
(a)
Interpretation:
The stoichiometry concept map is to be drawn and the mass of KHCO3 decomposed is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Stoichiometry measures the amount of reactant and product consumed or formed in a
Answer to Problem 26E
The stoichiometry concept map is shown below.
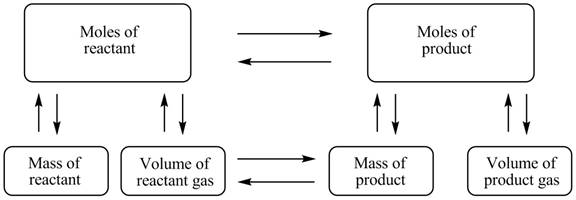
The mass of KHCO3 decomposed is 2.282 g.
Explanation of Solution
It is given that 255 mL of carbon dioxide is produced at STP.
The given chemical reaction is stated below.
KHCO3(s)→K2CO3(aq)+H2O(l)+CO2(g)…(1)
The stoichiometry concept map is shown below.
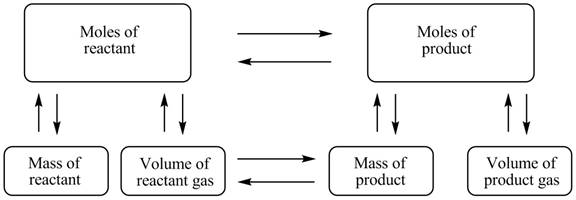
Figure 1
The chemical reaction (1) should be balanced first to calculate the mass of KHCO3 decomposed.
The number of potassium atom and the hydrogen atom are not equal on both sides. A coefficient of 2 is added in front of KHCO3 to balance the chemical reaction.
The balanced equation is stated below.
2KHCO3(s)→K2CO3(aq)+H2O(l)+CO2(g)…(2)
The equation (2) shows that 2 mole of KHCO3 is consumed to form 1 mole of carbon dioxide gas.
At STP the relation between KHCO3 and carbon dioxide gas is shown below.
1 mole of KHCO3=22.4 L CO2
Therefore, the number of moles of KHCO3 is calculated as shown below.
Number of moles of KHCO3=255 mL CO2×1 L1000 mL×1 mol CO222.4 L CO2×2 mol KHCO31 mol CO2=0.02276 mol KHCO3≈0.0228 mol KHCO3
The molar mass of potassium is 39.10 g mol−1.
The molar mass of oxygen is 16.00 g mol−1.
The molar mass of hydrogen is 1.01 g mol−1.
The molar mass of carbon is 12.01 g mol−1.
Total molar mass of KHCO3=(Molar mass of K+Molar mass of H+Molar mass of C+(3×Molar mass of O))=39.10 g mol−1+1.01 g mol−1+12.01 g mol−1+(3×16.00 g mol−1)=39.10 g mol−1+1.01 g mol−1+12.01 g mol−1+48.00 g mol−1=100.12 g mol−1 The mass of KHCO3 gas is calculated from the relation as shown below.
1 mol=Molar mass of KHCO31 mol=100.12 g of KHCO3
The number of moles of KHCO3 is 0.0228 mol.
The mass for 0.0228 mol of KHCO3 is calculated as shown below.
Mass of KHCO3=0.0228 mol×100.12 g KHCO31 mol KHCO3=2.282 g KHCO3
Therefore, the mass of KHCO3 is 2.282 g.
The stoichiometry concept map is shown in Figure 1. The mass of KHCO3 decomposed is 2.282 g.
(b)
Interpretation:
The stoichiometry concept map is to be drawn and the mass of the K2CO3 produced is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Stoichiometry measures the amount of reactant and product consumed or formed in a chemical reaction. It gives the relationship between the reactants and products. Stoichiometry concept maps are used to determine the relation of reactant and product in terms of stoichiometry.
Answer to Problem 26E
The stoichiometry map is shown below.
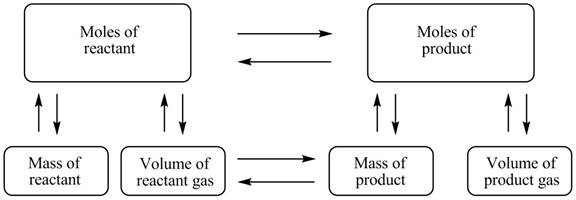
The mass of K2CO3 produced is 1.57 g.
Explanation of Solution
The stoichiometry concept mass is shown below.
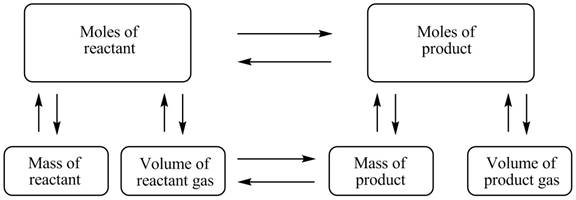
Figure 1
The number of potassium atom and the hydrogen atom are not equal on both sides. A coefficient of 2 is added in front of KHCO3 to balance the chemical reaction.
The balanced equation is stated below.
2KHCO3(s)→K2CO3(aq)+H2O(l)+CO2(g)…(2)
The equation (2) shows that 2 mole of KHCO3 is consumed to form 1 mole of K2CO3.
The molar mass of KHCO3 is calculated in part (a) is 100.12 g mol−1.
The mass calculated of KHCO3 in part (a) is 2.282 g.
The number of moles of K2CO3 is calculated as shown below.
Number of moles of K2CO3=2.282 g KHCO3×1 mol KHCO3100.12 g KHCO3×1 mol K2CO32 mol K2CO3=0.01139 mol≈0.0114 mol
The molar mass of potassium is 39.10 g mol−1.
The molar mass of oxygen is 16.00 g mol−1.
The molar mass of carbon is 12.01 g mol−1.
Total molar mass of K2CO3=((2×Molar mass of K)+Molar mass of C+(3×Molar mass of O))=(2×39.10 g mol−1)+12.01 g mol−1+(3×16.00 g mol−1)=78.20 g mol−1+12.01 g mol−1+48.00 g mol−1=138.21 g mol−1
The mass of K2CO3 gas is calculated from the relation as shown below.
1 mol=Molar mass of K2CO31 mol=138.21 g of K2CO3
The number of moles of K2CO3 is 0.0114 mol.
The mass for 0.0114 mol of K2CO3 is calculated as shown below.
Mass of K2CO3=0.0114 mol×138.21 g K2CO31 mol K2CO3=1.57 g K2CO3
Therefore, the mass of K2CO3 is 1.57 g.
The mass of K2CO3 produced after the reaction is 1.57 g.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Introductory Chemistry: Concepts and Critical Thinking (8th Edition)
- - Consider the data in the Table below to answer the following questions: Acidities of Substituted Benzoic and Acetic Acids pk,s at 25C Y-CH COOH Y Y - CH₂COOH meta para H 4.75 4.19 4.19 2.47 3.64 3.55 3.57 4.09 4.46 CN OCH 3 A. Draw the structure of the strongest acid in the table above. B. Explain why cyanoacetic acid and methoxyacetic acid are more acidic than their correspondingly substituted benzoic acid counterparts.arrow_forwardDraw the curved arrow mechanism for this reaction starting with 2-propanol in sulfuric acid. Show all nonzero formal charges and all nonbonded electrons in each step. Species not involved in a particular step do not need to be included in that step, and resonance forms do not need to be shown. Note that the alcohol is in much higher concentration than H₂O in this reaction. Harrow_forwardProvide reactions showing the following conversions: * see imagearrow_forward
- . Draw structures corresponding to each of the following names or Provide IUPAC names for each of the ollowing structures [for 4 ONLY]. A. 2-propylpentanoic acid. B. m-chlorobenzoic acid. D. C. O O HOC(CH2)3COH glutaricadd OH OH H3C CH3 C=C H COOH salicylicadd tiglicadd CH₂C=N Joe Marrow_forward. Provide structure(s) for the starting material(s), reagent(s) or the major organic product(s) of each of the ollowing reactions or sequences of reactions. Show all relevant stereochemistry [five only] A. O B. OET CH3 1. LIAIH, ether 2 H₂O O (CH3)2CH-C-CI + 0 0 ether (CH3)2CH-C-O-C-CH3 CH3 C. 0 OH HO CH3 ° Clarrow_forwardHow would you prepare each of the following compounds using either an acetoacetic ester synthesis or a alonic ester synthesis? Show all intermediate structures and all reagents.[Three only] A. B. COOH OH C. D. 0 H2C CHCH2CH2CCH3arrow_forward
- Fats and greases have mostly aliphatic regions which are hydrophobic. Provide a schematic of howsoaps/detergents remove fats and grease from the soiled material. * see imagearrow_forwardWhat chemical has the common name "lye"? Pick one of the 3 esters and show the hydrolysis mechanism to make a carboxylic acid. The organic “R” should be used to limit the redrawing time of the entire molecule. * see imagearrow_forwardProvide the products for each reaction. There are two and they are not related. *see imagearrow_forward
- d. a phenylal Give the major organic product(s) of each of the following reactions or sequences of reactions. Show all levant stereochemistry. [three only] 0 A. B. CH3 Bra CH3COOH OH 1. Br₂, PBrz 2 H₂O 12arrow_forward2arrow_forwardShow how the following conversions might be accomplished. Show all reagents and all intermediate ructures. More than one step may be required [2 ONLY]: A. B. ° C. OH 0 OH 0arrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
 General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning





