
(a)
Interpretation:
The order of the reaction should be determined with respect to oxygen atoms.
Concept Introduction:
Rate Law can be expressed as an integrated rate law and a differential rate law.
Differential Rate Law: This describes the change in the concentrations of reactant as a function of time.
Integrated Rate Law: This describes the initial concentrations and the measured concentration of one or more reactants as a function of time.
(a)
Answer to Problem 36E
The reaction is first order reaction with respect to oxygen.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Data is given as:
| Time (s) | |
| 0 | |
The order of reaction can be determined by plotting the graph between
For first order reaction:
For second order reaction:
For zero order reaction:
The given reaction is:
Now, if the reaction is first order with respect to oxygen, then the integrated law is expressed as:
If the reaction is second order with respect to oxygen, then the integrated law is expressed as:
If the reaction is zero order with respect to oxygen, then the integrated law is expressed as:
| Time (s) | ||
| 0 | 22.3327 | |
| 21.36512 | ||
| 20.3376 | ||
| 19.33697 |
The graph between
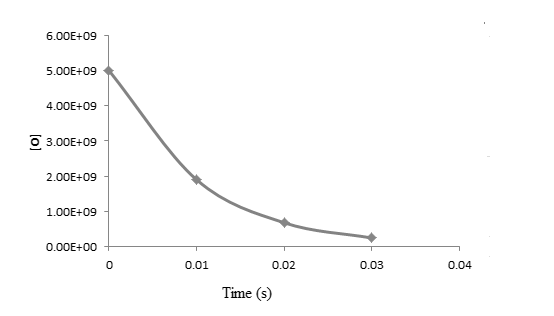 The graph between
The graph between
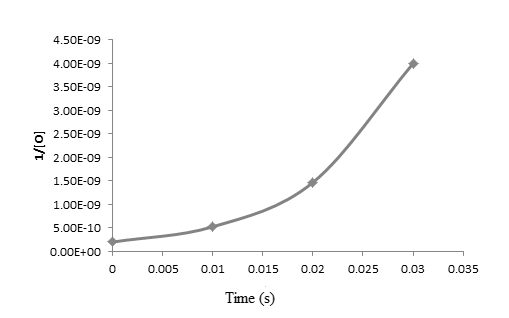
The graph between
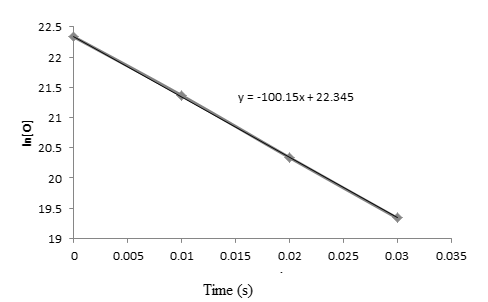
From the above graphs, it is clear that the reaction is first order reaction with respect to oxygen as the graph is straight line graph.
(b)
Interpretation:
The overall rate law and value of rate constant should be calculated.
Concept Introduction:
Rate Law can be expressed as an integrated rate law and a differential rate law.
Differential Rate Law: This describes the change in the concentrations of reactant as a function of time.
Integrated Rate Law: This describes the initial concentrations and the measured concentration of one or more reactants as a function of time.
(b)
Answer to Problem 36E
Rate law is expressed as:
Since, concentration of nitrogen dioxide is more in comparison to oxygen, thus, rate law is written as:
Rate constant for first order reaction is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Data is given as:
| Time (s) | |
| 0 | |
The order of reaction can be determined by plotting the graph between
For first order reaction:
For second order reaction:
For zero order reaction:
The given reaction is:
Rate Law for first is expressed as:
Since, it is given that nitrogen dioxide is present in large amount in comparison to oxygen.
Thus, rate law is expressed as:
Where,
Now, from the graph slope is given as:
Slope =
Put the values from graph,
Slope =
Slope =
Thus, value of
Now,
Put the values,
Thus, rate constant for first order reaction is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Chemical Principles
- 11.93 On a particular day, the ozone level in Milwaukee exceeded the EPAs 1-hour standard of 0.12 ppin by 10 ppb. How many ozone molecules would be present in 1 liter of air at the detection site?arrow_forwardWrite the reaction rate expressions for the reaction below in terms of the disappearance of the reactants and the appearance of products. Give the expressions for the disappearance of the reactants first, in the order written in the chemical equation. Then write the expressions for the appearance of the products in the order written in the chemical equation. Write the expressions in order of appearance in the equation in the form: 1 +* X Δ[Α] At 2H₂(g) + O₂(g) Rate of H₂= Rate of O₂ = Rate of H₂O = 1x X X X where is either a plus OR a minus sign, not both, X is an integer, and A is a chemical species. Do not include the state of matter. 2H₂O(g) A[H₂ At A[0₂] At A[H₂O] At 00 X Śarrow_forwardREIFUNG DISTING Pressure (atm) 1.6 1.4 1.2 1 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0 0 A B 5 10 15 ● · ● 20 25 Time (minutes) 30 35 C D 40 45 00 50arrow_forward
- (a) How is the rate at which ozone disappears related to the rate at which oxygen appears in the reaction 2 O3(g)-------->3 O2(g)?(b) If the rate at which O2 appears, Δ[O2]>Δt, is 6.0 x10-5 M/s at a particular instant, at what rate is O3 disappearing at thissame time, -Δ[O3]>Δt?arrow_forwardStep 1: (slow) Step 2: (fast) = CI The particle models shown above represent a proposed two-step mechanism for the destruction of ozone (O3) in the upper atmosphere. Based on the proposed mechanism, what is the balanced chemical equation for the overall reaction? A O3 (9) + Cl(g) O2(g) + CIO(g) B 2 03(g) + 2 Cl(g) → 2 O2(9) + 2 C1O(g) C) O3(g) + CI(g) + Cl0 (g) → 2 O2(9) + Cl2 (9) 2 03(9) 3 02 (g)arrow_forwardTwo gases X and Y are found in the atmosphere in only trace amounts because they decompose quickly. When exposed to ultraviolet light the half-life of X is 1.50 h, while that of Y is 135. min. Suppose an atmospheric scientist studying these decompositions fills a transparent 10.0 L flask with X and Y and exposes the flask to UV light. Initially, the partial pressure of X is 75.0% greater than the partial pressure of Y. As both gases decompose, will the partial pressure of X ever fall below the partial pressure of Y? yes Ox10 no If you said yes, calculate the time it takes the partial pressure of X to fall below the partial pressure of Y. Round your answer to 2 significant digits.arrow_forward
- The following were collected for the reaction: 2NO(g) + O2(g) → 2NO2(g) Calculate the order of reaction with respect to O2. 1.5 2 1 0arrow_forward2 ClO 2 (aq) + 2 OH - (aq) → ClO 3 - (aq) + ClO 2 - (aq) + H 2O (1) What is the overall order of the reaction?arrow_forwardA certain decomposition reaction has a half-life that depends on the initial concentration of the reactant, and its rate is observed to slow down as the reaction proceeds. Identify which statement is most likely correct for this reaction and explain why the other statements are incorrect. O2(g) + 2 NO(g) → 2 NO2(g) (i)The half-life of the reaction increases as the initial concentration increases. (ii)A doubling of the initial concentration of the reactant results in a quadrupling of the rate. (iii)A plot of the natural log of the concentration of the reactant as a function of time is linear.arrow_forward
- The lifetime of OH is determined by its reaction with trace gases in the atmosphere. The mostabundant trace gases that react with OH via second order reactions are CH4 and CO. Given that k(CH4)= 10^−14.19 cm3/(molecule·sec) and k(CO) = 10^−12.82 cm3/(molecule·sec), please determine the totallifetime of the OH radical with respect to these two reactions. The average tropospheric concentrationsof CH4 and CO are 1.5 ppm and 90 ppb, respectively.arrow_forwardStep 1: (slow) Step 2: O (fast) = CI The particle models shown above represent a proposed two-step mechanism for the destruction of ozone (03) in the upper atmosphere. Based on the proposed mechanism, what is the balanced chemical equation for the overall reaction? 03(9) + Cl(g) → 02(9) + ClO(g) 203(g) + 2C1(g) → 202(9) + 2C10(g) O3(g) + Cl(g) + ClO(g) → 202(g) + Cl2(g) 203(g) → 302(g)arrow_forwardGiven the following plot for the decomposition of N2O5, calculate the frequency factor (A):arrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning

