
Concept explainers
The number of carbon and hydrogen atoms in the unit cell of polyethylene.
Answer to Problem 2.19P
The number of carbon atoms in the unit cell of polyethylene is
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given figure is,
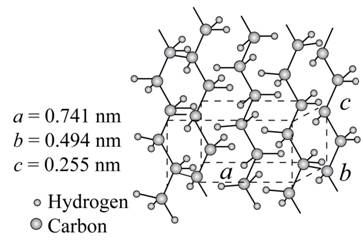
Figure (1)
The density of crystalline polyethylene
From above figure,
The lattice parameter
The lattice parameter
The lattice parameter
Formula used:
The equation for density of poly-ethylene is given by,
Here,
The hydrogen atoms are twice in number as that of carbon atoms.
Substitute
Here,
Calculation:
The molecular mass of carbon is
The molecular mass of hydrogen is
The value of Avogadro’s number is
Substitute
Since
Conclusion:
The number of carbon atoms in the unit cell of polyethylene is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Materials Science And Engineering Properties
- Two hypothetical metals are created with different elements that have the same atomic mass (g/mole) and the same atomic radius. Metal A has a density of 9.50 g/cm3 and metal B has a density of 8.73 g/cm3. If one of these metals has a BCC lattice structure and the other has an FCC lattice structure, identify the structure that corresponds to each of one of them. Justify your answer.arrow_forwardThe following statements are true about the structure of metals, EXCEPT: The knowledge of metal structure serves as a guide in controlling and predicting performance of metals. The knowledge of metal structure helps engineers predict properties of metals. All of the above. O None of the above. O Metal structure influences behavior and properties of metals.arrow_forwardCalcium has an FCC crystal structure, density of 1.55 Mg/m3, and atomic massof 40.08 g/mole.a. Calculate the volume of the unit cell in cubic meters.b. Calculate the radius of the calcium atom.arrow_forward
- The reciprocal of density isarrow_forward3.11 Each of the following statements describes a silicate mineral or mineral group. In each case, provide the appropriate name. a- The most common member of the amphibole group. b- The most common non ferromagnesian member of the mica family. c- The only silicate mineral made entirely of silicon and oxygen. d- A high-temperature silicate with a name that is based on its color. e-Characterized by striations. f- Originates as a product of chemical weathering.arrow_forwardQuestion 6 (of 8) 6. The density of platinum is 21500 kg/m³ and that of aluminum is 2702 kg/m³. Find the ratio of the volume of 1.80 kg of platinum to the volume of 1.17 kg of aluminum.arrow_forward
- A pure titanium cube has an edge length of 2.74 inin . How many titanium atoms does it contain? Titanium has a density of 4.50g/cm34.50g/cm3. Express your answer in atoms to three significant figures.arrow_forwardMetal X has an atomic weight of 43.1 g/mol, theoretical density of 6.40 g/cm^3, and atomic radius of 122 pm. Determine whether the crystal structure of Metal X is BCC, FCC, or simple cubic. Provide your complete solution.arrow_forwardDraw a bar diagram on your sketch paper based on the table below and determine the non-carbon hardness (permanent hardness) in mg/L of CaCO3. Atomic weight Equivalent weight or molecular Concentration (mg/L) meq/L concentration (mg/meq) weight (g/mol) 100 Ca2+ 40 150 mg/L as CaCO3 150/50=3 (g/mol)/2(eq/mol)=50 Mg2+ 24 100 mg/L as CACO3 100/50=2 Na+ 23 46 mg/L K+ 39 39 mg/L HCO3 61 225 mg/L as CaCO3 225/50=4.5 SO42- 96 72 mg/L CI 35.5 71 mg/L O 25 mg/L of CaCO3 O 50 mg/L of CaCO3 O 100 mg/L of CaCO3 O 150 mg/L of CaCO3arrow_forward
- Explain which kind of microstructures you expect to observe at room temperature if an iron-carbon alloy of eutectoid composition is cooled down following the red and blue curves. 800 727° 700 Coarse pearlite 600 a+ FeC Fine pearlite 500 y+ a+ Fe,C 400 Bainite 300 M5- 200 so - Mo 100 1 sec 1 min 1 hour 1 day 102 103 104 105 0.1 10 Time, secondsarrow_forwardFor a certain ionic bond, energy - interionic distance relationship is given by the following equation: 5.657x103 1.25x105 U=- p12 r is intermolecular distance in nm and U is in Joule (KJ). a) Determine the equilibrium distance ( ro) where the bond is most stable. 00.987 nm 00.601 nm 00.760 nm 00.4051 nm b) Determine the minimum Potential energy (Umin). O-0.850 KJ/molarrow_forwardThe figure below is a phase diagram for alloys of aluminum and silicon Atomic percentage, silicon "C 1,300 10 50 60 90 1,400 1,300 L 1,300 1,100 1000 900 800 700 660.437 600 300 400 300 x+L 16 136 -577- L+B 1414 a+B Al 20 20 90 Si 50 Weight percentage, silicon Part A Calculate the weight fraction of the a phase that is proeutectic in a 6 wt%, Si-94 wt% Al alloy at 576°C. Express your answer to three significant figures. Fraction proeutectic a = 0.628 The answer above is the CORRECT answer. Please give the correct solution method 70arrow_forward
 Materials Science And Engineering PropertiesCivil EngineeringISBN:9781111988609Author:Charles GilmorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Materials Science And Engineering PropertiesCivil EngineeringISBN:9781111988609Author:Charles GilmorePublisher:Cengage Learning
