
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Hydrogen atom that ionizes from the picric acid molecule has to be identified.
Concept Introduction:
The most common representation of oxy acid is given by
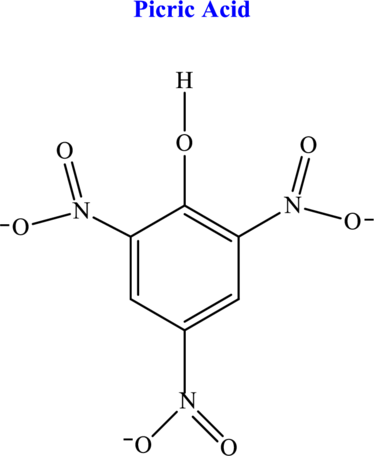
(b)
Interpretation:
Concept Introduction:
The formula to calculate
(c)
Interpretation:
Balanced chemical equation corresponding to decomposition of picric acid has to be written.
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(d)
Interpretation:
Whether substitution of
Concept Introduction:
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 15 Solutions
Chemistry: Principles and Practice
- The pH of a 0.10-M solution of propanoic acid, CH3CH2COOH, a weak organic acid, is measured at equilibrium and found to be 2.93 at 25 °C. Calculate the Ka of propanoic acid.arrow_forwardAcids You make a solution by dissolving 0.0010 mol of HCl in enough water to make 1.0 L of solution. a Write the chemical equation for the reaction of HCl(aq) and water. b Without performing calculations, give a rough estimate of the pH of the HCl solution. Justify your answer. c Calculate the H3O+ concentration and the pH of the solution. d Is there any concentration of the base OH present in this solution of HCl(aq)? If so, where did it come from? e If you increase the OH concentration of the solution by adding NaOH, does the H3O+ concentration change? If you think it does, explain why this change occurs and whether the H3O+ concentration increases or decreases. f If you were to measure the pH of 10 drops of the original HCl solution, would you expect it to be different from the pH of the entire sample? Explain. g Explain how two different volumes of your original HCl solution can have the same pH yet contain different moles of H3O+. h If 1.0 L of pure water were added to the HCl solution, would this have any impact on the pH? Explain.arrow_forwardExplain the difference between a strong acid and a weak acid.arrow_forward
- An acetic acid solution was prepared by dissolving 0.02 moles of acetic acid (HOAC) in water to give a final volume of 1L. The Ka of HOAC s 1.82 x 10°. (a) Calculate the pKa of acetic acid (b) Calculate the pH of the acetic acid solution (c) If 0.012 moles of concentrated NaOH was added to your prepared solution from above, what is the new pH (There is no appreciable chareo ine volumes).arrow_forward3c.) Suppose it is desired to maintain the pH of a solution at 4.2 using only acetic acid and sodium acetate. Would the concentration of acetic acid or sodium acetate have to be higher in the solution? O sodium acetate O acetic acidarrow_forward(a) Given that Ka for acetic acid is 1.8 x 10-5 and that hypochlorous acid is 3.0 x10-8 , which is a stronger acid? (b) Which is the stronger base, the acetate ion or the hypochlorite ion? (c) calculate the Kb values for the CHCOO- and ClO- .arrow_forward
- A solution is made by dissolving 44.1 g of Ba(NO₂)₂ in 500.0 mL of water. (a) Does Ba²⁺ have any acidic or basic properties? (b) Does NO₂⁻ have any acidic or basic properties? (c) As NO₂⁻ is a base, write the basic equilibrium equation that exists in solution (d) What is the value of Kb for NO₂⁻? The Ka of HNO₂ is 4.5 × 10⁻⁴. (e) Determine the pH of the solutionarrow_forwardIdentify the Lewis acid and Lewis base in each equation:arrow_forward(a) Papaverine hydrochloride is an alkaloid drug used as a muscle relaxant, particularly for acute myocardial infarctions and angina It is a weak acid. If a 0.205 M solution of papaverine hydrochloride has a pH of 3.31, what is its Ka?arrow_forward
- An important component of blood is the buffer combination of bicarbonate ion and carbonic acid. Consider blood with a pH of 7.42. (a) What is the ratio of [H2CO3] to [HCO3− ]?(b) What does the pH become if 14% of the bicarbonate ions are converted to carbonic acid? (c) What does the pH become if 26% of the carbonic acid molecules are converted to bicarbonate ions?arrow_forwardConsider two acids: HCO2H (formic acid, pKa = 3.8) and pivalic acid [(CH3)3CCO,H, pK = 5.0]. (a) Which acid has the larger K? (b) Which acid is the stronger acid? (c) Which acid forms the stronger conjugate base? (d) When each acid is dissolved in water, for which acid does the equilibrium lie further to the right? %3D The pKa values in Table 2.1 span a large range (-7 to 50). The pK, scale is logarithmic. small difference in pK, translates into a large numerical difference, For example, the diffe between the pK, of NH3 (38) and CH2=CH, (44) is six pKa units. This means that NH, is one million times more acidic than CH,=CH,.arrow_forwardSodium hypochlorite solution is also known as bleach. It contains the hypochlorite ion ClO-. (a) Write an equation for the reaction between hypochlorite ion and ammonium ion. Label the acids and bases in the forward and reverse reactions. Identify the two conjugate acid-base pairs. (b) This equilibrium favors the reactants. Which of the acids is stronger and donates protons more readily?arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co



