
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The most stable radical that can result from cleavage of
Concept introduction: A free radical is an atom or ion with unpaired electrons. They are reactive intermediates formed by the homolysis of covalent bond. Free radicals are classified as
Answer to Problem 15.2P
The most stable radical that can result from cleavage of
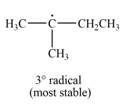
Explanation of Solution
The given species is,
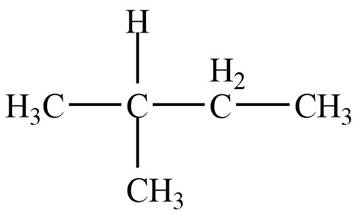
Figure 1
Three types of radicals can be formed by the cleavage of
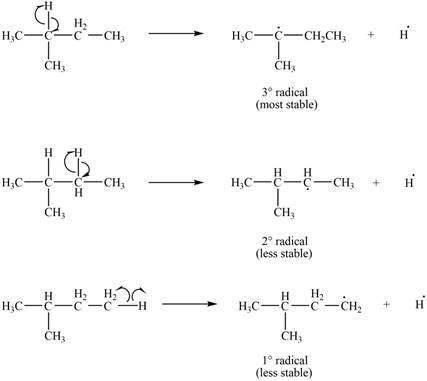
Figure 2
The number of alkyl substitutents increases, the stability of radical increases. The order of stability is
The most stable radical that can result from cleavage of
(b)
Interpretation: The most stable radical that can result from cleavage of
Concept introduction: A free radical is an atom or ion with unpaired electrons. They are reactive intermediates formed by the homolysis of covalent bond. Free radicals are classified as
Answer to Problem 15.2P
The most stable radical that can result from cleavage of
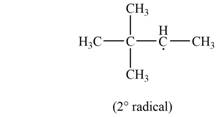
Explanation of Solution
The given species is,
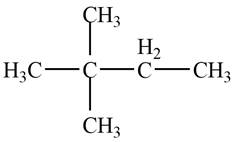
Figure 3
Two types of radicals can be formed from cleavage of
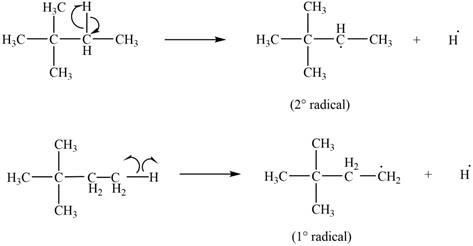
Figure 4
The number of alkyl substitutents increases, the stability of radical increases. The order of stability is
The most stable radical that can result from cleavage of
(c)
Interpretation: The most stable radical that can result from cleavage of
Concept introduction: A free radical is an atom or ion with unpaired electrons. They are reactive intermediates formed by the homolysis of covalent bond. Free radicals are classified as
Answer to Problem 15.2P
The most stable radical that can results from the cleavage of
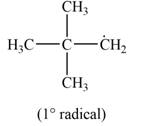
Explanation of Solution
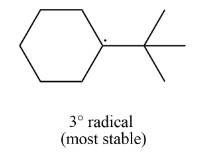
The given species is,
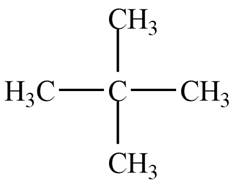
Figure 5
Only
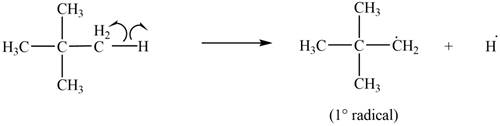
Figure 6
The most stable radical that can result from cleavage of
(d)
Interpretation: The most stable radical that can result from cleavage of
Concept introduction: A free radical is an atom or ion with unpaired electrons. They are reactive intermediates formed by the homolysis of covalent bond. Free radicals are classified as
Answer to Problem 15.2P
The most stable radical that can result from cleavage of
Explanation of Solution
The given species is,
Figure 7
Two types of radicals can be formed from cleavage of
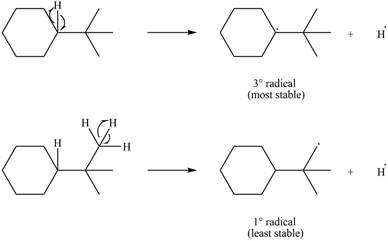
Figure 8
The number of alkyl substitutents increases, the stability of radical increases. The order of stability is
The most stable radical that can result from cleavage of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- 1. What is the bond angle in carbon tetrachloride? 2. What is the product of the reaction of pent-2-ene with Cl2? 3.Which statement is correct? * A. The bond length increases when the difference between the electronegativity of the atoms is higher B. The bond length increases when the number when there is an increase in pi bonds. C. Increasing the bond polarity increases the bond length. D. Sp2 has shorter bond length that sp. 4. How many moles of O2 gas is theoretically needed for 1 mole of hexane? 5. What is the MOST LIKELY product of the reaction of pent-1-ene with HCL? 6. Which one creates a sigma bond? * A. 2 pz atomic orbitals B. 2 py atomic orbitals C. 2 px atomic orbitals D. none of these 7.How many hydrogen atoms are there in trans-1-bromo-2-methylcyclohexane? 8.arrow_forward28) Which hydrogen atom has the smallest bond dissociation energy from the carbon it is bonding to? Hb- Ha A. 6 Hd Ho A. Ha B. Hb C. He D. Hd 29) How many hydrogen atoms exist on the following Grignard reagent? MgBr B. 7 C. 8 hinalitycers ex es ex- D. 9 E. 10arrow_forwardH b. H₂O (xs) H₂SO4arrow_forward
- Examine the reactant and product for each reaction. Label each transformation as an addition, elimination, or substitution. Br А. Br ОН elimination addition С. substitution D. B.arrow_forwardDraw three resonance structures for the ff: 1. a fully deprotonated carbonic acid H2CO3 2. pentanedienyl radicalarrow_forwardComplete the fourth resonance structure to determine which bond is shortest? Which compound will react fourth fastest with B-eBr ? d. e. F 14. Complete the fourth resonance structure to determine which bond is shortest? 15. Which compound will react fourth fastest with Br₂/FeBr3? a. b. d. -OH b darrow_forward
- Drew the mechanismarrow_forwardWhen free radical halogenation is performed with one of the compounds below, only a single product with the formula C5H11Cl is isolated. Which compound fits this description? Select one: a. 2,2-dimethylpropane b. cyclopentane c. pentane d. 2-methylbutanearrow_forwardWhy does bromination reactions occur only on more stable radicals? O a. Br₂ is less reactive than Cl₂. O b. Br₂ is more reactive than Cl₂. O c. Br₂ is less selective than Cl₂. O d. Both a and c.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





