
Concept explainers
Connecting the Concepts
1. In the primate phylogenetic tree below, fill in groups (a)–(e). Of the groups, which are anthropoids and which are apes?
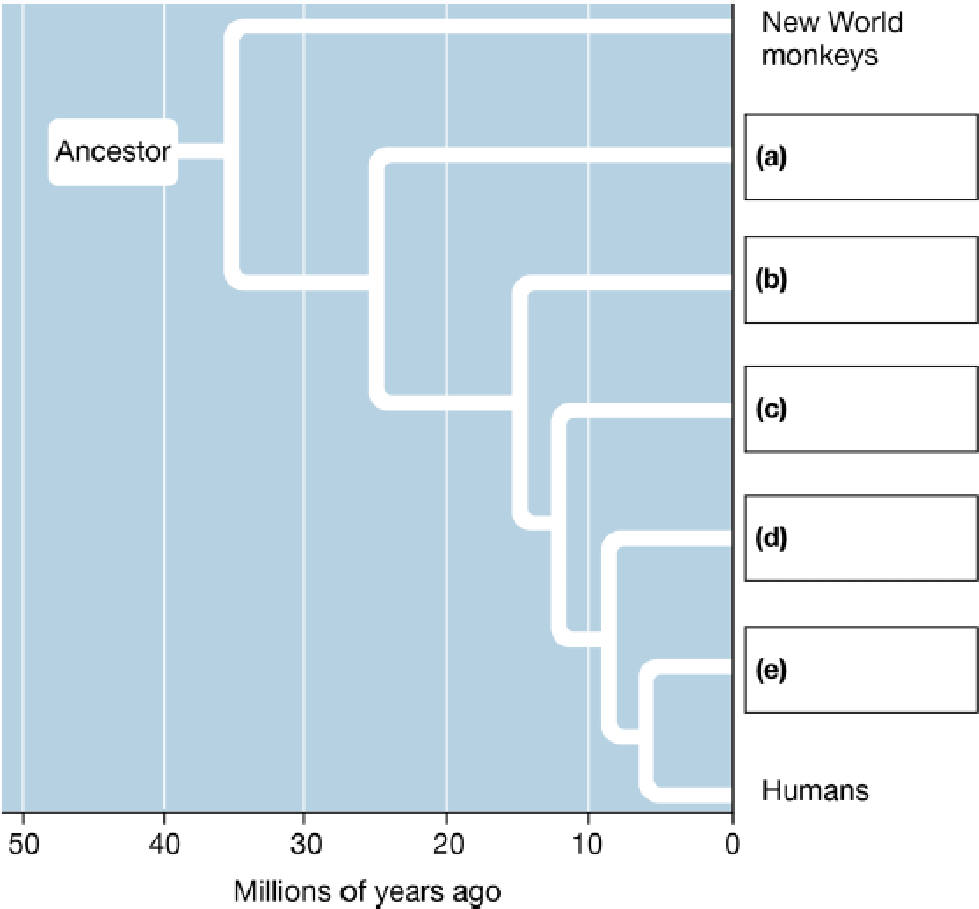
To complete: The primate phylogenic tree (containing apes and anthropoids).
Introduction:
Primates are evolved about 65 million years ago. The characters of primates include limber joints, grasping hands and feet with flexible digits, a short snout, and forward-pointing eyes. Living primates are lorises, bush babies, and lemurs; the tarsiers; and anthropoids (monkeys and apes).
All primates are anthropoids: gibbons, orangutans, gorillas, monkeys, chimpanzees, and humans, but humans and chimpanzees are apes. Apes have larger brains than other primates, which include gibbons, orangutans, gorillas, chimpanzees, and humans.
Answer to Problem 1CC
Fig. 1 represents various groups of the primate phylogenic tree.
Pictorial representation: A phylogenetic tree showing various groups of primates is given in Fig. 1.
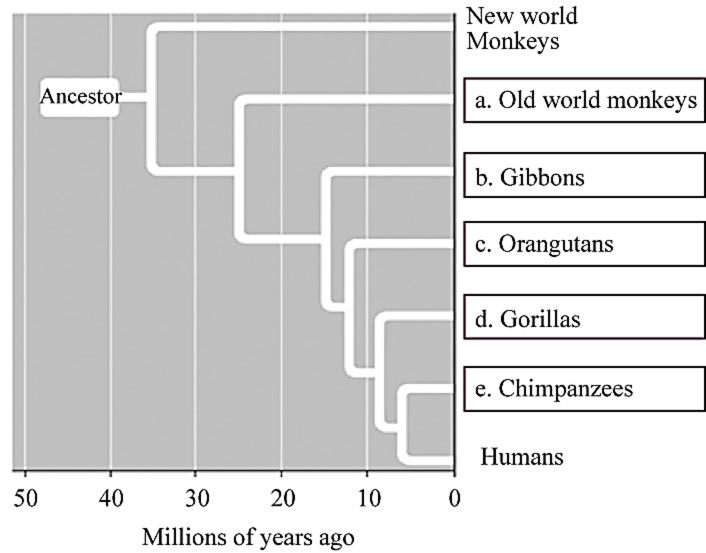
Fig.1: The primate phylogenic tree.
Explanation of Solution
(a)
Correct answer: Old world monkeys.
Old world monkeys are primates that belong to the super family Cercopithecoidea. Old world monkeys have tails. Hence, the correct answer is old world monkeys.
(b)
Correct answer: Gibbons.
Gibbons are the small, arboreal apes. They are distributed in the wild, in the tropical and subtropical forests of Southeast Asia. Hence the correct answer is gibbons.
(c)
Correct answer: Orangutans.
Orangutans are great apes, and they are closely related to humans. Hence, the correct answer is orangutans.
(d)
Correct answer: Gorillas.
Gorillas are ground-dwelling, herbivorous apes. They live mostly in the forests of central Sub-Saharan Africa. They show many human-like behaviors and emotions, (laughter and sadness). Hence, the correct answer is gorillas.
(e)
Correct answer: Chimpanzees.
Chimpanzees are the species of apes that are most closely related to humans. Chimpanzees are found in tropical forests and savannas of equatorial Africa. Hence, the correct answer is chimpanzees.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
CAMPBEL BIOLOGY:CONCEPTS & CONNECTIONS
- 1. Concept Check The similarity in bone structure and arrangement between cats and bats suggests that Humerus Radius Ulna Carpals Metacarpals Phalanges Human Cat Whale Bat a) bats originated from bird-like ancestors. b) bats originated from four-legged ancestors, such as cats. c) modern bats fly much faster than ancient bat species. © 2018 Pearson Education, Inc. 2. Concept Check Darwin proposed the theory of natural selection as the mechanism of evolution based on three observations about nature. Which of the following were part of Darwin's observations? a) Populations have the potential to produce more individuals than the environment can support. b) Individuals in some populations have varied characteristics. Variation in individuals appears to be inherited. d) all of the above © 2018 Pearson Education, Inc.arrow_forward1. Differenciate the difference between taxonomy and systematics and give a brief examplanation about their relations. 2. Give certain primitive characters with all members of kingdom Animalia (adapted from Krempel's and Lee, p.7-9). List four primitive characters all humans share with all other animal, but not with any other living things. 3. List as many derived characters as possible that make Homo Sapiens different from all other great apes. Restrict your list to truly BIOLOGICAL characters.arrow_forwardSpecies Embryo (A-F) Describe the Anatomical Changes from Early to Late Stages Human Chicken Rabbit Tortoise Salamander В Fish A Guide Questions: 1. Look again at the six embryos in their earliest stages. Describe the patterns you see. What physical similarities exist between each of the embryos? 2. Does this suggest an evolutionary relationship? Explain how these embryos can be used as evidence of a common ancestor between each of these six organisms.arrow_forward
- 20) The image depicts the anatomical structure of the forelimb of a dolphin and a bat, both mammals. Which hypotheses are consistent with the evolutionary relationship shown by this image? Select ALL that apply.arrow_forwardnvestigate the changes in taxonomy since Linnaeus. Note major changes, such as the recognition that sponges are not plants (Linnaeus thought they were), the changing classification of barnacles (Linnaeus thought they were bivalves), and the breakdown of Linnaeus’s phylum, Vermes (worms). 2) Draw a cladogram of the primates, referring to Chapter 22. Include Homo sapiens and the other extinct species of the genus Homo to the best of our current knowledge. Compare to the cladograms in several of the most recent references listed in Chapter 22.arrow_forward5c. What is wrong with this sentence “Humans are closely related to apes”?arrow_forward
- Make a list of at least 10 morphological characters that you might use to generate a phylogenetic tree of the Caminalcules. Ignore the numbers found next to each Caminalcules- they do not represent who evolved first, second, etc. 2.Construct a phylogenetic tree of relationships (Hint: it may be easiest to cut out the critters so you can move them easily and then paste on them on a paper and draw the branches accordingly). 3.Identify at least 2 recent common ancestors and write at least three critical morphological changes along the branches on which they occurred. For example, did the claws appear (or disappear) as the different species evolved? 4.Take a picture of your phylogenetic tree and submit it with this document. ***Please note, this lab can be frustrating because you are “creating” the evolutionary story of how these critters evolved and who is more closely related to who (or not) along the way. There is no wrong answer since every student will focus on different…arrow_forward1. Contrast homology and analogy. Give an example of homoplasy. 2. Discuss adaptation and preadaptation. 3. Compare and contrast divergent, convergent, parallel, and organic evolution. 4. What is a vestigial structure? A rudimentary structure? 5. Describe heterochrony – specifically paedogenesis, neoteny, and paedomorphosis.arrow_forwardANIMAL TREE - use for several questions that specify "Animal Tree" in the test. Bahama Oriole Chicken W Sauropod Dinosaurs Crocodiles Snakes X HUMANS Sea Urchin Yarrow_forward
- (e) Using your phylogenetics knowledge from the first exam material , how was the approximate time of divergence between bees and their sister taxa estimated ?arrow_forwardof this =rab or ditions ionary escen- se or 5. Describe two examples of vestigial structures that you can find among the Caminalcules. These are structures that have been reduced to the point that they are virtually useless. Ear muscles and the tail bones are examples of vestigial structures in our own species. Explain how vestigial structures provide clues about a species' evolutionary past. Illustrate your argument with vestigial structures found in humans or other real species.arrow_forwardWhat can we say about Homo sapiens? Select one: O a. Originated in Africa, shared a common ancestor with Neanderthals, Denisovans, and most likely descendants from a group related to Homo heildenbergensis O b. Migrated out of Africa, most likely 2 million years ago, hybridized with Homo floresiensis and differentiated from other Homo as the sole species to evolved language. O c. Migrated from Ethiopia 200,000 years ago, hybridized with Denisovans and Neanderthals to later replace them O d. Is the result of hybridization between Neanderthals and Denisovans, only lineage to show bipedalism and posses the largest brain capacity of all Homo O e. A and C are correctarrow_forward
 Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning

