
Concept explainers
Problem Set
Anchoring Cells to the ECM. Animal cells attach to several different kinds of proteins within the ECM.
(a) Briefly explain how the various domains of the fibronectin molecule (see Figure 15-16) or the laminin molecule (see Figure 15-18) are important for their function.
(b) Historically, an important strategy for disrupting the adhesion of integrins to their ligands is by using a synthetic peptide that mimics the binding site on the ECM molecule to which the integrin attaches. In the case of fibronectin, the amino acid sequence is arginine-glycine-aspartate (when written using the single letter designation for each amino acid, this sequence becomes RGD). Explain why addition of such synthetic peptides would disrupt binding of cells to their normal substratum.
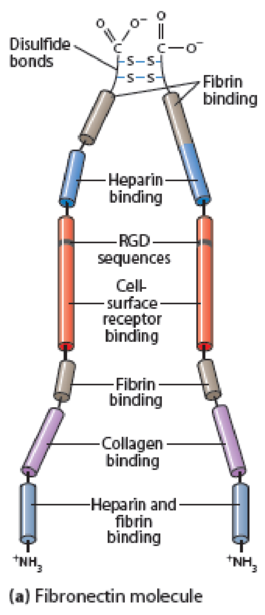
Figure 15-16 Fibronectin Structure. (a) A fibronectin molecule consists of two nearly identical polypeptide chains joined by two disulfide bonds near their carboxyl ends. Each polypeptide chain is folded into a series of domains linked by short, flexible segments. These domains have binding sites for ECM components or for specific receptors on the cell surface, including the tripeptide sequence RGD (arginine-glycine-aspartate), which is recognized by integrins. Besides the binding activities noted, fibronectin has binding sites for heparan sulfate, hyaluronate, and gangliosides (glycosphingolipids that contain sialic acid groups). (b) Myoblast cells on an ECM containing fibronectin in vitro, immunostained for fibronectin (green) and for DNA in the nucleus (blue).
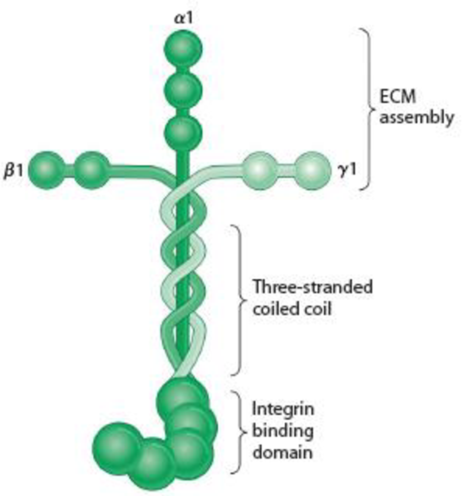
Figure 15-18 Laminin and the Basal Lamina. (a) A laminin molecule consists of three large polypeptides—α, β, and γ—joined by disulfide bonds into a crosslinked structure. A portion of the long arm consists of a three-stranded coil. Domains on the ends of the α chain are recognized by cell surface receptors; those at the ends of the two arms of the cross are specific for type IV collagen. The cross-arms also contain laminin-laminin binding sites, which enable laminin to form large aggregates. Laminin also contains binding sites for heparin, heparan sulfate, and entactin (not shown). (Adapted with permission from Macmillan Publishers Ltd: Fig. 1 from M. P. Marinkovich, “Laminin 332 in Squamous-Cell Carcinoma,” Nature Reviews Cancer 7:370-380. Copyright 2007.) (b) Laminin assembled into a basal lamina. Laminin associates with type IV collagen, perlecan, nidogen, and other components to form a mat of extracellular matrix. Cells attach to the basal lamina using integrins.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 15 Solutions
Becker's World of the Cell (9th Edition)
- Membrane Protein Insertion in the ER This figure displays five small hypothetical proteins. The a-helix secondary structure of the protein is bracketed and the number of amino acids in the helix is indicated. If the hypothetical ER localization sequence is green-yellow-yellow-green-yellow-red, what protein could potentially be a transmembrane protein in the plasma membrane? = Acidic = Basic = Polar (uncharged) O = Hydrophobic CO₂ T 20 CO2 T 20 NH₂ A. T 20 NH₂ B. NH₂ C. T 20 NH₂ D. NH₂ E. tot 10arrow_forwardExercise 5 Membrane receptors are proteins that are incorporated in the cytoplasmic membrane of a cell, allowing the detection of specific molecules such as (hormones, growth factor) and triggering a cascade of biochemical Synthesis of protein reactions. The adjacent schema represents the steps of the synthesis of these membrane receptors. 1. Label the structures from a to f. In order to study the biosynthesis and secretion of this protein (membrane receptors), a solution containing radioactive amino acid was injected in the blood of an animal. Samples of certain cells were taken at regular intervals of time. The intensity of radioactivity was measured in different cellular organelles. 2000 The table below represents the variations of the quantity of a membrane protein in different parts of the cell, as function of time. Time (min) 15 40 50 Structure X 26 12 2 1 Structure Z 0. 6. 10 6. Structure Y 0. 10 24 2. Represent the obtained results in the form 3. 3.1. Analyze the obtained…arrow_forwardNeed help, please. I know the answer isn't mitotic spindle or secretory and endocytic vesicle transport. I think the answer is option C, axon stiffening, and neurotransmitter vesicle transport, but I am not 100% sure. What function of the microtubule motor proteins dynein and kinesin is blocked by the use of colchicine to treat gout? Select one: O a. mitotic spindle b. secretory and endocytic vesicle transport c. axon stiffening and neurotransmitter vesicle transport O d. ER, Golgi, and mitochondria movementarrow_forward
- Multipass transmembrane proteins synthesized by ribosomes on the rough endoplasmic reticulum generally have which of the following arrangements of start-transfer and stop-transfer signals? multiple start signals and multiple stop signals (to allow multiple transmembrane regions) multiple start signals, but only one stop signal (to allow only one transmembrane region) only one start signal, but multiple stop signals (to allow only one transmembrane region) only one start signal, and only one stop signal (to allow only one transmembrane region) only one stop signal, and only one start signal (to allow only one transmembrane region)arrow_forwardBiolink 'Drugs and their Conformations' (a) Which drug is more likely to produce multiple physiological effects: a drug with conformational flexibility or a drug with a rigid structure? Explain. (b) Using the example of HIV drugs, describe how conformation flexbility helps us keep up with drug resistance.arrow_forwardGive typed full explanation Bradykinin is a plasma peptide and a potent vasodilator. It is derived from a large precursor called kininogen. Bradykinin has the following structure: Arg-Pro-Pro-Gly-Phe-Ser-Pro-Phe-Arg. Which amino acids in bradykinin have reactive functional groups in their side chains? What are these reactive functional groups? What does the name "kininogen" indicate?arrow_forward
- Protein purification table: A 50 ml crude skeletal muscle extract contains 32mg of protein per ml. Ten ul of the extract catalyzes a reaction at a rate of 0.14 µmol product per minute. The extract was fractionated by ammonium sulfate precipitation, and the fraction precipitating between 20% and 40% saturation was dissolved in 10ml. The solution contains 50mg/ml protein. Ten ul of this purified fraction catalyzes the reaction at a rate of 0.65 µmol/min (a) What is the degree of purification (fold purification)? (b) What is the percent yield of the enzyme recovered in the purification?arrow_forwardDynamic instability causes microtubules either to grow or to shrink rapidly. Consider an individual microtubule that is in its shrinking phase. What would need to happen at the end of the microtubule in order for it to stop shrinking and to start growing again? Be specific! What would happen if only GDP, but no GTP, were present in the solution? What would happen if the solution contained an analog of GTP that cannot be hydrolyzed?arrow_forwardFrog poison. Batrachotoxin (BTX) is a steroidal alkaloid from the skin of Phyllobates terribilis, a poisonous Colombian frog (the source of the poison used on blowgun darts). In the presence of BTX, Na+Na* channels in an excised patch stay persistently open when the membrane is depolarized. They close when the membrane is repolarized. Which transition is blocked by BTX?arrow_forward
- Participation Problem: Chapter 10, Problem 4: The lipid portion of a typical bilayer is about 30 Å thick. (a) Calculate the minimum number of residues in an a-helix required to span this distance. (b) Calculate the minimum number of residues in a ß-strand required to span this distance. Skip part (c) (d) The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) has a single transmembrane helix. Find it in this partial sequence. ...RGPKIPSIATGMVGALLLLVVALGIGILFMRRRH... Table for reference (for parts a-b): TABLE 6.1 Parameters of some polypeptide secondary structures Structure Type B Strand (antiparallel) B Strand (parallel) a helix 310 helix Polypeptide II helix Residues per Turn 2.0 2.0 3.6 3.0 3.0 Rise (h) per Residue 3.4 Å 3.2 Å 1.5 Å 2.0 Å 4.7 Å Pitch (p) 6.8 Å 6.4 Å 5.4 Å 6.0 Å 9.4 Åarrow_forwardProblem: From the following information determine the amino acid sequence of a peptide. N-terminal Edman gives PTH-Alanine C terminal carboxypeptidase treatment, no observable reaction Trypsin cleavage gives three products Arg Peptide containing Ala, Lys Peptide containing Asp, Met, Phe, Pro Mild Chymotrypsin cleavage gives 2 peptides Peptide containing Asp, Pro Peptide containing Ala, Arg, Lys, Met, Phe CNBr cleavage gives 2 peptide Peptide containing Ala, Arg, Lys and homoserine Peptide containing Asp, Phe, Pro You must supply the answer as the 3-letter amino acid sequence from N-terminus to C-terminus in the form (you must use dashes, not spaces between the amino acids)arrow_forwardProblem: From the following information determine the amino acid sequence of a peptide. N-terminal Edman gives PTH-Alanine C terminal carboxypeptidase treatment, no observable reaction Trypsin cleavage gives three products Arg Peptide containing Ala, Lys Peptide containing Asp, Met, Phe, Pro Mild Chymotrypsin cleavage gives 2 peptides Peptide containing Asp, Pro Peptide containing Ala, Arg, Lys, Met, Phe CNBr cleavage gives 2 peptides Peptide containing Ala, Arg, Lys and homoserine Peptide containing Asp, Phe, Pro You must supply the answer as the 3-letter amino acid sequence from N-terminus to C-terminus in the form (you must use dashes, not spaces between the amino acids) Met-Thr-Glu-Trparrow_forward
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
