
Concept explainers
(a)
To graph: The
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Hooke’s law states that the force
| Force, | Elongation, |
Graph:
To graph the points on scatter plot, follow the steps using graphing calculator.
First press the
Go to
Now, press the
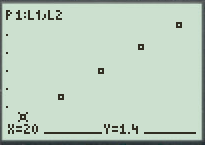
Figure (1)
(b)
To find: The equation of line that seems to best fit for the data.
(b)
Answer to Problem 19E
The equation of line that seems to best fit for the data is equal to
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Hooke’s law states that the force
| Force, | Elongation, |
Calculation:
Assume that the line is equal to
As given the value of
Substitute
Substitute
Subtract both the equations.
Substitute
Therefore, the equation of line that seems to best fit for the data is equal to
(c)
To find: The linear model for the data with the help of regression of graphing utility.
(c)
Answer to Problem 19E
The linear model for the data is equal to
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Hooke’s law states that the force
| Force, | Elongation, |
Calculation:
For the regression linear model of data follow the steps below:
First press the
Go to
Now enter the keystrokes
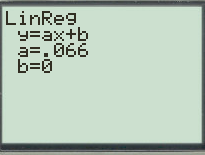
Figure(1)
Therefore, the linear model for the data is equal to
(d)
To find: The elongation of the spring when a force of
(d)
Answer to Problem 19E
The elongation of the spring when a force of
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Hooke’s law states that the force
| Force, | Elongation, |
Calculation:
As found in part(c), the model for the best fit of data is equal to
Substitute
Therefore, the elongation of the spring when a force of
Chapter 1 Solutions
Precalculus with Limits: A Graphing Approach
- Which degenerate conic is formed when a double cone is sliced through the apex by a plane parallel to the slant edge of the cone?arrow_forward1/ Solve the following: 1 x + X + cos(3X) -75 -1 2 2 (5+1) e 5² + 5 + 1 3 L -1 1 5² (5²+1) 1 5(5-5)arrow_forwardI need expert handwritten solution.to this integralarrow_forward
- Example: If ƒ (x + 2π) = ƒ (x), find the Fourier expansion f(x) = eax in the interval [−π,π]arrow_forwardExample: If ƒ (x + 2π) = ƒ (x), find the Fourier expansion f(x) = eax in the interval [−π,π]arrow_forwardPlease can you give detailed steps on how the solutions change from complex form to real form. Thanks.arrow_forward
- Examples: Solve the following differential equation using Laplace transform (e) ty"-ty+y=0 with y(0) = 0, and y'(0) = 1arrow_forwardExamples: Solve the following differential equation using Laplace transform (a) y" +2y+y=t with y(0) = 0, and y'(0) = 1arrow_forwardπ 25. If lies in the interval <0arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





