
(a)
Interpretation: The value of
Given:
Concept Introduction:
Crystal field theory is the theory given to explain the bonding in the coordination complexes. As ligand approaches towards the metal ion, the d-orbital of metal ion divide according to the energy of metal ion. On the basis of energy and degeneracy, the d-orbital can be classified as
In octahedral complex, the
(a)
Answer to Problem 101CP
Explanation of Solution
For
Calculate Ecell from Nernst equation:
(b)
Interpretation: The stronger oxidizing agent out of
Concept Introduction:
Crystal field theory is the theory given to explain the bonding in the coordination complexes. As ligand approaches towards the metal ion, the d-orbital of metal ion divide according to the energy of metal ion. On the basis of energy and degeneracy, the d-orbital can be classified as
In octahedral complex, the
(b)
Answer to Problem 101CP
Explanation of Solution
For the given reaction;
A stronger oxidizing agent will be the more easily reduced species therefore the more positive standard reduction potential will be associated with strong oxidizing agent. Hence
(c)
Interpretation: The crystal field model for the stronger oxidizing agent out of
Concept Introduction:
Crystal field theory is the theory given to explain the bonding in the coordination complexes. As ligand approaches towards the metal ion, the d-orbital of metal ion divide according to the energy of metal ion. On the basis of energy and degeneracy, the d-orbital can be classified as
In octahedral complex, the
(c)
Answer to Problem 101CP
Since en is a stronger-field ligand than H2O, the d-orbital splitting is larger for
Explanation of Solution
In aqueous solution,
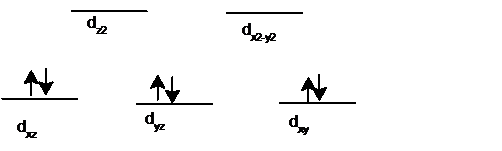
Since, en is a stronger-field ligand than H2O, the d-orbital splitting is larger for
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
Chemical Principles
- An aqueous solution of an unknown salt of gold is electrolyzed by a current of 2.75 amps for 3.39 hours. The electroplating is carried out with an efficiency of 93.0%, resulting in a deposit of 21.221 g of gold. a How many faradays are required to deposit the gold? b What is the charge on the gold ions (based on your calculations)?arrow_forwardAn electrode is prepared from liquid mercury in contact with a saturated solution of mercury(I) chloride, Hg2Cl, containing 1.00 M Cl . The cell potential of the voltaic cell constructed by connecting this electrode as the cathode to the standard hydrogen half-cell as the anode is 0.268 V. What is the solubility product of mercury(I) chloride?arrow_forwardCopper(I) ion disproportionates to copper metal and copper(ll) ion. (See Study Question 99.) 2 Cu+(aq) Cu(s) + Cu2 + (aq) (a) What two half-reactions make up the disproportionation reaction? (b) Use values of the standard reduction potentials for the two half-reactions in part (a) to determine whether this disproportionation reaction is product-favored at equilibrium. (c) What is the equilibrium constant for this reaction? If you have a solution that initially contains 0.10 mol of Cu+ in 1.0 L of water, what are the concentrations of Cu+ and Cu2+ at equilibrium?arrow_forward
- A galvanic cell is based on the following half-reactions: In this cell, the copper compartment contains a copper electrode and [Cu2+] = 1.00 M, and the vanadium compartment contains a vanadium electrode and V2+ at an unknown concentration. The compartment containing the vanadium (1.00 L of solution) was titrated with 0.0800 M H2EDTA2, resulting in the reaction H2EDTA2(aq)+V2+(aq)VEDTA2(aq)+2H+(aq)K=? The potential of the cell was monitored to determine the stoichiometric point for the process, which occurred at a volume of 500.0 mL H2EDTA2 solution added. At the stoichiometric point, was observed to be 1 .98 V. The solution was buffered at a pH of 10.00. a. Calculate before the titration was carried out. b. Calculate the value of the equilibrium constant, K, for the titration reaction. c. Calculate at the halfway point in the titration.arrow_forwardCalculate the cell potential of a cell operating with the following reaction at 25C, in which [Cr2O32] = 0.020 M, [I] = 0.015 M, [Cr3+] = 0.40 M, and [H+] = 0.60 M. Cr2O72(aq)+6I(aq)+14H+(aq)2Cr3+(aq)+3I2(s)+7H2O(l)arrow_forwardAn electrochemical cell consists of a nickel metal electrode immersed in a solution with [Ni2+] = 1.0 M separated by a porous disk from an aluminum metal electrode immersed in a solution with [Al3+] = 1.0 M. Sodium hydroxide is added to the aluminum compartment, causing Al(OH)3(s) to precipitate. After precipitation of Al(OH)3 has ceased, the concentration of OH is 1.0 104 M and the measured cell potential is 1.82 V. Calculate the Ksp value for Al(OH)3. Al(OH)3(s)Al3+(aq)+3OH(aq)Ksp=?arrow_forward
- Order the following oxidizing agents by increasing strength under standard-state conditions: Mg2+(aq), Hg2+(aq), Pb2+(aq).arrow_forwarda Calculate the equilibrium constant for the following reaction at 25C. Sn(s)+Pb2+(aq)Sn2+(aq)+Pb(s) The standard cell potential of the corresponding voltaic cell is 0.010 V. b If an excess of tin metal is added to 1.0 M Pb2+, what is the concentration of Pb2+ at equilibrium?arrow_forwardAn electrochemical cell is made by placing a zinc electrode in 1.00 L of 0.200 M ZnSO4 solution and a copper electrode in 1.00 L of 0.0100 M CuCl2 solution. a What is the initial voltage of this cell when it is properly constructed? b Calculate the final concentration of Cu2+ in this cell if it is allowed to produce an average current of 1.0 amp for 225 s.arrow_forward
- Consider the following cell reaction at 25C. 2Cr(s)+3Fe2+(aq)2Cr3+(aq)+3Fe(s) Calculate the standard cell potential of this cell from the standard electrode potentials, and from this obtain G for the cell reaction. Use data in Appendix C to calculate H; note that Cr(H2O)63+(aq) equals Cr3+(aq). Use these values of H and G to obtain S for the cell reaction.arrow_forwardAn electrochemical cell consists of a nickel metal electrode immersed in a solution with [Ni2+] = 1.0 M separated by a porous disk from an aluminum metal electrode. a. What is the potential of this cell at 25C if the aluminum electrode is placed in a solution in which [Al3+] = 7.2 103 M? b. When the aluminum electrode is placed in a certain solution in which [Al3+] is unknown, the measured cell potential at 25C is 1.62 V. Calculate [Al3+] in the unknown solution. (Assume Al is oxidized.)arrow_forward
 General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
 Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning





