
Power System Analysis and Design (MindTap Course List)
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781305632134
Author: J. Duncan Glover, Thomas Overbye, Mulukutla S. Sarma
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 2, Problem 2.31P
Consider two interconnected voltage sources connected by a line of impedance
(a) Obtain expressions for
(b) Determine the maximum power transfer and the condition for it to 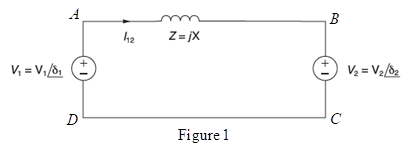
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Home Works
the following networks, determine the total current:-
4k
Ω
12ΚΩ
24ΚΩ
8k
72V
9k
3k
Ω
Ω
Ω
120
6k
Ω
Answer the question one and two step by step with drawing both of using by hand not Ai
I need expe
Part c Assuming no leakage current, calculate the V
min
OH of the inverter. If,
instead, there is a leakage current with equivalent resistance of 3 MΩ
when VGS < VT , determine the adjusted V
min
OH . Calculate the power lost
when Vi =
VT
2
in these circumstances.
Chapter 2 Solutions
Power System Analysis and Design (MindTap Course List)
Ch. 2 - The rms value of v(t)=Vmaxcos(t+) is given by a....Ch. 2 - If the rms phasor of a voltage is given by V=12060...Ch. 2 - If a phasor representation of a current is given...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.4MCQCh. 2 - Prob. 2.5MCQCh. 2 - Prob. 2.6MCQCh. 2 - Prob. 2.7MCQCh. 2 - Prob. 2.8MCQCh. 2 - Prob. 2.9MCQCh. 2 - The average value of a double-frequency sinusoid,...
Ch. 2 - The power factor for an inductive circuit (R-L...Ch. 2 - The power factor for a capacitive circuit (R-C...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.13MCQCh. 2 - The instantaneous power absorbed by the load in a...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.15MCQCh. 2 - With generator conyention, where the current...Ch. 2 - Consider the load convention that is used for the...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.18MCQCh. 2 - The admittance of the impedance j12 is given by...Ch. 2 - Consider Figure 2.9 of the text, Let the nodal...Ch. 2 - The three-phase source line-to-neutral voltages...Ch. 2 - In a balanced three-phase Y-connected system with...Ch. 2 - In a balanced system, the phasor sum of the...Ch. 2 - Consider a three-phase Y-connected source feeding...Ch. 2 - For a balanced- load supplied by a balanced...Ch. 2 - A balanced -load can be converted to an...Ch. 2 - When working with balanced three-phase circuits,...Ch. 2 - The total instantaneous power delivered by a...Ch. 2 - The total instantaneous power absorbed by a...Ch. 2 - Under balanced operating conditions, consider the...Ch. 2 - One advantage of balanced three-phase systems over...Ch. 2 - While the instantaneous electric power delivered...Ch. 2 - Given the complex numbers A1=630 and A2=4+j5, (a)...Ch. 2 - Convert the following instantaneous currents to...Ch. 2 - The instantaneous voltage across a circuit element...Ch. 2 - For the single-phase circuit shown in Figure...Ch. 2 - A 60Hz, single-phase source with V=27730 volts is...Ch. 2 - (a) Transform v(t)=75cos(377t15) to phasor form....Ch. 2 - Let a 100V sinusoidal source be connected to a...Ch. 2 - Consider the circuit shown in Figure 2.23 in time...Ch. 2 - For the circuit shown in Figure 2.24, compute the...Ch. 2 - For the circuit element of Problem 2.3, calculate...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.11PCh. 2 - The voltage v(t)=359.3cos(t)volts is applied to a...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.13PCh. 2 - A single-phase source is applied to a...Ch. 2 - Let a voltage source v(t)=4cos(t+60) be connected...Ch. 2 - A single-phase, 120V(rms),60Hz source supplies...Ch. 2 - Consider a load impedance of Z=jwL connected to a...Ch. 2 - Let a series RLC network be connected to a source...Ch. 2 - Consider a single-phase load with an applied...Ch. 2 - A circuit consists of two impedances, Z1=2030 and...Ch. 2 - An industrial plant consisting primarily of...Ch. 2 - The real power delivered by a source to two...Ch. 2 - A single-phase source has a terminal voltage...Ch. 2 - A source supplies power to the following three...Ch. 2 - Consider the series RLC circuit of Problem 2.7 and...Ch. 2 - A small manufacturing plant is located 2 km down a...Ch. 2 - An industrial load consisting of a bank of...Ch. 2 - Three loads are connected in parallel across a...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.29PCh. 2 - Figure 2.26 shows three loads connected in...Ch. 2 - Consider two interconnected voltage sources...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.35PCh. 2 - Prob. 2.36PCh. 2 - Prob. 2.37PCh. 2 - Prob. 2.38PCh. 2 - Prob. 2.39PCh. 2 - A balanced three-phase 240-V source supplies a...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.41PCh. 2 - A balanced -connected impedance load with (12+j9)...Ch. 2 - A three-phase line, which has an impedance of...Ch. 2 - Two balanced three-phase loads that are connected...Ch. 2 - Two balanced Y-connected loads, one drawing 10 kW...Ch. 2 - Three identical impedances Z=3030 are connected in...Ch. 2 - Two three-phase generators supply a three-phase...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.48PCh. 2 - Figure 2.33 gives the general -Y transformation....Ch. 2 - Consider the balanced three-phase system shown in...Ch. 2 - A three-phase line with an impedance of...Ch. 2 - A balanced three-phase load is connected to a...Ch. 2 - What is a microgrid?Ch. 2 - What are the benefits of microgrids?Ch. 2 - Prob. CCSQCh. 2 - Prob. DCSQ
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- I need to figure out how to make an oscilliscope sketch from the VDC and VAC values.arrow_forwardDraw the equation by using Hand not Ai then solve using double integral please i need expert answerarrow_forwardcalculete all the parameters (g11/g12/g21/g22 and r11/r12/r21/r22) for the representations: voltage controlled and current controlled.voltage controlledi1=g11v1+g12v2i2=g21v1+g22v2current controlledv1=r11i1+r22i2v2=r21i1+r22i2arrow_forward
- Don't use ai to answer I will report you answerarrow_forwardcalculate the parameters (h11/h12/h21/h22) for hybrid 2 and hybrid 1 HYBRID2 i1=h11v1+h12i2 v2=h21v1+h22i2HYBRID 1v1 = h11i1 + h12v2i2 = h21i1 + h22v2arrow_forwardDescribe the flow control and load sharing features implemented in the MTP3 protocol of SS7. Explain the use of the SLS field and discuss SS7 network structure. Explain the error control mechanisms used in SS7, including preventive cyclic retransmission. Draw a diagram for the protocol model of SS7 and explain the function of each part. List the four classes of SCCP service which are available and explain one briefly. Describe the advantages and disadvantages of common channel signalling. Describe in detail the function of MTP layer 1, 2 and 3. Show the structure of message signal units (MSUS) and describe the fields used. Describe the call control procedures used in DSSI to set up and release a connection. Use a diagram to show the signalling message flows. Give details of three examples of supplementary services provided by the ISDN user part of SS7. Describe a service provided by the transaction capabilities application part. Describe the subscriber line signalling methods used for…arrow_forward
- I need to know the derivative of the blocking probability of TSSST switcharrow_forwardDraw the equation USE BY HANarrow_forwardProblem a. (i) Sketch the ideal power curve of the turbine with the following characteristics: • rated speed is 14 m/s ⚫rated power is 1.25 MW ⚫ cut-in speed is 5 m/s ⚫furling or cut-out speed is 20 m/s (ii) Given part (i), calculate the energy produced in one day if the wind blows continuously between 15 and 20 m/s all day (iii) Can the energy produced in one year be determined if you are told that the average wind speed is 14 m/s? Explain why.arrow_forward
- Problem b. Suppose an anemometer mounted at a height of 10 m with a 20-m/s average wind speed (i) Estimate the average wind power at a height of 10 m, assuming Rayleigh statistics and under the following weather conditions • 15°C (ii) Suppose a 1300-kW wind turbine with 60-m rotor diameter is located in those winds with speed computed in the first condition of part (i). Determine the annual energy production with a 30% wind turbine efficiency (iii) Evaluate the wind turbine capacity factorarrow_forwardQ3/Using Kirchhoff's laws to determine: (6degrees) a) The current (Irsa) b) The voltage across the Ri (V750) c) Calculate the power by each voltage source. d) Calculate the power of each resistor of the network. V3 12V V2 R1 3V R2 1250arrow_forwardQ1/For the network shown in the figure below, Use MESH analysis and find the current through (50) resistor. (6degrees) R. - 3 Ո 20 V R3 ΔΩ Rs ww 50 202 202 w R2 Ra 142arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Power System Analysis and Design (MindTap Course ...Electrical EngineeringISBN:9781305632134Author:J. Duncan Glover, Thomas Overbye, Mulukutla S. SarmaPublisher:Cengage Learning
Power System Analysis and Design (MindTap Course ...Electrical EngineeringISBN:9781305632134Author:J. Duncan Glover, Thomas Overbye, Mulukutla S. SarmaPublisher:Cengage Learning

Power System Analysis and Design (MindTap Course ...
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781305632134
Author:J. Duncan Glover, Thomas Overbye, Mulukutla S. Sarma
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Maximum Power Transfer Theorem Using Nodal Analysis & Thevenin Equivalent Circuits; Author: The Organic Chemistry Tutor;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8CA6ZNXgI-Y;License: Standard Youtube License