.
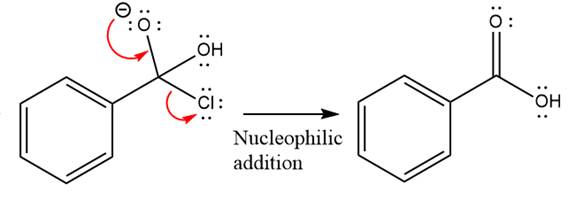
Thus, the complete mechanism can be drawn as
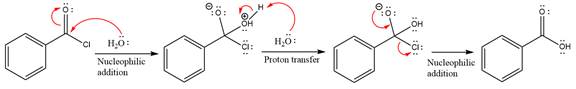
The product and mechanism of the given reaction were determined based on nucleophilic addition-elimination mechanism.
(b)
Interpretation:
The complete, detailed mechanism of a given compound synthesized from an acid chloride and water is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acid derivatives undergo acyl group substitution reactions when treated with appropriate nucleophiles. The reaction occurs via nucleophilic addition-elimination involving a tetrahedral intermediate. It may also involve proton transfer step(s), particularly when the nucleophile being added in the first step is not a strong nucleophile. The reaction occurs if the possible product is more stable than the reactant. If the two are of comparable stability, the reaction will occur reversibly.
Answer to Problem 21.40P
The complete mechanism is
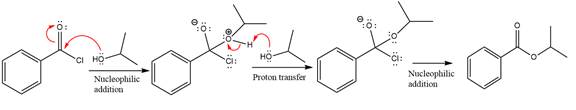
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is
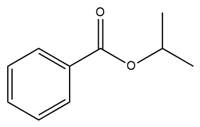
The ester formation requires isopropanol as a nucleophile in the nucleophilic addition step. In this reaction,
In the first step, isopropanol acts as a nucleophile and adds to the carbonyl carbon of the acid chloride to produce a protonated intermediate ion. The
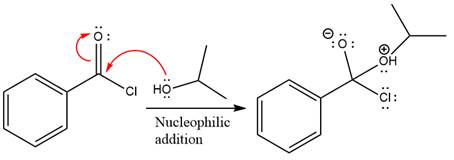
The protonated alcohol is then deprotonated by a second molecule of the isopropanol.
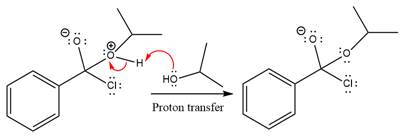
Finally, one lone pair on the negatively charged oxygen will move back to reform the carbonyl group, eliminating the chloride and forming the product.
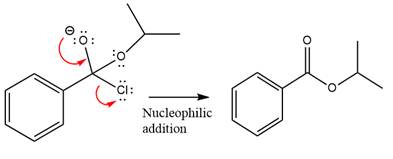
Thus, the complete mechanism can be drawn as

The product and mechanism of the given reaction were determined based on nucleophilic addition-elimination mechanism.
(c)
Interpretation:
The complete, detailed mechanism of a given compound synthesized from an acid chloride and water is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acid derivatives undergo acyl group substitution reactions when treated with appropriate nucleophiles. The reaction occurs via nucleophilic addition-elimination involving a tetrahedral intermediate. It may also involve proton transfer step(s), particularly when the nucleophile being added in the first step is not a strong nucleophile. The reaction occurs if the possible product is more stable than the reactant. If the two are of comparable stability, the reaction will occur reversibly.
Answer to Problem 21.40P
The complete mechanism is
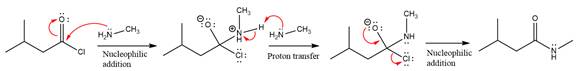
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is
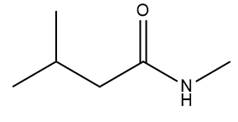
The amide formation requires
In the first step, amine acts as a nucleophile and adds to the carbonyl carbon of the acid chloride to produce a protonated intermediate ion. The
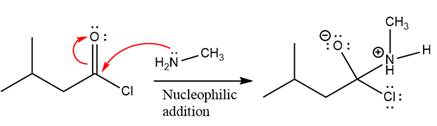
The protonated amine is then deprotonated by a second molecule of the amine.
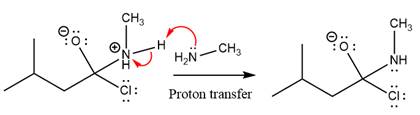
Finally, one lone pair on the negatively charged oxygen will move back to reform the carbonyl group, eliminating the chloride and forming the product.
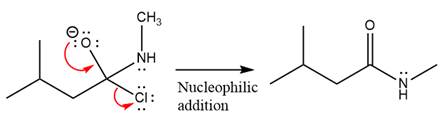
Thus, the complete mechanism can be drawn as
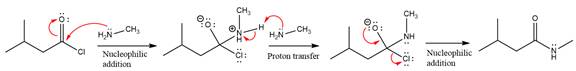
The product and mechanism of the given reaction were determined on the basis of nucleophilic addition-elimination mechanism.
(d)
Interpretation:
The complete, detailed mechanism of given compound synthesized from an acid chloride and water is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acid derivatives undergo acyl group substitution reactions when treated with appropriate nucleophiles. The reaction occurs via nucleophilic addition-elimination involving a tetrahedral intermediate. It may also involve proton transfer step(s), particularly when the nucleophile being added in the first step is not a strong nucleophile. The reaction occurs if the possible product is more stable than the reactant. If the two are of comparable stability, the reaction will occur reversibly.
Answer to Problem 21.40P
The complete mechanism is
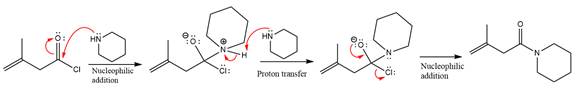
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is
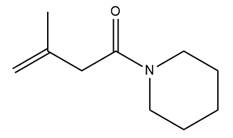
The amide formation requires amine as a nucleophile in the nucleophilic addition step. In this reaction,
In the first step, pyridine acts as a nucleophile and adds to the carbonyl carbon of the acid chloride to produce a protonated intermediate ion. The
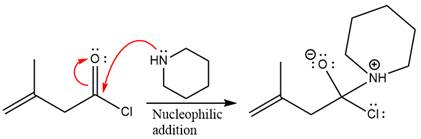
The protonated pyridine is then deprotonated by a second molecule of the amine.
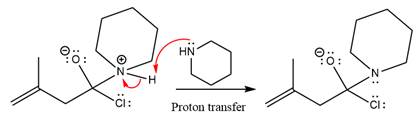
Finally, one lone pair on the negatively charged oxygen will move back to reform the carbonyl group, eliminating the chloride and forming the product.
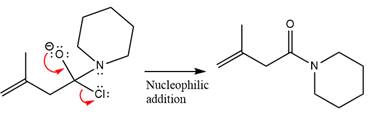
Thus, the complete mechanism can be drawn as
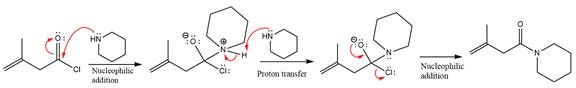
The product and mechanism of the given reaction were determined based on nucleophilic addition-elimination mechanism.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Principles And Mechanisms
- (12) Which one of the following statements about fluo- rometry is FALSE? a) Fluorescence is better detected at 90 from the exci- tation direction. b) Fluorescence is typically shifted to longer wave- length from the excitation wavelength. c) For most fluorescent compounds, radiation is pro- duced by a transitionarrow_forwardDon't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardDon't used Ai solutionarrow_forward
- Don't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardIndicate the correct option.a) Graphite conducts electricity, being an isotropic materialb) Graphite is not a conductor of electricityc) Both are falsearrow_forward(f) SO: Best Lewis Structure 3 e group geometry:_ shape/molecular geometry:, (g) CF2CF2 Best Lewis Structure polarity: e group arrangement:_ shape/molecular geometry: (h) (NH4)2SO4 Best Lewis Structure polarity: e group arrangement: shape/molecular geometry: polarity: Sketch (with angles): Sketch (with angles): Sketch (with angles):arrow_forward
- 1. Problem Set 3b Chem 141 For each of the following compounds draw the BEST Lewis Structure then sketch the molecule (showing bond angles). Identify (i) electron group geometry (ii) shape around EACH central atom (iii) whether the molecule is polar or non-polar (iv) (a) SeF4 Best Lewis Structure e group arrangement:_ shape/molecular geometry: polarity: (b) AsOBr3 Best Lewis Structure e group arrangement:_ shape/molecular geometry: polarity: Sketch (with angles): Sketch (with angles):arrow_forward(c) SOCI Best Lewis Structure 2 e group arrangement: shape/molecular geometry:_ (d) PCls Best Lewis Structure polarity: e group geometry:_ shape/molecular geometry:_ (e) Ba(BrO2): Best Lewis Structure polarity: e group arrangement: shape/molecular geometry: polarity: Sketch (with angles): Sketch (with angles): Sketch (with angles):arrow_forwardDon't used Ai solutionarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





