
A 15-ft beam weighing 500 Ib is lowered by mean of two cables unwinding from overhead cranes. As the beam approaches the ground, the crane operators apply brakes to slow the unwinding motion. Knowing that the deceleration of cable A is 20 ft/s2 and the deceleration of cable B is 2 ft/s2, determine the tension in each cable.
The tension in each cable.
Answer to Problem 16.60P
The tension in cable
The tension in cable
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The length of the beam is
The below figure represent the kinetics of the beam.
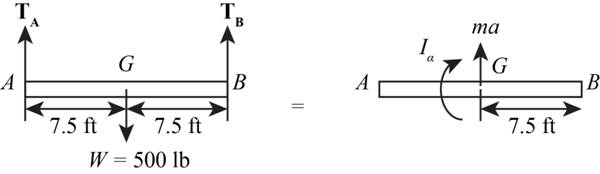
Figure-(1)
Write the expression of total force applied on the beam.
Here, the mass of the beam is
Consider the tension in the cable
Write the expression of deceleration of cable
Here, the acceleration of cable
Write the expression of total acceleration on the beam.
Here, the acceleration of the cable
Write the expression of moment of inertia of beam.
Here, the mass of the slender rod is
Write the expression of mass of the rod.
Here, the weight of the beam is
Write the expression of total moment about point
Here, the effective moment is
Write the expression of moment about point
Here, the tension in the cable
Write the expression of effective moment about point
Here, the angular acceleration of the rod is
Write the expression of generated torque in the beam.
Here, the of inertia of beam is
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Write the expression of total force applied on the beam by equilibrium of the beam as shown in Figure-(1).
Substitute
Calculation:
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Conclusion:
The tension in cable
The tension in cable
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics
- 1.A person is to be released from rest on a swing pulled away from the vertical by an angle of 20.0°. The two frayed ropes of the swing are 2.75 m long, and will break if the tension in either of them exceeds 355 N. (a) What is the maximum weight the person can have and not break the ropes? (b)If the person is released at an angle greater than 20.0°, does the maximum weight increase, decrease, or stay the same? (c)Solve in Newton Law, Conversation Law, and Work-Kinetic Theorem.arrow_forwardHelparrow_forward3A. A 100-N block on a rough 30o-incline is acted upon by a force P as shown causing it to accelerate at 2 m/s2 up the plane. The coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.30. (a) Draw the FBD of the block (b) Find the magnitude of P.arrow_forward
- To test the deflection of the uniform 125-kg beam the 70-kg boy exerts a pull of 100 N on the rope rigged as shown. Compute the force supported by the pin at the hinge O.arrow_forward10. It can be shown that if a pendulum mass on a string is dropped from a height as shown the finalvelocity will be √2?ℎ. (we did this in the energy lab) This is because allof the mass is located at the end of the string giving it a moment ofinertia of mL2. If instead a solid rod of the same mass and length wasallowed to swing the same distance, and knowing the moment ofinertial to be 1/3 mL2 what is the velocity of the very tip of the rod at thebottom? (if you want you can use a mass of 1 and a length of 1, hint: choose PEG carefully)arrow_forwardAsap plzarrow_forward
- Q2) The slotted arm pivots about O and maintains the relation between the motions of sliders A and B and their control rods. Each small pivoted block is pinned to its respective slider and is constrained to slide in its rotating slot. Show that the displacement x is proportional to the reciprocal of y. Then estab- lish the relation between the velocities vA and vg. Also, if v, is constant for a short interval of motion, determine the acceleration of B. b y 'Barrow_forwardQ5 / Two cable are tied together at (c) and are loaded as shown in fig (5). Determine the tension in cable Ac and Bc ? Notice : use the law of sines to solve the question 5. Fig(5) B 75 75° 200 kgarrow_forwardPROBLEM 1 The continuous cable that wraps around the small pulleys at A, B, C, and D has a length of 8m. The springs are both unstretched when d = 4m. Neglect the weight of the pulleys and cords. If the mass of each block is 25 kg and it causes each spring to be stretched by 500 mm, determine 1) the angle 0 when the 2 blocks are applied; (2) the tension on the continuous cable; and (3) the spring constant k (N/m). Use g= 9.81 m/s². k D B d berty so do noe it in any way as if it were roperty so do se it in any way as if it ere A your own. your own. karrow_forward
- Q.5) A steel bar OC with attached spring at B and cable at C can rotate freely in a horizontal plane about support at O as shown below. The spring is upstretched when C is coincident with A. Determine the tension T required to hold the steel bar OC in the 40° position shown as a function of k and L. Neglect the weight of the bar OC and the diameter of the pulley at D. 40° L/2 B m T L/2 25°arrow_forwardThe beam shown is supported by a pin at A and rope BDE as shown. Knowing that L = 1.5 m and that the mass suspended from C is 31 kg, determine the tension in rope BDE and the reactions at A. Enter the magnitude of the tension in rope BDE below, in N to the nearest whole N. (Take g = 9.81 m/s²) 2 m B m E Marrow_forwardPin B weighs 0.1kg and is free to slide in a horizontal plane along therotating arm OC and along the circular slot DE of radius b=500mm.Neglecting friction and assuming that θ= 15 rad/s andθ=250 rad/s2 for the position θ= 20o , determine for that position(a) the radial and transverse components of the resultant forceexerted on pin B, (b) the forces P and Q exerted on pin B,respectively, by rod OC and the wall of slot DE.arrow_forward
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
