
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The given radical is to be classified as
Concept introduction: A free radical is an atom or ion with unpaired electron. They are reactive intermediates formed by the homolysis of covalent bond. Free radicals are classified as
Answer to Problem 15.1P
The given free radical is classified as
Explanation of Solution
The given species is,
![]()
Figure 1
The given free radical is attached to two carbon atoms. Thus, it is classified as
The given free radical is classified as
(b)
Interpretation: The given radical is to be classified as
Concept introduction: A free radical is an atom or ion with unpaired electron. They are reactive intermediates formed by the homolysis of covalent bond. Free radicals are classified as
Answer to Problem 15.1P
The given free radical is classified as
Explanation of Solution
The given species is,
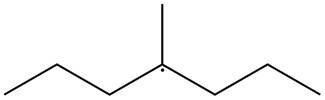
Figure 2
The given free radical is attached to three carbon atoms. Thus, it is classified as
The given free radical is classified as
(c)
Interpretation: The given radical is to be classified as
Concept introduction: A free radical is an atom or ion with unpaired electrons. They are reactive intermediates formed by the homolysis of covalent bond. Free radicals are classified as
Answer to Problem 15.1P
The given free radical is classified as
Explanation of Solution
The given species is,
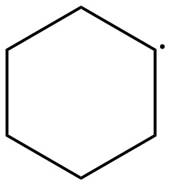
Figure 3
The given free radical is attached to two carbon atoms. Thus, it is classified as
The given free radical is classified as
(d)
Interpretation: The given radical is to be classified as
Concept introduction: A free radical is an atom or ion with unpaired electrons. They are reactive intermediates formed by the homolysis of covalent bond. Free radicals are classified as
Answer to Problem 15.1P
The given free radical is classified as
Explanation of Solution
The given species is,
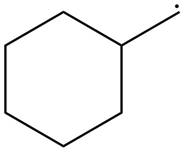
Figure 4
The given free radical is attached to one carbon atom. Thus, it is classified as
The given free radical is classified as
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- this is an organic chemistry question please answer accordindly!! please post the solution draw the figures on a paper please hand drawn and post, please answer EACH part till the end and dont just provide wordy explanations, please draw them on a paper and post clearly!! answer the full question with all details EACH PART CLEARLY please thanks!! im reposting this please solve all parts and draw it not just word explanations!!arrow_forwardA mixture of 0.412 M C12, 0.544 M F2, and 0.843 M CIF is enclosed in a vessel and heated to 2500 K. C12(g) + F2(g )2CIF(g) Kc = 20.0 at 2500 K Calculate the equilibrium concentration of each gas at 2500 K. [C12] = M [F2] = M [ CIF] =arrow_forwardShow reaction mechanism with explanation. don't give Ai generated solutionarrow_forward
- Don't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardthis is an organic chemistry question please answer accordindly!! please post the solution draw the figures and post, answer the question in a very simple and straight forward manner thanks!!!!! please answer EACH part till the end and dont just provide wordy explanations wherever asked for structures or diagrams, please draw them on a paper and post clearly!! answer the full question with all details EACH PART CLEARLY please thanks!! im reposting this kindly solve all parts and draw it not just word explanations!!arrow_forwardPlease correct answer and don't used hand raitingarrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
