
Concept explainers
(a)
The angular velocity and force exerted on the hands of the gymnast after he has rotated through 90°.
Answer to Problem 17.20P
Explanation of Solution
Given:
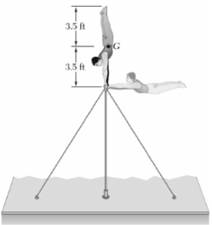
Calculation:
Position 1: Directly above the bar.
Elevation:
Potential energy:
Speeds:
Kinetic energy:
Position 2: Body at level of bar after rotating 90°.
Elevation:
Potential energy:
Speeds:
Kinetic energy:
Applying Principle of conservation of energy
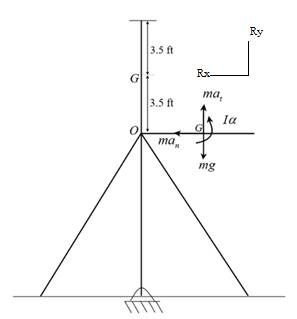
From the kinematics of figure:
Taking moment about point O,
Now,
Taking horizontal reaction,
Vertical reaction,
Conclusion:
The angular velocity and force exerted on the hands of the gymnast is
(b)
The angular velocity and force exerted on the hands of the gymnast after he has rotated through 180°.
Answer to Problem 17.20P
Explanation of Solution
Given:
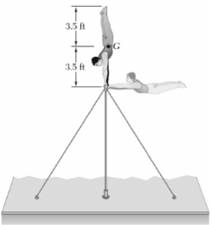
Calculation:
Position 3: Directly below the bar after rotating 180°.
Elevation:
Potential energy:
Speeds:
Kinetic energy:
Applying Principle of conservation of energy
From the kinematics of figure:
Taking moment about point O,
Now,
Taking horizontal reaction,
Vertical reaction,
Conclusion:
The angular velocity and force exerted on the hands of the gymnast is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics
- The uniform rectangular plate is released from rest in the position shown. Determine the maximum angular velocity w during the ensuing motion. Friction at the pivot is negligible. b 2.4 b Answer: w - i | be|arrow_forwardThe 40-kg gymnast drops from her maximum height of h = 0.5 m straight down to the bar as shown. Her hands hit the bar and clasp onto it, and her body remains straight in the position shown. Her center of mass is 0.75 meters away from her hands, and her mass moment of inertia about her center of mass 7.5 kg.m2. is Assuming that friction between the bar and her hands is negligible and that she remains in the same position throughout the swing, determine her angular velocity when she swings around to 0 = 135°.arrow_forwardSHOW COMPLETE STEP by STEP SOLUTION for an UPVOTE The small end rollers of the 8-lb uniform slender bar (length = 4 ft) are constrained to move in the slots, which lie in the vertical plane. At the instant when θ = 30°, the velocity of roller A is 12ft/s down the vertical slot. Determine the angular acceleration of the bar, the acceleration of mass center G, and the reactions of points A and B, under the action of the 6-lb force P. Neglect the friction and the mass of the small rollers.arrow_forward
- The 30-kg turbine disk has a centroidal radius of gyration of 175 mm and is rotating clockwise at a constant rate of 60 rpm when a small blade of weight 0.5 N at point A becomes loose and is thrown off. Neglecting friction, determine the change in the angular velocity of the turbine disk after it has rotated through (a ) 90°, (b ) 270°.arrow_forwardDynamic Problem, reply as soon as posible. The double pulley system weighs 30 lbs. and has a 6.5-inch center radius of gyration. Cylinders A and B areconnected to the double pulley by cords that wrap around the circles whose radii are shown. Thecoefficient of kinetic friction between block B and the surface is 0.25. If the system is released from rest atposition shown, determine:A) The velocity of cylinder A just before hitting the ground.B) The total distance cylinder B travels before coming to rest.arrow_forwardEnd A of the 8-kg uniform rod AB is attached to a collar that can slide without friction on a vertical rod. End B of the rod is attached to a ver- tical cable BC. If the rod is released from rest in the position shown, determine immediately after release (a) the angular acceleration of the rod, (b) the reaction at A. Please show clear diagrams.arrow_forward
- Part A The 21-kg roll of paper has a radius of gyration kA = 90 mm about an axis passing through point A. It is pin supported at both ends by two brackets AB. The roll rests against a wall for which the coefficient of kinetic friction is u = 0.2. Neglect the mass of paper that is removed. (Figure 1) Determine the magnitude of the constant vertical force F that must be applied to the roll to pull off 1 m of paper in t = 3 s starting from rest. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. TH HẢ ? F = Value Units Submit Request Answer Provide Feedback Figure < 1 of 1 300 mm 125 mmarrow_forwardPart A The 100-kg spool is resting on the inclined surface for which the coefficient of kinetic friction is u. = 0.11. The radius of gyration about the mass center is kg = 0.28 m. (Figure 1) Determine the angular velocity of the spool, measured clockwise, when t = 6 s after it is released from rest. Express your answer using three significant figures. Enter positive value if the angular velocity is clockwise and negative value if the angular velocity is counterclockwise. vec W = rad/s Submit Previous Answers Request Answer X Incorrect; Try Again; 4 attempts remaining Provide Feedback Ne Figure < 1 of 1 0.4 m 0.2 m 30°arrow_forwardTitle The uniform slender rod has a mass 15 kg Determine the horizontal and vertical components of... Description The uniform slender rod has a mass 15 kg Determine the horizontal and vertical components of reaction at the pin O , and the angular acceleration of the rod just after the cord is cut.arrow_forward
- 5. An 80 kg gymnast dismounts from a high bar. He starts the dismount at full extension, then tucks to complete a number of revolutions before landing. His moment of inertia when fully extended can be approximated as a rod of length 1.8 m and when in the tuck a rod of half that length. If his rotation rate at full extension is 1.0 rev/s and he enters the tuck when his center of mass is at 3.0 m height moving horizontally to the floor, how many revolutions can he execute if he comes out of the tuck at 1.8 m height? High bar 1.8 m 3 m ANS. Moment of inertia at full extension, I = 21.6 kg-m^2 Moment of inertia at the tuck I' = 5.4 kg-m^2 Angular velocity at the tuck = 4 rev/sec Time interval in the tuck = 0.5 sec i.e. In 0.5 s, he will be able to execute two revolutions at 4.0 rev/s.arrow_forwardA 1-kg bar is held by a cable at one end, and then released from the other while in the horizontal position as shown. Assume the mass of the cable is negligible. Determine the following: (a) Draw the free body and kinetic diagrams of the bar showing the acceleration of the centre of gravity, the angular acceleration of the bar, and the acceleration of point B. C 1 kg 30° B A 500 mmarrow_forwardProblem 19.8 The assembly weighs 5.0 lb and has a radius of gyration kg = 0.59 ft about its center of mass G. The kinetic energy of the assembly is 26 ft-lb when it is in the position shown. (Figure 1) Figure 1 of 1 > 0.8 ft 1 ft 1 ft 3 of 17 Review Part A If it rolls counterclockwise on the surface without slipping, determine its linear momentum at this instant. Express your answer using three significant figures. |VD| ΑΣΦ | Η vec • L = slug ft/s Submit Request Answer Provide Feedback Next >arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





