
Concept explainers
Gear A weighs 1 lb and has a radius of gyration of 1.3 in.; gear B weighs 6 lb and has a radius of gyration of 3 in.; gear C weighs 9 lb and has a radius of gyration of 4.3 in. Knowing a couple M of constant magnitude of 40 lb·in. is applied to gear A, determine (a) the angular acceleration of gear C, (b) the tangential force that gear B exerts on gear C.
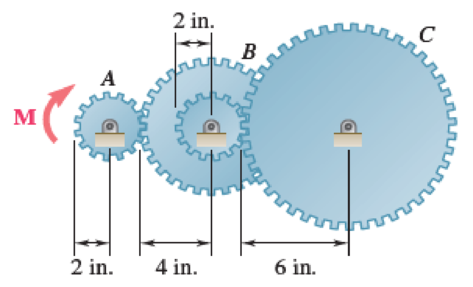
Fig. P16.37
(a)
Find the angular acceleration of the gear C
Answer to Problem 16.37P
The angular acceleration of the gear C
Explanation of Solution
The weight of the gear A
The weight of the gear B
The weight of the gear C
The radius of gyration of the gear A
The radius of gyration of the gear B
The radius of gyration of the gear C
The couple of the constant magnitude applied to gear A (M) is
The radius of the gear A
The radius of the outer gear B
The radius of the inner gear B
The radius of the gear C
The angular acceleration of the gear A is
The angular acceleration of the gear B is
The angular acceleration of the gear C is
Calculation:
Consider the acceleration due to gravity (g) is
Convert the unit of the couple (M):
Convert the unit of the radius of the gear A
Convert the unit of the radius of the outer gear B
Convert the unit of the radius of the inner gear B
Convert the unit of the radius of the gear C
Calculate the mass of the gear A
Substitute
Calculate the mass of the gear B
Substitute
Calculate the mass of the gear C
Substitute
Calculate the mass moment of inertia of the gear A
Substitute
Calculate the mass moment of inertia of the gear B
Substitute
Calculate the mass moment of inertia of the gear C
Substitute
The point of contact between A and B:
Substitute
The point of contact between B and C:
Substitute
Therefore, the angular acceleration of the gear A is
Show the free body diagram of the gear A as in Figure 1.
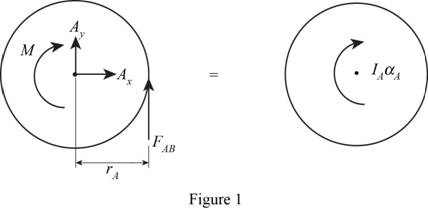
Here,
Refer to Figure 1.
Calculate the moment about point A by applying the equation of equilibrium:
Substitute
Show the free body diagram of the gear B as in Figure 2.
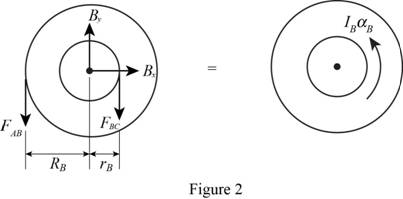
Here,
Refer to Figure 2.
Calculate the moment about point B by applying the equation of equilibrium:
Substitute
Show the free body diagram of the gear C as in Figure 3.
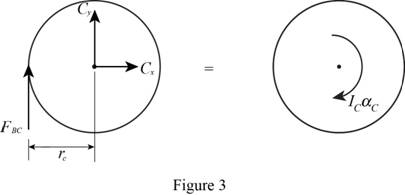
Here,
Refer to Figure 3.
Calculate the moment about point C by applying the equation of equilibrium:
Calculate the angular acceleration of the gear C
Substitute
Hence, the angular acceleration of the gear C
(b)
Find the tangential force which gear B exerts on gear C.
Answer to Problem 16.37P
The tangential force which gear B exerts on gear C
Explanation of Solution
The weight of the gear A
The weight of the gear B
The weight of the gear C
The radius of gyration of the gear A
The radius of gyration of the gear B
The radius of gyration of the gear C
The couple of the constant magnitude applied to gear A (M) is
The radius of the gear A
The radius of the outer gear B
The radius of the inner gear B
The radius of the gear C
The angular acceleration of the gear A is
The angular acceleration of the gear B is
The angular acceleration of the gear C is
Calculation:
Refer the part (a).
Calculate the tangential force which gear B exerts on gear C
Substitute
Hence, the tangential force which gear B exerts on gear C
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Automotive Technology: Principles, Diagnosis, And Service (6th Edition) (halderman Automotive Series)
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals and Applications
Problem Solving with C++ (10th Edition)
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
- ४ B: Find the numerical solution for the 2D equation below and calculate the temperature values for each grid point shown in Fig. 2 (show all steps). (Do only one trail using following initial values and show the final matrix) [T1] T₂ T3 [T] 1 = [0] 0 0 d dx dx) (ka)+4(ka) = dy -20xy, k = 1 + 0.3 T ge L=3cm, 4x= Ay B.Cs.: at x=0=LT=0°C at y=0-L T=10°C Fig. (2)arrow_forward: +0 العنوان use only Two rods fins) having same dimensions, one made orass (k = 85 Wm K) and the mer of copper (k = 375 W/m K), having of their ends inserted into a furna. At a section 10.5 cm a way from furnace, the temperature of brass rod 120 Find the distance at which the ame temperature would be reached in the per rod ? both ends are ex osed to the same environment. ns 2.05 ۲/۱ ostrararrow_forwardFor the beam show below, draw A.F.D, S.F.D, B.M.D 6 kN/m 1 M B. 3 M Marrow_forward
- 1. Two long rods of the same diameter-one made of brass (k=85w/m.k) and the other made of copper (k=375 w/m.k) have one of their ends inserted into a furnace (as shown in the following figure). Both rods are exposed to the same environment. At a distance of 105 mm from the furnace, the temperature of the brass rod is 120°C. At what distance from the furnace will the same temperature be reached in the copper rod? Furnace 105 mm T₁ Brass rod ⑪ h Too- x2- Ti Copper rodarrow_forward: +0 العنوان use only Two rods fins) having same dimensions, one made orass (k = 85 Wm K) and the mer of copper (k = 375 W/m K), having of their ends inserted into a furna. At a section 10.5 cm a way from furnace, the temperature of brass rod 120 Find the distance at which the ame temperature would be reached in the per rod ? both ends are ex osed to the same environment. ns 2.05 ۲/۱ ostrararrow_forwardمشر on ۲/۱ Two rods (fins) having same dimensions, one made of brass(k=85 m K) and the other of copper (k = 375 W/m K), having one of their ends inserted into a furnace. At a section 10.5 cm a way from the furnace, the temperature brass rod 120°C. Find the distance at which the same temperature would be reached in the copper rod ? both ends are exposed to the same environment. 22.05 ofthearrow_forward
- The composite wall of oven with A= 1m² as in Fig.1 consists of three materials, two of with kA = 20 W/m K and kc = 50 W/m K with thickness, LA=0.3 m, L= 0.15 m and Lc 0.15 m. The inner surface temperature T1=900 K and the outer surface temperature T4 300 K, and an oven air temperature of To=1100 K, h=25 W/m². K. Determine kɛ and the temperatures T2 and T3 also draw the thermal resistance networkarrow_forwardTwo rods (fins) having same dimensions, one made of brass (k = 85 Wm K) and the other of copper (k = 375 W/m K), having one of their ends inserted into a furnace. At a section 10.5 cm a way from the furnace, the temperature of brass rod 120°C. Find the distance at which the same temperature would be reached in the copper rod ? both ends are exposed to the same environment. Ans 22.05arrow_forwardA long wire (k-8 W/m °C.) with ro 5 mm and surface temperature Ts=180°C as shown in Fig.2. Heat is generated in the wire uniformly at a rate of 5 x107 W/m³. If the energy equation is given by: d 11(77) + - =0 k r dr dr Derive an expression for T(r) and determine the temperature at the center of the wire and at r=2 mm. Air Th T KA LA T2 T3 T Fig.1 KB kc 180°C Го Fig.2arrow_forward
- B: Find the numerical solution for the 2D equation below and calculate the temperature values for each grid point shown in Fig. 2 (show all steps). (Do only one trail using following initial values and show the final matrix) T₂ 0 T3 0 I need a real solution, not artificial intelligence locarrow_forwardCan I solve this problem by calculating the initial kinetic energy with respect to G instead of A.arrow_forwardB: Find the numerical solution for the 2D equation below and calculate the temperature values for each grid point shown in Fig. 2 (show all steps). (Do only one trail using following initial values and show the final matrix) T₂ 0 T3 0 locarrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





