
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
13th Edition
ISBN: 9780133923605
Author: Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 14, Problem 36P
For the network in Fig. 14.81 and the applied source:
a. Determine the sinusoidal expression for the source voltage Us.
b. Find the sinusoidal expression for the currents i1, and i2.
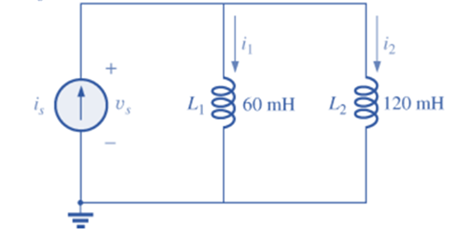
Fig. 14.81
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
A certain element has a phasor voltage of V = 200/30 V and current of I = 6Z120 A The angular frequency is 500 rad/s. Determine the nature of the element.
The element is an inductance.
• The element is a capacitance.
The element is a resistance
Previous Answers
v Correct
Impedance of AC circuit and Admittance of AC circuitSHOW THE CIRCUIT USING ANY SOFTWARE OR YOU CAN DRAW IT MANUAALYY thNAKSS
Please hand written solution
Chapter 14 Solutions
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Ch. 14 - Plot the following waveform versus time showing...Ch. 14 - Repeat Problem 1 for the following sinusoidal...Ch. 14 - What is the derivative of each of the following...Ch. 14 - The voltage across a 20 resistor is as indicated....Ch. 14 - The current through a 6.8 k ) resistor is as...Ch. 14 - Determine the inductive reactance (in ohms) of a 2...Ch. 14 - Determine the closest standard value inductance...Ch. 14 - Determine the frequency at which a 47 mH...Ch. 14 - The current through a 20 inductive reactance is...Ch. 14 - The current through a 0.1 H coil is given. What is...
Ch. 14 - The voltage across a 40 inductive reactance is...Ch. 14 - The voltage across a 0.2 H coil is given. What is...Ch. 14 - Determine the capacitive reactance (in ohms) of a...Ch. 14 - Determine the closest standard value capacitance...Ch. 14 - Determine the frequency at which a 3.9 F capacitor...Ch. 14 - The voltage across a 2.5 capacitive reactance is...Ch. 14 - The voltage across a 1 F capacitor is given. What...Ch. 14 - The current through a 2 k capacitive reactance is...Ch. 14 - The current through a 0.56 F capacitor is given....Ch. 14 - For the following pairs of voltages and currents,...Ch. 14 - Repeat Problem 20 for the following pairs of...Ch. 14 - Plot XL versus frequency for a 3 mH coil using a...Ch. 14 - Plot XC versus frequency for a 1 F capacitor using...Ch. 14 - At what frequency will the reactance of a 1 F...Ch. 14 - The reactance of a coil equals the resistance of a...Ch. 14 - Determine the frequency at which a 1 F capacitor...Ch. 14 - Determine the capacitance required to establish a...Ch. 14 - Find the average power loss and power factor for...Ch. 14 - If the current through and voltage across an...Ch. 14 - A circuit dissipates 100 W (average power) at 150...Ch. 14 - The power factor of a circuit is 0.5 lagging. The...Ch. 14 - In Fig.14.77, e=120sin(260t+20). a. What is the...Ch. 14 - In Fig. 14.78, e=220sin(1000t+60). a. Find the...Ch. 14 - In Fig. 14.79, i=30103sin(2500t20). a. Find the...Ch. 14 - For the network in Fig. 14.80 and the applied...Ch. 14 - For the network in Fig. 14.81 and the applied...Ch. 14 - Convert the following from rectangular to polar...Ch. 14 - Convert the following from rectangular to polar...Ch. 14 - Convert the following from polar to rectangular...Ch. 14 - Convert the following from polar to rectangular...Ch. 14 - Perform the following additions in rectangular...Ch. 14 - Perform the following subtractions in rectangular...Ch. 14 - Perform the following operations with polar...Ch. 14 - Perform the following multiplications in...Ch. 14 - Perform the following multiplications in polar...Ch. 14 - Perform the following divisions in polar form:...Ch. 14 - Perform the following divisions, and leave the...Ch. 14 - Perform the following operations, and express your...Ch. 14 - Prob. 49PCh. 14 - Determine a solution for x and y if...Ch. 14 - Determine a solution for x and y if...Ch. 14 - Express the following in phasor from:...Ch. 14 - Express the following in phasor form:...Ch. 14 - Express the following phasor currents and voltages...Ch. 14 - For the system in Fig. 14.82, find the sinusoidal...Ch. 14 - For the system in Fig. 14.83 find the sinusoidal...Ch. 14 - Find the sinusoidal expression for the voltage Ua...Ch. 14 - Find the sinusoidal expression for the current i1...Ch. 14 - Plot icandUc versus time for the network in Fig....Ch. 14 - Plot the magnitude and phase angle of the current...Ch. 14 - Plot the total impedance of the configuration in...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A capacitor has a reactance of 80 ohms when connected to a 50 Hz supply. Calculate the value of capacitance.a. 39.79 microfaradb. 39.97 microfaradc. 93.79 microfaradd. 93.97 microfaradKindly provide a CLEAR and COMPLETE solution.arrow_forwardi need the answer quicklyarrow_forwardProblem #7) Specify whether each of the statements are TRUE or FALSE. D Reactive Power is a measure of the average power consumed by reactive (capacitive and inductive) loads. When connected to an AC voltage source, the instantaneous power (rate of energy transfer) supplied to a resistor varies at a frequency that is 2x the frequency of the applied source voltage. The magnitude of the impedance of a capacitor supplied by an AC source will increase as the source frequency increases. An AC source that has an RMS magnitude of 100V will supply the same average power to a resistor compared to a 100V DC source. The voltage across a capacitor is proportional to the rate of change of the current flowing through the capacitor. The magnitude of the impedance of a resistor supplied by an AC source does not vary as the source frequency increases. A complex impedance Z=R+jX, that has non-zero resistive and reactive components, will consume both real and reactive power when supplied by an AC source.…arrow_forward
- Determine the capacitance and voltages (Vrms) across the resistor and capacitor and prove that the phasor sum of the series components is equal to the source voltage. Also, solve for its total circuit impedance and total circuit current.ps. we need a neat solution. thank you in advance!arrow_forward2. Find L{sin³ t}, L{e2t sin³ t}.arrow_forwardDon't use ai to answer I will report your answer Solve it Asap with explanation and calculation.arrow_forward
- 9arrow_forward5) Find the reactance the inductance and impedance of the circuit. Calculate the current of this circuit and the sketch waveform of current and voltage. V1 10 V 60 Hz R1 m 100kQ 12 Vrms 1000 Hz 0° 6) Find the reactance the inductance and impedance of the circuit. Calculate the currents of this circuit R www 502 L L1 106mH eee 10 mHarrow_forward14:30 E P VS +23324657 2888 July 15, 14:03 EE 287 SINUSOIDAL STEADY STATE ANALYSIS ASSIGNMENT 3 1. Determine Vo in the circuit below 42 2H ww- 32 sin 4r V 4 cos 4r A HORTNE BREATH 2 Determinc lo in the circuit below using superposition principle 24 V 2 H ww 22 2 cos 3t 42 10 sin(t-30°) V()arrow_forward
- Single-phase Series Circuits In a particular circuit a voltage of 10 V at 25 c/s produces 100 mA, while the same voltage at 75 c/s produces 60 mA. Draw the circuit diagram and insert values of the constants, At what frequency will the value of the impedance be twice that at 50 c/s ? [R = 88-1 2 and L = 0-8 H in series ; 95 c/s.] An inductance of 1 H is in series with a capacitance of 1 µF. Find the impedance of the circuit when the freauency is la) 50arrow_forwardFor the network determine the sinusoidal Expression for the voltage V3 using superpositionarrow_forward:D A docs.google.com/forms/d/1 o المرحلة والشعبة: * A non-sinusoidal voltage (e=20+15sin1000t+ 10sin3000t+5sin4000t) Volt is applied to the circuit shown. Find the ?total power iT 42 İL -J92 J42 44.03 W 86.08 W 88.06 W 44.04 W n-sinusoidal wave can be طلب الإذن بالتعديل of sine waves with .harmonic frequencies IIarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
02 - Sinusoidal AC Voltage Sources in Circuits, Part 1; Author: Math and Science;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8zMiIHVMfaw;License: Standard Youtube License