
Concept explainers
A bowler projects an 8-in.-diameter ball weighing 12 lb along an alley with a forward velocity v0 of 15 ft/s and a backspin

(a)
Find time
Answer to Problem 16.71P
Time
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Mass
Radius
Initial velocity
Friction coefficient
Angular velocity
Concept used:
Following formula is used:
1. Sum of horizontal forces,
2. Sum of moments about mass center,
Calculation:
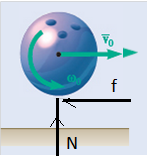
Friction force,
Sum of horizontal forces,
Sum of moments about mass center,
Velocity equation,
Angular velocity equation,
From above both equation,
Conclusion:
Thus we get,
Time
(b)
Find speed of ball at that time.
Answer to Problem 16.71P
Speed
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Mass
Radius
Initial velocity
Friction coefficient
Angular velocity
Concept used:
Following formula is used:
1. Sum of horizontal forces,
2. Sum of moments about mass center,
Calculation:
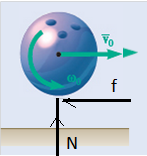
Friction force,
Sum of horizontal forces,
Sum of moments about mass center,
Velocity equation,
Angular velocity equation,
From above both equation,
Speed
Conclusion:
Thus we get,
Speed
(c)
Find distance travelled by ball.
Answer to Problem 16.71P
Distance travelled
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Mass
Radius
Initial velocity
Friction coefficient
Angular velocity
Concept used:
Following formula is used:
1. Sum of horizontal forces,
2. Sum of moments about mass center,
Calculation:
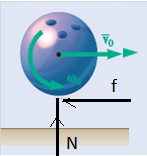
Friction force,
Sum of horizontal forces,
Sum of moments about mass center,
Velocity equation,
Angular velocity equation,
From above both equation,
Distance travelled,
Conclusion:
Thus we get,
Distance travelled
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
Vector Mechanics For Engineers
- d₁ = = Two solid cylindrical road AB and BC are welded together at B and loaded as shown. Knowing that 30mm (for AB) and d₂ 50mm (for BC), find the average normal stress in each road and the total deformation of road AB and BC. E=220GPa H.W 5.3 60kN A For the previous example calculate the value of force P so that the point A will not move, and what is the total length of road AB at that force? P◄ A 125kN 125kN 0.9m 125kN 125kN 0.9m B B 1.3m 1.3marrow_forwardClass: B Calculate the load that will make point A move to the left by 6mm, E-228GPa The cross sections of the rods are as shown in fig. below. 183 P- Solution 1.418mm 200mm 80mm 3P- 18.3 A 080mm B 200mm 3P- 0.9m إعدادات العرض 1.3m 4.061mmarrow_forwardH.W6 Determine the largest weight W that can be supported by two wires shown in Fig. P109. The stress in either wire is not to exceed 30 ksi. The cross- sectional areas of wires AB and AC are 0.4 in2 and 0.5 in2, respectively. 50° 30° Warrow_forward
- Find equation of motion and natural frequency for the system shown in fig. by energy method. H.W2// For the system Fig below find 1-F.B.D 2-Eq.of motion 8wn 4-0 (5) m. Jo marrow_forward2. Read the following Vernier caliper measurements. (The scales have been enlarged for easier reading.) The Vernier caliper is calibrated in metric units. (a) 0 1 2 3 4 5 سلسلسله (b) 1 2 3 4 5 6 سلسل (c) 1 23456 (d) 1 2 3 4 5 6 سلسلسarrow_forwardExplain why on the interval 0<x<1000 mm and 1000<x<2000mm, Mt is equal to positive 160 Nm, but at x= 0mm and x=1000mm Mt is equal to -160 Nm (negative value!). What is the reason for the sign change of Mt?arrow_forward
- 20 3. 2-233 2520 Тр Gears 1079 A pair of helical gears consist of a 20 teeth pinion meshing with a 100 teeth gear. The pinion rotates at Ta 720 r.p.m. The normal pressure angle is 20° while the helix angle is 25°. The face width is 40 mm and the normal module is 4 mm. The pinion as well as gear are made of steel having ultimate strength of 600 MPa and heat treated to a surface hardness of 300 B.H.N. The service factor and factor of safety are 1.5 and 2 respectively. Assume that the velocity factor accounts for the dynamic load and calculate the power transmitting capacity of the gears. [Ans. 8.6 kWarrow_forward4. A single stage helical gear reducer is to receive power from a 1440 r.p.m., 25 kW induction motor. The gear tooth profile is involute full depth with 20° normal pressure angle. The helix angle is 23°, number of teeth on pinion is 20 and the gear ratio is 3. Both the gears are made of steel with allowable beam stress of 90 MPa and hardness 250 B.H.N. (a) Design the gears for 20% overload carrying capacity from standpoint of bending strength and wear, (b) If the incremental dynamic load of 8 kN is estimated in tangential plane, what will be the safe power transmitted by the pair at the same speed?arrow_forwardDetermine the stress in each section of the bar shown in Fig. when subjected to an axial tensile load shown in Fig. The central section is 30 mm hollow square cross- section; the other portions are of circular section, their diameters being indicated What will be the total deformation of the bar? For the bar material E = 210GPa. 20mi О 30mm 30mmm 2.6 15mm 30kN 1 2 10kN - 20kN 3 -329 91mm 100mm 371mmarrow_forward
- Calculate the load that will make point A move to the left by 6mm, E=228GPa. The diameters of the rods are as shown in fig. below. 2P- PA 80mm B 200mm 2P 0.9m 1.3m.arrow_forwardIf the rods are made from a square section with the dimension as shown. Calculate the load that will make point A move to the left by 6mm, E=228GPa. 2P- P A 80mm B 200mm 2P 0.9m 1.3marrow_forward3. 9. 10. The centrifugal tension in belts (a) increases power transmitted (b) decreases power transmitted (c) have no effect on the power transmitted (d) increases power transmitted upto a certain speed and then decreases When the belt is stationary, it is subjected to some tension, known as initial tension. The value of this tension is equal to the (a) tension in the tight side of the belt (b) tension in the slack side of the belt (c) sum of the tensions in the tight side and slack side of the belt (d) average tension of the tight side and slack side of the belt The relation between the pitch of the chain (p) and pitch circle diameter of the sprocket (d) is given by 60° (a) p=d sin (c) p=d sin (120° T where T Number of teeth on the sprocket. 90° (b) p=d sin T 180° (d) p=d sin Tarrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





