
Concept explainers
(a)
To Explain: Random variables to use to convey the net income of the bicycle store.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Deluxe Model mean = 3.2 bikes
Deluxe Model standard deviation = 0.8 bikes
Basic Model price (B) = $120
Basic Model standard deviation = 1.2 bikes
Fixed cost = $200
Deluxe Model price (D) = $150
Basic Model mean = 5.4 bikes
Calculation:
It will display net income as the amount of sales of the simple model motorcycles (B)and deluxe model bikes (D) minus the $200 fixing cost.
Net income 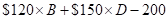
(b)
To find: the mean of the total income.
(b)
Answer to Problem 44E
$928
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Deluxe Model mean = 3.2 bikes
Deluxe Model standard deviation = 0.8 bikes
Basic Model price (B) = $120
Basic Model standard deviation = 1.2 bikes
Fixed cost = $200
Deluxe Model price (D) = $150
Basic Model mean = 5.4 bikes
Calculation:
The Net Income Equation of Part (a), and the B and D variable for the bikes defined for both models, must be used to measure the mean Net Income. The average simple model is 5.4 bikes with the average deluxe model 3.2.
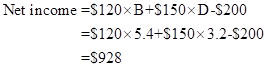
Thus, the mean total income is $928.
(c)
To find: the standard deviation of the total income.
(c)
Answer to Problem 44E
$187.45
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Deluxe Model mean = 3.2 bikes
Deluxe Model standard deviation = 0.8 bikes
Basic Model price (B) = $120
Basic Model standard deviation = 1.2 bikes
Fixed cost = $200
Deluxe Model price (D) = $150
Basic Model mean = 5.4 bikes
Calculation:
The net income equation of part (a) without a fixed cost of $200 is needed to measure the standard variance of net income, since this is the constant variance and the squared price of the units is measured as standard deviation for the two. The standard model deviation is 1.2 motorbikes and 0.8 motorcycles.
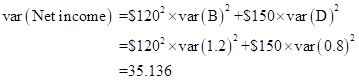
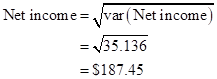
Thus, the standard deviation of the total income is $187.45
(d)
To Explain: that need to create any assumptions in estimating the mean and about the standard deviation.
(d)
Explanation of Solution
In estimating the total net income, it had no calculations to make. However, it had to conclude that the sales of the two motorcycle models were separate, which implies that the selling for one model has little effect on the sell for the other model, when measuring the standard deviation of the net income.
Chapter 16 Solutions
Stats: Modeling the World Nasta Edition Grades 9-12
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
Statistics for Business and Economics (13th Edition)
STATS:DATA+MODELS-W/DVD
Intro Stats, Books a la Carte Edition (5th Edition)
Essentials of Statistics (6th Edition)
Introductory Statistics (10th Edition)
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman





